respiratory 6
advertisement

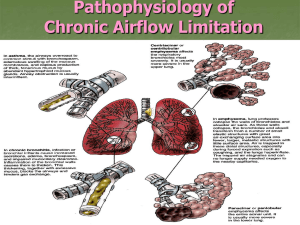
By Dr. Mohamed Seyam Ass. Professor of physical therapy for Cardiovascular \Respiratory Disorder and Geriatrics COPD is a general term that refers to a number of chronic pulmonary conditions (chronic bronchitis, emphysema) characterized by: Narrowing and obstruction of airways. Increased retention of pulmonary secretions. Structural deterioration of alveoli. Other terms used: CORD : chronic obstructive respiratory disease. COAD: chronic obstructive airways dysfunction. COLD : chronic obstructive lung disease. CAL :chronic airway limitation. Chronic Bronchitis Inflammation of the bronchi that causes irritating and productive cough that lasts up to 3 months and repeated over at least for 2 successive years. causes 1. Cigarette smoking (Predominant cause) 2. Atmospheric pollution (e.g. industrial smoke, smog ( A form of air pollution) and coal dust. pathology The hallmark is hypertrophy and increase in number of, mucous glands in the large bronchi and evidence of inflammatory changes in the small airways. Some irritative substance stimulates over activity of the mucus-secreting glands and the goblet cells in the bronchi and bronchioles which causes secretion of excess mucus. The cells increase in size and their ducts become dilated and may occupy as much as two-thirds of the wall thickness. The airways become narrowed. Clinical picture Cough Sputum Wheeze Dyspnea or shortness of breath Exercise intolerance Cyanosis Cor pulmonale Deformity - barrel chest investigation 1) PULMONARY FUNCTION TEST: Decrease in FVC, FEV1, FEV1/FVC, PEFR Increase in RV, TLC 2) ABG : Respiratory acidosis, ↓PaO2, PaCO2 3) Auscultation signs - Expiratory wheeze - Coarse crepitations - Vesicular breath sounds 4) X-ray - Flattening of the diaphragm It is a chronic inflammation , thickening and destruction of respiratory bronchioles and alveoli. Types and causes Congenital Or Primary Emphysema * May be caused by alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency. Secondary Emphysema: to other factors obstructive airways disease - e.g. asthma, cystic fibrosis, chronic bronchitis occupational lung diseases - e.g. pneumoconiosis compensatory to contraction of one section of the lung - e.g. fibrous collapse or removal pathology Toxins (smoke) cause inflammation Infiltration of neutrophils, macrophages and lymphocytes Inflammatory cytokines increase protease activity, inhibiting normal antiprotease activity (antitrypsin- It protects tissues from enzymes of inflammatory cells) Alveoli are destroyed because elastin is being broken down by proteases Clinical picture Progressive dyspnea Barrel chest Pursed lip breathing- Fish like inspiratory gasp Tachpynea with prolonged expiration Hypoxemia &/or hypercapnia Chronic hypoventilation (later stage) X-ray Flattened diaphragm Hyperinflation Translucency of lung Hypertrophy of heart Emphysematous Bullae (small air filled cyst) What is asthma? It is an obstructive lung disease seen in young patients , related to hypersensitivity of the trachea and bronchi pathology Sever spasm of smooth muscles of the bronchial tree. Narrowing of airways. Inflammation of the mucosal lining of the tracheobronchial tree. Hyper secretion of mucus. Sever asthma over a prolonged number of years can lead to emphysema. COPD: Diagnostic Tests Pulmonary Function Testing An arterial blood gas test Evaluation of functional exercise capacity Pulmonary Function Testing Examples of functional assessment walk tests the 2-min walk test (2MWT), 6-min walk test (6MWT), 12-min walk test (12MWT), Record Blood pressure Heart rate Oxygen saturation Dyspnoea score.*.Borg scale The Borg Scale is a simple method of rating perceived exertion (RPE) and can be used to determine a patient level of intensity in training. Types of scales There are a number of RPE scales but the most common are the 15 point scale (6-20), and the 11 point scale (0-10). complication chronic respiratory failure Pneumothorax Chronic pulmonary heart disease Medical management Stop smoking Avoid environment pollution Antibiotic therapy Bronchodilators- β2 - agonists Glucocorticoids Expectorant – Mucolytics Oxygen therapy surgery Lung volume reduction surgery Lung transplantation Physical therapy for COPD General clinical problems-: dyspnea on exertion. Prolonged expiration. Air trapped as airways narrowed during expiration. Chronic accumulation of pulmonary secertions. Decreased endurance and exercise capacity. Associated postural defects. Physical therapy for COPD 1- to relief dysnea by: Relaxed positions Physical therapy for COPD 1- To relief dysnea by: 2-breathing exercises Diaphragmatic Pursed lip breathing posterior lower basal Diaphragmatic breathing ex 3-respiratory ms training Pursed lip breathing Physical therapy for COPD 1- To relief dysnea by: 3-Respiratory ms training A- Inspiratory Muscle Trainer B-Incentive Spirometer Inspiratory muscle trainer Incentive Spirometer Physical Therapy of COPD 2) To remove secretions by: 1-cough. 2-postural drainage. 3-vibration. 4-percussion. 5- PEP Positive Expiratory Pressure The RC-Cornet The Flutter The Flutter Different postural drainage positions: Physical therapy for COPD Aims Methods 3) To increase exercise training:exercise tolerance – Treadmill Walking. – Bicycling on bicycle. – Free Walking. Physical therapy for COPD Aims 4) To accessory muscles respiration. Methods relax • • of Massage or hot application for the neck and upper back muscles Physical therapy for COPD Aims 5)To prevent postural defomities Methods Exercise connected with respiration stretching exercises Quiz Explain role of CO2 in maintaining exercise intensity. What is criteria for discontinuing postural drainage 10 Point Scale 0 - Nothing at all 1 - Very light 2 - Fairly light 3 - Moderate 4 - Some what hard 5 - Hard 6 7 - Very hard 8 9 10 - Very, very hard 15 Point Scale 6 - 20% effort 7 - 30% effort - Very, very light (Rest) 8 - 40% effort 9 - 50% effort - Very light - gentle walking 10 - 55% effort 11 - 60% effort - Fairly light 12 - 65% effort 13 - 70% effort - Somewhat hard - steady pace 14 - 75% effort 15 - 80% effort - Hard 16 - 85% effort 17 - 90% effort - Very hard 18 - 95% effort 19 - 100% effort - Very, very hard 20 - Exhaustion