Equations of motion and Newton's Law
advertisement
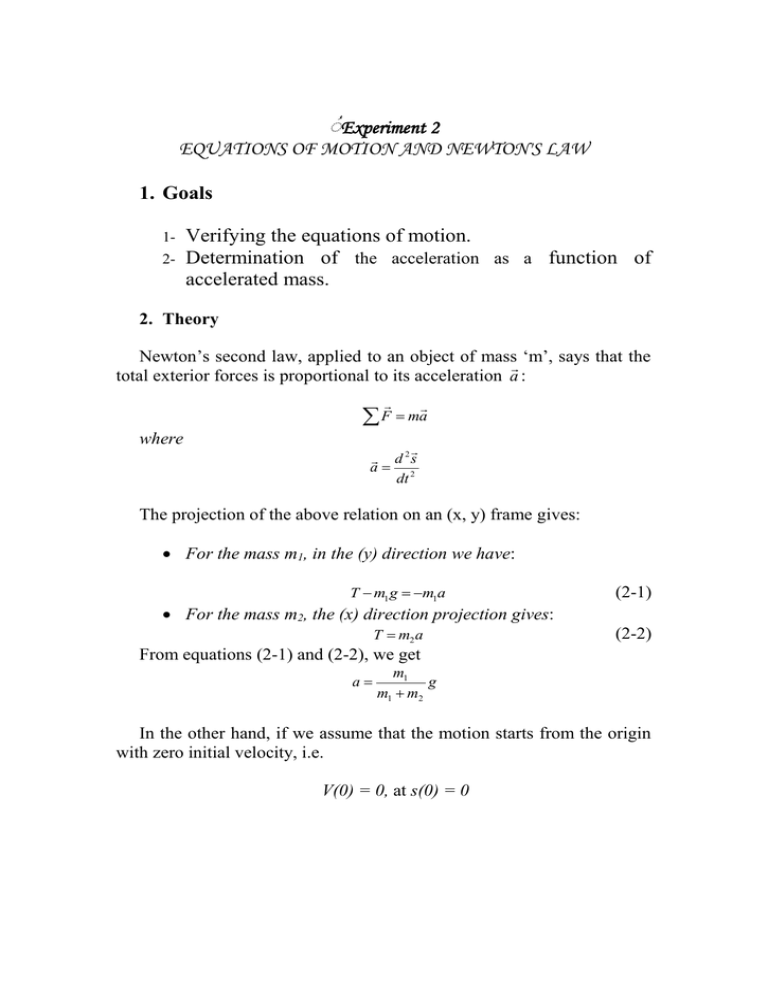
ُExperiment 2 EQUATIONS OF MOTION AND NEWTON'S LAW 1. Goals 12- Verifying the equations of motion. Determination of the acceleration as a function of accelerated mass. 2. Theory Newton’s second law, applied to an object of mass ‘m’, says that the total exterior forces is proportional to its acceleration a : F ma where d 2s a 2 dt The projection of the above relation on an (x, y) frame gives: For the mass m1, in the (y) direction we have: T m1 g m1a (2-1) T m2 a (2-2) For the mass m2, the (x) direction projection gives: From equations (2-1) and (2-2), we get a m1 g m1 m2 In the other hand, if we assume that the motion starts from the origin with zero initial velocity, i.e. V(0) = 0, at s(0) = 0 التجربة رقم 2 قانون نيوتن .1الهدف من التجربة: -1ايجاد المسافة المقطوعة باالعتماد على الزمن. -2ايجاد السرعة باالعتماد على الزمن. -3ايجاد التسارع باالعتماد على قيمة الكتلة المتسارعة. .2النظرية: ينص قانون نيوتن الثاني على أن مجموع القوى الخارجية المؤثرة على جسم كتلته ""m يتناسب طرديا مع قيمة تسارعه " "aجيث أن: F ma علما بأن d 2s a 2 dt عند تمثيل المعادلة المـذكورة أعاله بيانيا على االحداثيات السينية والصادية فاننا نحصل على التالي: بالنسبة للكتلة األولى " "m1فان االحداثيات الصادية تمثل بالمعادلة: T m1 g m1a بالنسبة للكتلة الثانية " "m2فان االحداثيات السينية تمثل بالمعادلة: T m2 a من المعادلتين ( )1و ( )2نحصل على: m1 g m1 m2 a واذا افترضنا أن الحركة بدأت من نقطة األصل وبسرعة ابتدائية تساوي صفرا أي أن: V(0) = 0, at s(0) = 0 the position ‘s’ of the mass ‘m’ is written as: s (t ) 1 2 at 2 So, if we know the position ‘s’ and its corresponding time ‘t’, we can determine the acceleration ‘a’ for given masses m1 and m2. The evaluation is now illustrated by the following sample measurements. 3. Set-up An experimental set-up similar to the one used is shown in the figure. The starting device is mounted in such a manner that the triggering unit releases the glider without giving it an initial impulse when triggered. The two light barriers are connected with the control input jacks on the timer. بما أن تحديد الموقع ’ ‘sللكتلة ’ ‘mيتم من خالل العالقة: 1 2 at 2 s (t ) لذا فانه بمعرفة الموقع " "Sوالزمن المصاحب لذلك نستطيع تحديد قيمة التسارع " "aلكل من الكتلتين " "m1و"."m2 .3 الجهاز: يبين الشكل أعاله اعدادات عملية شبيهة بتلك المستخدمة في المختبر ،حيث يتم تثبيت العربة األولى بوحدة االطالق " " cوالتي بدورها تؤمن انطالق العربة دون وجود أي زخم ابتدائي لحظة االنطالق ،كما أن الحاجزين الضوئيين موصولين بوحدة التوقيت لقياس الزمنيين االبتدائي والنهائي. 4. Data and Analysis Calculation of the distance in terms of the time, and the average velocity 1. Place the two light barriers in the positions listed in the table. 2. Fix the mass m1 at m1 = 10g. 3. Connect the light barriers to the timer. 4. Start the glider (fix the vacuum air power to position 6) and record the time t1 for each corresponding position s(t). 5. Repeat the operation for another time t2. 6. Fill the following table: s (m) t1 (s) t2 (s) t t1 t 2 2 t2 vav s t 1.20 1.00 0.08 0.06 0.04 7. Plot ‘s’ in terms of ‘t2’. 8. Find the slope of the straight line and deduce the acceleration 1 Slope a 2 Calculation of the acceleration in terms of the mass 1. Attach 10 hanging weights to the string, each of 1 g a piece, to obtain m1 = 10 g. 2. Determine the mass of the glider without the supplementary slotted weights by weighing it mo = 90 g 3. Fix the position between the two light barriers to be s = 80 cm. 4. Add metal weights to the glider by always placing weights having the same mass on the gliders weight – bearing pins, as optimum gliding properties are provided only with symmetrical loading. .4 القراءات والتحليل: حساب المسافة باالعتماد على الزمن والسرعة المتوسطة: -1ثبت الحجزين الضوئيين بحيث تكون المسافة بينهما كما هو موضح في القيم المعطاة في الجدول أدناه. -2ثبت الكتلة " "m1لتساوي 10غم. -3صل الحاجزين الضوئيين بوحدة التوقيت. ( -4تأكد من اختيار الرقم 6في لوحة التحكم بقوة دفع هواء المكنسة الكهربائية) قم بتشغيل المكنسة الكهربائية ،سوف تبدأ العربة بالتحرك تلقائيا .قم بتسجيل الزمن " "t1الذي لزم العربة لقطع المسافة المحددة " ،"sدون قراءتك في الجدول أدناه. -5أعد الخطوة 4مرة أخرى ألخذ الزمن "."t2 -6امأل باقي الجدول أدناه. s t vav t2 t1 t 2 2 t )t2 (s )t1 (s )s (m 1.20 1.00 0.08 0.06 0.04 -7ارسم " "sبداللة "."t2 -8أوجد ميل الخط المستقيم ثم احسب قيمة التسارع باستخدام المعادلة: 1 Slope a 2 حساب التسارع بداللة الكتلة: -1علق 10أوزان بالحبل ،قيمة كل وزنة 1غم لتحصل على وزنة كلية تساوي 10غم. 1. Determine the time ‘t’ that make the glider to reach it. 2. Determine the corresponding acceleration as: s (t ) a where 3. 1 2 at 2 2 s (t ) t2 Record the obtained results below. m2 m1 m1 m2 t (sec) m0 m0 + 100 m0 + 200 m0 + 300 m0 + 400 m1 . m1 m2 4. Plot ‘a’ in terms of 5. 6. Determine the slope of the straight line. Deduce the acceleration of the gravity ‘g’. a 2 s (t ) t2 سجل النتائج في الجدول المبين أدناه ) 2 s (t t2 a )t (sec m1 m1 m2 m2 m0 m0 + 100 m0 + 200 m0 + 300 m0 + 400






