Presented by: Ivan Aguilar
advertisement

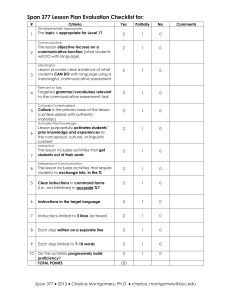
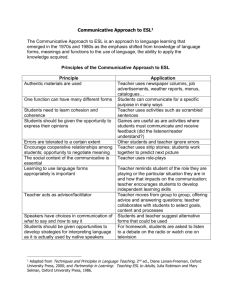
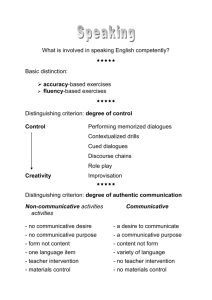
Presented by: Ivan Aguilar Communicative language teaching (CLT) is an approach to the teaching of second and foreign languages that emphasizes interaction as both the means and the ultimate goal of learning a language. It is also referred to as “communicative approach to the teaching of foreign languages” or simply the “communicative approach”.(Wikipedia) Its origins are many, insofar as one teaching methodology tends to influence the next. The communicative approach could be said to be the product of educators and linguists who had grown dissatisfied with the audiolingual and grammar-translation methods of foreign language instruction. (Center for Applied linguisitcs) This method aims at developing procedures for the teaching of the four skills that acknowledge the interdependence of language and communication. It aims at having students become communicatively competent.(Yemen Times) A set of principles about teaching including recommendations about method and syllabus where the focus is on meaningful communication not structure, use not usage. In this approach, students are given tasks to accomplish using language, instead of studying the language.(ESL Glossary) METHOD APPROACH DESIGN PROCEDURE 1.Approach An approach refers to theories about the nature of language and language learning that serve as the resources of practices and principles of language teaching. 2.Design This specifies the relationship of theories of language and learning to the selection and organization of language content (syllabus), to the types of tasks and learning activities and the role of the learners, teachers and materials 3.Procedure Comprises the classroom techniques and practices that are consequences of particular approaches and designs. The nature of language The nature of Learning a language Activities that involve real communication promote learning. Activities in which language is used for carrying out meaningful communication promote learning Language that is meaningful to the learner supports the learning process. The Goal of language teaching: Communicative competence Knowledge of the grammar, vocabulary, phonology , and semantics of the language Knowledge of the relationship between the language and its nonlinguistic (social) context. Knowledge of how to begin and end conversation (Discourse competence: cohesion and coherence) Knowledge of strategies to compensate other weak areas. Teacher’s role The teacher has to assume the role of a facilitator or monitor, rather then simply being the model for correct speech and the one with the primary responsibility of making students produce plenty of errorfree sentences. The teacher has to develop a different view of students errors and his/her own role in facilitating language learning. Learner’s role In the CLT, learners have to participate in classroom activities that are based on a cooperative rather than in a individualistic approach to learning. Students have to become comfortable with listening to their peers in pair or group work tasks, rather than relying on the teachers for a model. The Syllabus Grammar based Skills based (Listening, Speaking, Writing, Reading) Functions based (Greeting, Introducing, Telling stories) Task based (Discover the differences, Solve the problems) What kind of syllabus does your course book have? In general most course books that advocate the CLT Approach create more eclectic syllabi in which they consider the different aspects of learning a language. Types of activities Accuracy/Fluency Mechanical meaningful and communicative practice Information Gaps Information gathering Role plays Opinion sharing Accuracy Reflect classroom use of language Focus on the formation of correct examples of language Practice language out of context Practice small samples of language Do not require meaningful communication. Control choice of language Fluency Reflect natural use of language Focus on achieving communication Require meaningful use of language Require the use of communication strategies Produce language that may not be predictable. Seek to link language use to context Task: Identify activities aimed at developing Accuracy and Fluency in the coursebook. Mechanical, meaningful, and communicative practice. Mechanical practice: He _____________ (is/are) a soldier. Meaningful practice: On the weekend, I’m going to_________________ in the morning. I’m going to _____________ in the afternoon, but I’m not going to __________. Communicative practice: Ask your classmate about three things he considers when selecting a movie. Task 2: Identify these types of practice in your coursebook Some types of activities Information gaps (Activity 2) Information gathering (Activity 1) Role-plays Opinion sharing