小学研讨会 ─ 每班人数与学生表现和教学质素的关系 (13/12/2003)
advertisement

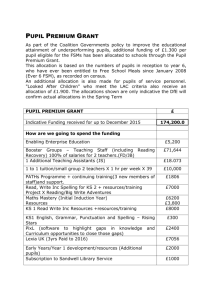
Is Small Better? The Effect of Class Size on Pupil Performance and Teaching Quality Maurice Galton Faculty of Education, University of Cambridge UK Presentation Seminar for Education & Manpower Bureau, Government of the HKSAR 13 December 2003 Some Contrasting Views Studies and research into the effects of class size have for the most part failed to demonstrate that pupils necessarily do better in small classes (OFSTED 1995) The research suggests that for states, districts and even schools, class size is a very basic and significant variable in improving educational outcomes (Egelson et al 1995) Some Early Evidence • Meta-analysis of 77 studies of class size and achievement (Glass et al. 1982) Pupils in classes of 20 taught for 100 hours would exceed performance of pupils in classes of 40 by 60%. • Effects are not linear (+ve for classes < 20; -ve for classes > 30) Optimum effect in classes of 15 and Grades 1 & 2. • Larger effect sizes (>0.20) can be achieved through paired work, co-operative learning and individualized instruction for weakest pupils (Slavin 1989) Teachers’ Views (Bennett 1996) • • • • More time for individual instruction Increase in pupil motivation Less pupil misbehavior Improved teacher-pupil personal relationships • More time for marking and assessment • Less stress Tennessee Student-Teacher Achievement Ratio (STAR) Project • 7000 pupils randomly assigned to small (13-17), regular (22-25) and (regular + teaching assistant) • Small classes did better from kindergarten to grade 3 • ethnic minority pupils did particularly well and had highest self-concept scores • effects still present when pupils moved to regular classes from grade 4 to 6 (Nye et al. 2000) Limitations of STAR • Reanalysis of data using multi-level modeling reduces effect sizes, shows school vs. size and subject interactions • No baseline measure so uncertainty about random assignment • Too narrow a range of classes: in many countries class size is around 35 • Restricted range of school types (large, single age entry) (Goldstein & Blatchford 1997) IoE Class Size Study (Blatchford 2003) • 9 Local Authorities,199 Schools, 330 classes and 7142 pupils • Baseline Literacy (reception entry), standardized tests of literacy and maths (reception & Y1) and National Tests (Y2) • Systematic Classroom Observation • 79 classes (10-20), 163 (21-25), 294 (26-30), 133 (31+) • Teacher Opinion survey Class size vs. Attainment (Reception Year ) Blatchford (2003) 0.8 0.6 Gain score 0.4 0.2 0 -0.2 12 18 24 -0.4 -0.6 -0.8 class size 30 36 Maths Literacy Class size vs. Attainment (Year 1) Gain score Blatchford (2003) 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 -0.1 -0.2 Literacy 16 21 26 class size 31 36 Main Findings on Performance from Blatchford (2003) • Effects are largest in reception class • Effects are still present for literacy in Y1 but less pronounced by Y3 • In literacy both high, medium and low ability groups benefit in classes of 25. Below this only low ability pupils benefit • In general, for mathematics effects are smaller Teacher-Pupil Interactions [Number of observations] (Blatchford 2003) 175 150 125 100 Small Large 75 50 25 0 Task Preparation Procedure Pupil-Pupil Interactions [Number of observations] (Blatchford 2003) 50 40 30 Small Large 20 10 0 Task Procedure Social Disruption Main Findings on Teaching from Blatchford (2003) • More one to one teaching • Teacher more actively involved in whole class or groups • More task interactions • Less task pupil-pupil interactions Class Size and Teacher Interaction Hargreaves & Galton (1998) Teacher-Pupil Interaction Pearson Correlation Task questions - 0.23 Challenging questions - 0.25 Task feedback - 0.34 Monitoring + 0.49 ** Routine Class Management + 0.37 ** Critical Control + 0.28 Sustained Interactions (Hargreaves & Galton 1998) % observation 25 20 15 10 5 0 15 20 25 class size 30 Holywells Case Study • A Suffolk secondary school in special measures: Some 50% of pupils arrive in Y7 (11 year-olds) below national Literacy and numeracy standard (Level 4). • Pupils Level 3 (or below) at Key Stage 2 placed in 4 classes, size 20. Others in classes of 30 or more. • Integrated teaching approach for English, maths and humanities. Reduced timetable for science, arts and French. Change in Level for English and Maths 50 40 30 English Maths 20 10 0 up 1 up 2 up 3 stay 3 stay 4 Other Changes • Attribution change from “I’m in the small class because I’m only Level 2” (ability) to “I can cope in the Y8 bigger class if I work hard” (effort) • Despite fewer lessons in Y7 around 33% of pupils are in the top sets in Y8 for Science and French • Improved behaviour, less truancy • Critical of primary school experiences”Teachers didn’t listen; didn’t explain properly.” Cultural Contexts (Jin & Cortazzi 1998) Western Approach Pacific Rim Approach Individual Short spontaneous Exchanges Prepared extended exchanges Groups Tasks planned but spontaneous talk & later class feedback Individual teacher-pupil exchanges Speaker orientated Teacher facilitated Task and talk prepared with immediate feedback Whole class responses Whole Class Principles Listener orientated, Teacher controlled Pre and Post Literacy Hour Questions (KS2) 80 70 60 50 closed open 40 30 20 10 0 1976 1996 2001 2002 Some Key Questions • Do teachers always maximize the benefits of smaller classes? Is there a need for special training? • Should other classroom interventions (e.g. peer tutoring, use of teaching assistants) be viewed as an alternative to class size reductions or a way of boosting their effects? • Could initial teacher training offer opportunities of working with half the class while class teacher takes the remaining pupils elsewhere? • Would flexible time tabling allow more pupils to experience small classes ( Is half the time in a class half the size more valuable?) • When learning to learn is there a case for giving greater priority to pupils in the 9-11 range or in transfer years? Some Key References Blatchford, P. (2003) The Class Size Debate: Is small better? Maidenhead, UK. Open University Press. Galton, M [Ed] (1998) ‘Class Size and Pupil Achievement,’ Special Edition International Journal of Educational Research, 29 (8). Nye, B. et al. (2000) ‘The Effects of Class Size on Academic Achievement: The results of the Tennessee class size experiment’ American Educational Research Journal, 37 (1): 123-151. Finn.J.et al. (2003) ‘The “Why’s” of Class Size: Student Behaviour in Small Classes, Review of Educational Research, 73 (3): 321-368.