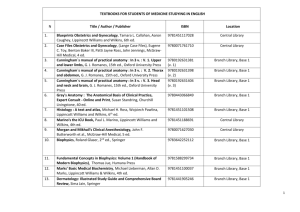
Foundations of Therapeutic Exercise Chapter 1 Introduction to Therapeutic Exercise

Foundations of Therapeutic
Exercise
Chapter 1
Introduction to Therapeutic Exercise and the Modified Disablement Model
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy includes diagnosis and management of movement dysfunction and enhancement of physical and functional abilities: restoration, maintenance, and promotion of optimal physical function, optimal fitness and wellness, and optimal quality of life as it relates to movement and health; and prevention of the onset, symptoms, and progression of impairments, functional limitations, and disabilities that may result from diseases, disorders, conditions, or injuries.
Guide to Physical Therapy
Practice. Phys Ther 2001;81:1
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Physical Therapy (PT) Includes
Examining patients with impairments, functional limitations, and disability or other health-related conditions to determine a diagnosis, prognosis, and intervention.
Alleviating impairments and functional limitations by designing, implementing, and modifying therapeutic interventions.
Preventing injury, impairments, functional limitations, and disability.
Engaging in consultation, education, and research.
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Impairment Question
“What impairments are related to reduced function and disability for this patient and which exercises can improve functional performance and disability by addressing the appropriate impairments?”
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Therapeutic Exercise Intervention
Patients – Persons with diagnosed impairments or functional limitations.
Clients – Persons who are not necessarily diagnosed with impairments or functional limitations, but seek services for prevention or promotion of health, wellness, and fitness.
Both seek and benefit from Physical Therapy
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Therapeutic Exercise = Core Element
Enables Patient/Client to:
Remediate or reduce impairments
Enhance function
Reduce risk
Optimize overall health
Enhance fitness and well-being
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Therapeutic Exercise
Individual Goal-Oriented Treatment
Provide comprehensive and personalized patient management.
Rely on clinical decision-making skills.
Implement a variety of therapeutic interventions that are complimentary.
Promote patient independence (when possible) through home treatment, self-management exercise programs, and patient-related instructions.
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
The Disablement Process
Disablement – “Various impact(s) of chronic and acute conditions on the functioning of specific body systems, on basic human performance, and on people’s functioning in necessary, usual, expected, and personally desired roles in society.”
Nagi, SZ, Disability and Rehabilitation. Columbus, Ohio:
Ohio State University Press, 1969.
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Why Define the Process of
Disablement?
To understand the complex relationships of pathology and disease, impairments, functional limitations and disability and to provide a conceptual basis for organizing elements of patient/client management that are produced by physical therapists.
To enable the therapist to make sound decisions regarding therapeutic exercise intervention.
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Definitions
Impairment – Loss or abnormality of anatomic, physiologic, or psychologic structure or function.
Secondary Impairment – An impairment that originates from other, preexisting impairments.
Primary impairments can create secondary impairments.
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Functional Limitation
“A restriction of the ability to perform, at the level of the whole person, a physical action, activity, or task in an efficient, typically expected or competent manner.”
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Disability
The inability to perform or limitation in the performance of actions, tasks, and activities usually expected in specific social roles that are customary for the individual or expected for the person’s status or role in a specific sociocultural context and physical environment.
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Therapeutic Exercise
Consider the functional loss and disability of the patient.
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Evolution of Disablement Model
World Health Organization (WHO)
International Classification of Impairments,
Disabilities, and Handicaps (ICIDH)
Saad Nagi (NAGI)
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
ICIDH
Disease
Active
Pathology
Impairment
Disability
NAGI SCHEME
Handicap
Impairment
Functional
Limitation
Disability
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Primary Differences
ICIDH – Functional limitation and disability are not differentiated.
Handicap – Final element.
Limitation – Lacks consideration of cause of limitations in performing societal roles.
NAGI – Considers distinction between functional limitation and disability.
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Modified Disablement Model
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Impairments
Physiologic – function.
An alteration in any physiologic
Anatomic – An abnormality or loss of structure.
Psychologic – Any abnormality related to the psychologic system.
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQL)
Added to the final 2 elements of pathway
(Functional Limitations and Disability)
Definition – Generally corresponding to total well being, encompassing 3 major components.
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
3 Components of HRQL
Physical Function Component , which includes Basic Activities of Daily Living
(BADLs) and Instrumental Activities of Daily
Living (IADLs).
Psychological Component, which includes the “various cognitive, perceptual, and personality traits of a person”; and
Social Component, which involves the interaction of the person “within a larger social context or structure.”
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Risk Factors
Demographic, social lifestyle, behavioral, psychologic, and environmental factors
Comorbidities
Physiologic impairments
Anatomic impairments
Functional performance factors
Risk factors are predisposing in that they exist before the onset of the disablement process.
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Prevention and Promotion of Health,
Wellness, and Fitness
Key Preventions in Physical Therapy
Primary – Prevention of disease in a susceptible or potentially susceptible population through specific measures such as general health promotion offers.
Secondary – Efforts to decrease duration of illness, severity of disease, and sequelae through early diagnosis and prompt intervention.
Tertiary – Efforts to decrease the degree of disability and promote rehabilitation and restoration of function in patients with chronic and irreversible diseases.
Promotion of Health, Wellness, and Fitness – Critical
Foundation of Therapeutic Exercise Intervention!!
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Use Of Disablement Model – Empowers the Physical Therapist to:
Develop comprehensive and efficient examinations and evaluations of impairments and functional limitations relating to the patient’s unique disability profile.
Reach an accurate diagnosis based on logical classification of pathology, impairments, and functional limitations.
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Disablement Model (cont.)
Develop a prognosis based on the evaluation and the patient’s goals.
Create and implement effective and efficient interventions.
Reach a desirable functional outcome for the patient as quickly as possible.
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Through understanding the Disablement Model, practitioners may develop a plan to satisfy the demands of all involved.
Clinical Value =
Functionally
Meaningful
Patient
Outcomes
+
Patient
Satisfaction
Financial and
Social Costs of
Providing Care
Copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins