ALKANES AND ELKIN دادعإ : ملاس هرون
advertisement

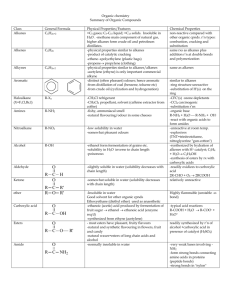
ALKANES AND ELKIN إعداد :نوره سالم المطيري ALKANES: Alkanes in organic chemistry is a saturated hydrocarbon chain consisting of an open ring, which is where the molecule by the maximum of the hydrogen atoms and therefore do not have the double bonds. Alkanes also known as paraffins, or collectively, the "chain paraffins" and these terms can also be used to alkenes, which are carbon atoms with a series of single, non-branching, and when there is a forest in a series of alkanes is called "Oazoberavit" and belong alkanes vehicle aliphatic. General equation for the installation of alkanes CnH2n +2, and the simplest alkane on this, methane, CH4, followed by ethane, C2H6, and so on. And all the carbon atoms in alkanes with hybridization sp3. NAMING ALKANES: Naming alkanes: called by two organic compounds, commonly called, which may vary from place to place, and the designation of specific international system according to IUPAC, which rely on the name of alkanes. And alkanes may be branched or branched groups contain any side 1. Determine the longest unbroken chain of carbon atoms. 2. Start numbering the atoms of one of the parties to the other party, that party will be the beginning was the closest to the branching groups in the case of their existence. 3. Determine the groups related to the string in the order and the start of typing the name of alkanes as follows: 1. Number of carbon atoms related to the sub-groups, and in the case of a branch is more than writing numbers branching order of numbering in the main chain (3.2 - not 2.3 -. 4.1 - not 1.4 -. And so on) 2. In the case of a connection to the same group more than once Bslsh alkanes, we use the following prefixes according to the number of iterations: "binary", "three", "four", and so on. 3. Name of the group or groups related to the chain, with the same numbering arrangement applied to the series. 4. Ends with name type the name of the longest straight chain. PHYSICAL PROPERTIES: -Alkanes do not dissolve in water. -Alkanes density less than water. -Increase the melting point and boiling points of alkanes generally increase the molecular weight and also increase the length of the main carbon chain. -In standard conditions, the alkanes from C4H10 to CH4 are in the gaseous state, and C5H12 to C17H36 are in the liquid state, and after C18H38 be in the solid state. CHEMICAL PROPERTIES: Alkanes Nchatitha low because the links between unilateral CC, and CH sigma type and that are relatively stable, and difficult cracking and non-polar. Alkanes do not react with acids, Alalekalat, metals, oxidizing agents. Ironically, the oil (octane) does not react with concentrated sulfuric acid, sodium metal, potassium, manganese. This inactivity is the origin of the word "paraffins" (originally the Latin "Barra" + "Lavigne", here means there is no attraction). Chemical properties ALKENE: Alkene in organic chemistry is a saturated hydrocarbon containing at least one association between two carbon atoms. Be simple alkenes, which contain one double and the Association of homogeneous series, the alkenes with general formula CnH2n. The simplest alkene is known as the "ethylene", while his official name according to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) is called Athen. THE FORM OF ALKENES: As Mnouka according to engineering the molecule it occurs repulsion between a pair of electrons (see "covalent bonds"), and thus the angle between the two atoms of carbon in the double bond will be 120 °, has become the angle largest according to the stress effect of interactions non-relational, which occur from groups linked to seed carbon. For example, the angle between the CCC in propene (propylene) of 123.9123.9 °. PHYSICAL PROPERTIES: Almost like alkanes. Physical state depends on molecular mass. Chemical properties: Alkenes are generally stable compounds, but more active than alkanes. MANUFACTURE OF ALKENES: 1. More common industrial methods for the manufacture of alkenes is the cracking of petroleum. 2. Can manufacture alkene reactions of alcohols other than removal, which is the removal of the water molecule the molecule: H3C-CH2-OH + H2SO4 → H3C-CH2-O-SO3H + H2O → H2C = CH2 + H2SO4. 3. Catalytic processing of large alkenes of the type α-alkene, which can be obtained from the reaction of ethylene with tri ethyl aluminum organometallic compound in the presence of nickel, or cobalt, or platinum ADDITION REACTIONS: Catalytic addition of catalytic Hedroginagrjh of alkenes produces the corresponding alkanes. Interaction is under pressure in the presence of a catalytic metal. It is common industrial catalysts use platinum, nickel, palladium, for use in laboratories. And is often used Raney nickel, an alloy of aluminum and Alnica. The next equation describes the hydrogenation of ethylene for ethane: CH2 = CH2 + H2 → CH3-CH3. Add passionate electrons Most addition reactions to alkenes follow the mechanism similar passion for electrophilic addition. Halogenated: Add bromine or chlorine in their racism and alkenes to produce binary Fasenall bromo-, and dichloro alkene, respectively. And the process of stripping chlorine from a solution of bromine in water is the analytical method to test the presence of alkene: CH2 = CH2 + Br2 → BrCH2-CH2Br