Managers & Management MGT 101 - Principles of Management and Business
advertisement

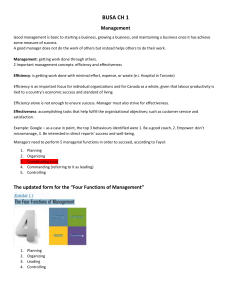
MGT 101 - Principles of Management and Business Managers & Management Week 1 Objectives ✤ To recognize the need for managers. ✤ To know the definition of organization and its characteristics ✤ To understand different types of organizational members ✤ To know the factors that reshape and redefine management Who needs managers? ORGANIZATIONS Organizations? What is an organization? ✤ Organization: a deliberate arrangement of people brought together to accomplish some specific purpose. ✤ Organization characteristics: ✤ Goals: An organization has a distinct purpose, expressed in terms of a goal or a set of goals. ✤ People: who can achieve the purpose of the organization. They make decisions and engage in work activities. ✤ Structure: deliberate and systematic. It defines and limits behaviors of its members. Organizational Members ✤ Managers: individuals in an organization who direct and oversee the activities of other people in the organization. ✤ Nonmanagerial Employees: people who work directly on a job or a task and have no responsibility for overseeing the work of others. Management Levels ✤ ✤ ✤ Top mangers: ✤ Definition: those at or near the top of an organization. ✤ Examples: CEO, vice president, chancellor.. etc. Middle managers: ✤ Definition: managers found between the lowest and top levels of the organization. ✤ Examples: department head, division manager, store manager.. etc. First-line managers: ✤ Definition: individuals responsible for directing day-to-day activities of nonmanagerial employees. ✤ Examples: supervisor, team leader, unit coordinator.. etc. Management Level Pyramid Management ✤ Management the process of getting things done, effectively and efficiently, through other people. ✤ Process a set of ongoing and interrelated activities. Efficiency and Effectiveness ✤ Efficiency doing a task correctly (“doing things right”) and getting the most output from the least amount of inputs. ✤ Effectiveness “doing the right things” by doing those work tasks that help the organization reach its goals. Interrelation between Efficiency and Effectiveness Means Efficiency Ends Effectiveness R E S O U R C E G O A L U S A G E GOALS Low waste High attainment A T T A I N M E N T Scientific Management Scientific management is the use of scientific methods to define “one best way” for a job to be done. What Managers Do 4 Management Functions Planning Organizing Achieving the organization’s stated purpose Controlling Leading Manager’s Functions: Planning and Organizing ✤ ✤ Planning: ✤ defining goals ✤ establishing strategy ✤ developing plans to coordinate activities Organizing: ✤ determining what tasks are to be done ✤ how the tasks are to be grouped ✤ who reports to whom ✤ where decision are to be made Manager’s Functions: Leading and Controlling ✤ ✤ Leading: ✤ motivating employees ✤ directing activities of others ✤ selecting the most effective communication channel ✤ resolving conflicts Controlling: ✤ monitoring work performance ✤ comparing it with goals ✤ correcting any significant deviations Mintzberg’s Managerial Roles ✤ Managerial Roles: Specific categories of managerial actions or behaviors of expected of a manager. ✤ Grouped under one three primary headings: ✤ Interpersonal roles ✤ Information roles ✤ Decisional roles Interpersonal Roles ✤ Definition: involve people (subordinates and people outside the organization) and other duties that are ceremonial and symbolic in nature. ✤ Three interpersonal roles: ✤ Figurehead ✤ Leader ✤ Liaison Informational Roles ✤ Definition involves collecting, receiving, and disseminating information. ✤ Three informational roles ✤ Monitor ✤ Disseminator ✤ Spokesperson Decisional Roles ✤ Definition entail making decisions or choices. ✤ Four decisional roles ✤ Entrepreneur ✤ Disturbance handler ✤ Resource allocator ✤ Negotiator Skills that Managers Need ✤ Conceptual Skills A manager’s ability to analyze and diagnose a complex situation. ✤ Interpersonal Skills A manager’s ability to work with, understand, mentor, and motivate other both individually and in groups. ✤ Technical Skills Job-specific knowledge and techniques needed to perform work tasks. ✤ Political Skills A manager’s ability to build a power base and establish the right connections. Is the manager’s job universal? ✤ Factors affecting the manager’s job: ✤ Level in the organization ✤ Profit versus Not-For-Profit ✤ Size of organization ✤ ✤ Small business: an independent business having fewer than 500 employees and which doesn’t necessarily engage in any new or innovative practices and which has relatively little impact on the industry. Management concepts and national borders Learning Outcomes ✤ Organizations have three characteristics: 1) Purpose, 2) People, and 3) structure. ✤ Managers lead organizations to their goals using three functions: 1) Planning, 2) Organizing, 3) Leading, and 4) Controlling. ✤ Mangers should be able to get things done efficiently and effectively. ✤ There are 3 roles that managers have: 1) Interpersonal, 3) Informational, and 3) decisional roles. ✤ Four skills that managers have: 1) Conceptual, 2) Interpersonal, 3) Technical, and 4) Political. ✤ Management is not a universal job. It differs based on different factors.