Syllable Structure- Phonetically and phonologically
advertisement

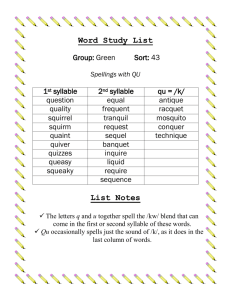
Syllable Our presentation will cover…. Syllable definition Syllable structure Syllabification why to know syllable… Understanding syllable will help us understand stress patterns and thus pronunciation of a language Syllable The syllable is a basic unit of speech studied at both the phonetic and phonological levels of analysis. we refer to syllables (Greek letter sigma ….. ) Words can be cut up into units called syllables. Humans seem to need syllables as a way of segmenting the stream of speech. Syllables don't serve any meaning-signalling function in language; they exist only to make speech easier for the brain to process. A word contains at least one syllable. Phonetic definition Phonetically syllables “are usually described as consisting of a centre which has little or no obstruction to airflow and which sounds comparatively loud; before and after that centre, there will be greater obstruction to airflow and/or less loud sound”. In the monosyllable (one-syllable word) cat /kæt/, the vowel /æ/ is the “centre” at which little obstruction takes place, whereas we have complete obstruction to the airflow for the surrounding plosives /k/ and /t/. Phonological definition Laver (1994: 114) defines the phonological syllable as “a complex unit made up of nuclear and marginal elements”. Nuclear elements are the vowels or syllabic segments; marginal elements are the consonants or nonsyllabic segments. In the syllable paint /peɪnt/, the diphthong /eɪ/ is the nuclear element, while initial consonant /p/ and the final cluster /nt/ are marginal elements. Structure of Syllable Syllable Structure It is the combination of allowable segments and typical sound sequences, and is language specific, e.g. plant Onset: Onset: the beginning sounds of the syllable; the ones preceding the nucleus. These are always consonants in English. In the following words, the onset is in bold; the rest underlined. read flop strap If a word contains more than one syllable, each syllable will have the usual syllable parts: win.dow to.ma.to Rhyme (or rime) Rhyme: The rest of the syllable, after the onset The rhyme can also be divided up: Rhyme = nucleus + coda Coda The Coda includes all consonants that follow the Peak (nucleus) in a syllable. Some syllables consist only of a nucleus with no coda. The following single-syllable words end in a nucleus and do not have a coda (phonologically): Examples: Glue /glu:/ I The syllable structure analysis of the words 'read', 'flop', 'strap' and 'window' are as follows (IPA symbols are used to show the sounds in the word/syllable): read = one syllable Onset = [ r ] Rhyme = [ id ] (within the rhyme:) Nucleus = [ i ] Coda = [ d ] flop = one syllable Onset = [ f l ] Rhyme = [ a p ] Nucleus = [ a ] Coda = [ p ] Types of Syllable 1. Monosyllable A word that consists of a single syllable (like dog) is called a monosyllable (and is said to be monosyllabic). Bear dish deal Ball bat 2. Disyllable A word that consists of a two syllables (like window) is called a disyllable (and is said to be disyllabic). arrow barrow bellow billow 3. Trisyllable It is for a word of three syllables; Beautiful Terrible Horrible carefully 4. Polysyllable Which may refer either to a word of more than three syllables or to any word of more than one syllable. Polysyllable Trisyllable