6th Grade 3rd 6 Weeks Numerical Fluency
advertisement
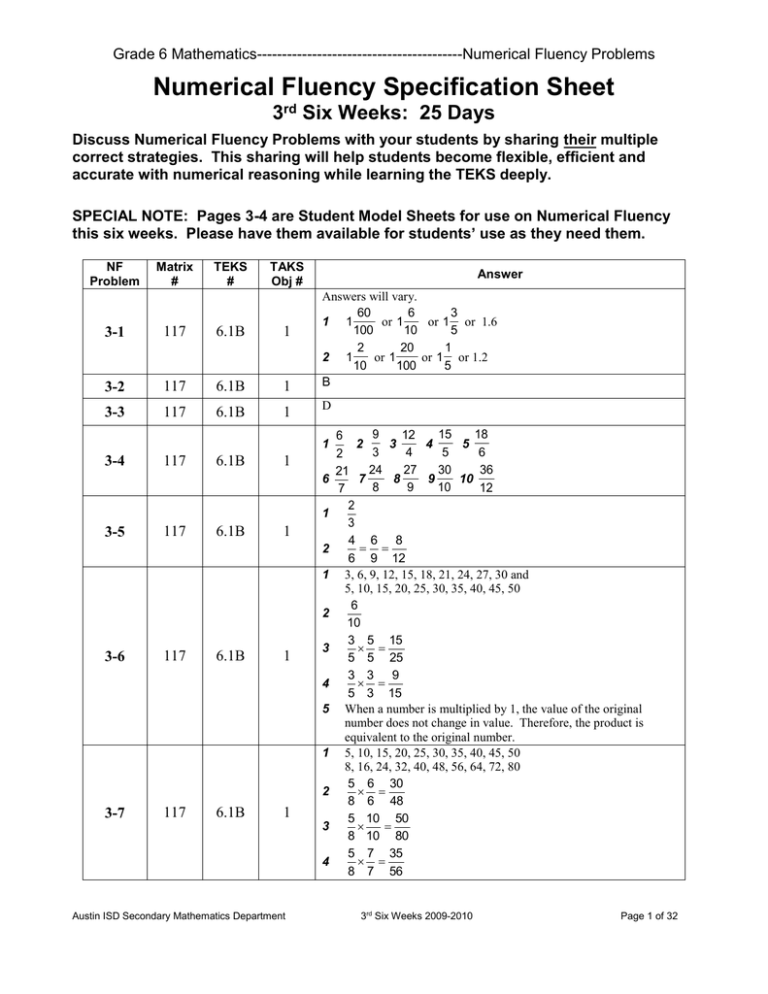
Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency Specification Sheet 3rd Six Weeks: 25 Days Discuss Numerical Fluency Problems with your students by sharing their multiple correct strategies. This sharing will help students become flexible, efficient and accurate with numerical reasoning while learning the TEKS deeply. SPECIAL NOTE: Pages 3-4 are Student Model Sheets for use on Numerical Fluency this six weeks. Please have them available for students’ use as they need them. NF Problem Matrix # TEKS # TAKS Obj # 3-1 117 6.1B 1 3-2 117 6.1B 1 3-3 117 6.1B 1 Answer Answers will vary. 60 6 3 1 1 or 1 or 1 or 1.6 100 10 5 2 20 1 2 1 or 1 or 1 or 1.2 10 100 5 B D 1 3-4 117 6.1B 1 6 1 3-5 117 6.1B 1 2 1 2 3-6 117 6.1B 1 3 4 5 1 2 3-7 117 6.1B 1 3 4 Austin ISD Secondary Mathematics Department 9 15 18 12 6 2 3 4 5 3 5 6 4 2 24 27 30 36 21 7 8 9 10 8 9 10 12 7 2 3 4 6 8 6 9 12 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30 and 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 6 10 3 5 15 5 5 25 3 3 9 5 3 15 When a number is multiplied by 1, the value of the original number does not change in value. Therefore, the product is equivalent to the original number. 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80 5 6 30 8 6 48 5 10 50 8 10 80 5 7 35 8 7 56 3rd Six Weeks 2009-2010 Page 1 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems NF Problem Matrix # TEKS # TAKS Obj # Answer 1 of the trip is more than 4 1 1 1 1 Marta’s distance of of the trip. > because is a larger 5 4 5 4 1 portion of one whole amount than of the whole amount. Fewer 5 parts of whole make larger portions of the whole. 1 2 Neither Marta or John has reach Pleasanton yet since of the 3 1 1 distance is further than either or a of the distance. Also, 5 4 20 15 12 1 20 1 15 1 12 , , and . . 60 60 60 3 60 4 60 5 60 4 Jesse paid more for his soda because of a dollar is $0.80 and 5 3 Andrea paid of a dollar, which is $0.75 for her soda. 4 1 3-8 110 6.1A 1 110 6.1A 1 117 6.1B 1 110 6.1A 1 117 6.1B 1 110 6.1A 1 117 6.1B 1 110 6.1A 1 117 6.1B 1 3-9 3-10 3-11 3-12 John made more progress because Bill finished the race before Holly because 1.25 < 1.33333… 1 1.33333… is equivalent to 1 . 3 North Austin received more rain than South Austin because 2.4 > 3 2.375. 2.375 is another name for 2 . 8 1 The investors lost more money on Monday since of a dollar which 4 2 1 equals of a dollar is greater than of a dollar. 8 8 7 9 1 2 9 4 3 9 5 1 7 2 2 7 3 3 7 See the number line below for approximations. 1 3-13 110 6.1A 1 3-14 110 6.1A 1 3-15 110 117 6.1A 6.1B 1 Austin ISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd Six Weeks 2009-2010 Page 2 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems NF Problem 3-16 Matrix # TEKS # 110 6.1A 117 6.1B TAKS Obj # Answer 1 1 2 2 7 5 2 3 7 3 See the number line below for approximations. See the number line below for approximations. 1 B 2 D 1 3-17 110 6.1A 1 3-18 110 6.1A 1 3-19 110 6.1A 1 3-20 217 217 6.3B 6.3B 2 2 3-21 218 6.3A 2 3-22 218 6.3A 2 3-23 132 6.1C 1 Austin ISD Secondary Mathematics Department See number line below for approximate locations. 3 5 5 11 9 3 6 7 1 0.9 ; 2 2 ; 1 ; 2.5 ; 6 6 10 5 10 4 4 2 1 C For NF #72, any equivalent ratio is acceptable as well, but students should be able to demonstrate why it is an equivalent ratio. 1 9 to 15 or 9 : 15 2 6 to 15 or 6 : 15 3 Two other ways to answer #1 are 3 to 5 or 3 : 5. Two other ways to answer #2 are 2 to 5 or 2 : 5. 4 6 to 10 or 6 : 10 5 4 to 10 or 4 : 10 6 Two other ways to answer #4 are 3 to 5 or 3 : 5. Two other ways to answer #5 are 2 to 5 or 2: 5. 1 C 2 D 1 D 2 B 3rd Six Weeks 2009-2010 Page 3 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems 1 2 3 3-24 217 6.3B 2 4 3-25 134 1 These strategies help students remember the value of the digits. Tradition multiplication algorithms, especially when communicated without regard to place value, do NOT help students understand the magnitude of the numbers involved. 80 21 2 21 1680 42 1722 20 82 1 82 1640 82 1722 40 21 40 21 2 21 820 820 42 1722 Austin ISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd Six Weeks 2009-2010 Page 4 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Additional answers are below. NF 3-17 3 1 6 1 4 0 1 1 2 2 1 3 1 5 NF 3-18 0 1 1 2 1 3 4 3 0.3 NF 3-15 0 9 10 NF 316 1 0 Austin ISD Secondary Mathematics Department 1 1 5 2 1 3 4 1 2 1 4 7 4 5 6 2 3rd Six Weeks 2009-2010 2 3 5 3 Page 5 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Student Model Sheet Choose any model or draw your own model to justify your work. Austin ISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd Six Weeks 2009-2010 Page 6 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 7 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-1 1 The shaded area below represents 1 whole. Record the amount shaded below using at least 5 different names. 2 Give at least 5 different names for the bold point on the number line. 0 AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 1 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 2 Page 8 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-2 Which statement about 2.07 is true? A 2.07 < .207 B 2.07 > 2.007 C .027 > 2.07 D 20.7 < 2.07 AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 9 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-3 To collect data for an experiment, four classmates measured their heights. Roberto was 1.76 meters tall, Jorge was 1.6 meters tall, Tony was 1.67 meters tall, and Luis was 1.7 meters tall. Which list shows their heights in order from tallest to shortest? A 1.6 m, 1.67 m, 1. 76 m, 1.7 m B 1.6 m, 1.7 m, 1.67 m, 1.76 m C 1.76 m, 1.67 m, 1.7 m, 1.6 m D 1.76 m, 1.7 m, 1.67 m, 1.6 m AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 10 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-4 Three fraction strips are placed end to end as shown below. Record your answer to each question as a fraction. 1 How many halves are equivalent to 3 fraction strips? 2 How many thirds are equivalent to 3 fraction strips? 3 How many fourths are equivalent to 3 fraction strips? 4 How many fifths are equivalent to 3 fraction strips? 5 How many sixths are equivalent to 3 fraction strips? 6 How many sevenths are equivalent to 3 fraction strips? 7 How many eighths are equivalent to 3 fraction strips? 8 How many ninths are equivalent 3 fraction strips? 9 How many tenths are equivalent to 3 fraction strips? 10 How many twelfths are equivalent to 3 fraction strips? AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 11 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-5 The three large rectangles below represent cake pans of equal size. The shaded part represents the number of equal-size pieces of cake remaining in each cake pan. Cake Pan #1 Cake Pan #2 Cake Pan #3 1 What part of the cake remains in each cake pan? 2 Using the shaded part of the cake pans as a guide, 2 write three fractions equivalent to . Be prepared 3 to explain why the fractions are equivalent. 2 = 3 AISD Secondary Mathematics Department = = 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 12 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-6 1 Complete the multiplication table for the unshaded rows. X 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Complete each equation in #2-#4. 2 3 x 5 2 = 3 x 5 4 9 = 2 5 3 3 x 5 = Explain why multiplying by a form of one produces an equivalent fraction. 5 AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 13 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-7 1 Complete the multiplication table for the unshaded rows. x 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Complete each equation in #2-#4. 6 2 3 5 x 8 5 x 8 = 10 4 5 = AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 5 x 8 = 56 What other fractions are 5 equivalent to ? 8 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 14 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-8 John and Marta are driving from Austin to Harlingen for the holidays. John left Austin at 3:00 p.m. and has completed 1 of the trip. Marta left at 2:45 p.m. and has 4 completed 1 of the trip. The small town of Pleasanton, 5 is about 1 of the way to Harlingen. 3 Austin Harlingen 1 Who has made more progress in the trip? Explain your reasoning. 2 Has either Marta or John reached Pleasonton yet? Explain your reasoning. AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 15 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-9 Jesse paid 4 of a dollar for a soda. Andrea paid $0.75 5 for her soda. Who spent the most for their soda? Explain your reasoning. AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 16 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-10 Holly ran the Capitol 10K race in 1 1 hours. Her 3 husband, Bill ran the race in 1.25 hours. Who finished the race in the least amount of time? Explain your reasoning. AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 17 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-11 After a stormy night, a family from north Austin reported they had received 2.4 inches of rain. A rain gauge in south Austin received 2 3 inches of rain. 8 According to these reports, what part of Austin received the most rain? Explain your reasoning. AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 18 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-12 On Friday, Dell stock dropped 1 of a dollar. The 8 following Monday, the stock dropped another 1 of a 4 dollar. On which day did the investors lose more money? Explain your reasoning. Extension: About how much money did one share of Dell stock lose over the 2 days? AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 19 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-13 4 1 7 9 Choose 2 of the digits above to find the “Mystery Fraction” for each description below. 1 Mystery Fraction: Description: the number closest to one whole 2 Mystery Fraction: Description: the number closest to zero 3 Mystery Fraction: Description: the number closest to one-half AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 20 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-14 3 5 7 2 Choose 2 of the digits above to find the “Mystery Fraction” for each description below. 1 Mystery Fraction: Description: the number closest to one whole 2 Mystery Fraction: Description: the number closest to zero 3 Mystery Fraction: Description: the number closest to one-half AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 21 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-15 Use the number line below to locate the following numbers. Be prepared to explain your reasoning. 0 1 4 .3 0 3 4 AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 1 Page 22 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-16 1 Using the number line below, find and label the following: 9 5 3 7 5 1 , , 2 , , 6 10 5 4 2 1 2 2 3 For each of the numbers listed above, give at least one more number that describes an equivalent amount. 1 5 = 6 9 = 10 2 3 = 5 7 = 4 5 = 2 AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 23 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-17 A 0 1 B 2 3 4 1 What number is indicated by point A on the number line above? 2 What number is indicated by point B on the number line above? 3 On the number line below, locate and 1 1 1 1 , , , , 6 5 4 3 1 . 2 AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 24 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-18 Use the number line below to locate the following numbers. Be prepared to explain your reasoning. 1 2 1 0 AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 4 3 1 3 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 25 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-19 1 2 By 12:30 p.m., 75% of the Burnet Middle School students had eaten lunch. What fractional part of the Burnet Middle School students had NOT yet eaten lunch? A 1 25 B 1 4 C 7 5 D 3 4 1 What statement about the mixed number 1 is 5 true? A B C D 1 1 1 >1 5 4 1 1 1 >1 10 5 1 2<1 5 1 1 1 <1 10 5 AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 26 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-20 Each parallelogram below is divided into sections of 2 equal size. Which parallelogram has 66 % of its total 3 area shaded? A B C D AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 27 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-21 1 What is the ratio of the shaded part of the rectangle to the total rectangle below? 2 What is the ratio of the unshaded part of the rectangle below to the total rectangle below? 3 What is another way to answer #1 and #2? 4 What is the ratio of the number of stars to the total number of objects in the set below? 5 What is the ratio of the number of moons to the total number of objects in the set below? 6 What is another way to answer #4 and #5? AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 28 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-22 1 2 A used car lot has 24 cars and 16 trucks for sale. What is the ratio of cars to trucks? A 2 to 3 B 3 to 5 C 3 to 2 D 5 to 3 If the ratio of tulips to roses is 2 to 5, which of these shows possible numbers of tulips and roses? A 12 tulips, 35 roses B 25 tulips, 10 roses C 15 tulips, 6 roses D 16 tulips, 40 roses AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 29 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-23 1 2 The high temperature on Monday was 12 degrees below zero. On Tuesday, the high temperature was 3 degrees above zero. What integer represents the high temperature on Monday? A 3 B –3 C 12 D –12 On Wednesday, a video store gave away a free video when the total DVD rental fees were $30 or more. There were 22 DVD rental fees that were $30 or higher that day. What integer represents the change in the number of free videos the store had in stock by the end of the day on Wednesday? A –30 B –22 C 22 D 30 AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 30 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-24 Three out of every five 6th graders use the Internet to check their email. Represent this ratio in each of the following grid models. Be prepared to justify your reasoning. 1 2 3 4 AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 31 of 32 Grade 6 Mathematics-----------------------------------------Numerical Fluency Problems Numerical Fluency 3-25 A theatre has 82 rows of seats. There are 21 seats in each row. How many seats are in the theatre? Solve this problem using two different strategies. Be prepared to explain your strategies. AISD Secondary Mathematics Department 3rd 6 Weeks 2009-2010 Page 32 of 32




