Determination of Calcium
advertisement

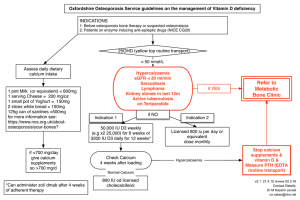
Outline of Today’s lecture 1. Introduction 2. Distribution of calcium 3. Calcium functions 4. Sources of calcium 5. Clinical significance of calcium 6. Principle of calcium estimation Objectives To determine serum calcium level. Master how to determine the conc. of calcium in serum. Discuss calcium functions. Discuss the hypercalcaemia and hypocalcaemia Introduction Calcium is the most common mineral in the human body. Calcium has a lot of cellular and tissue effects involving contractile machinery, structural roles, enzymatic reactions etc. Calcium found in the blood and fluid must be maintained within a narrow concentration range for normal physiological functioning. Distribution of Ca 99% of calcium in the body is part of bone . 1% in the blood : - 45% circulates as free Ca ions. - 40% bound to albumin. - 15% bound to anions. ► Both total calcium and ionized calcium measurements are available in many laboratories. Physiological functions of Calcium Bone mineralization. Blood coagulation. Important in muscle contraction. Affecting enzyme activity. Affecting hormone secretion. Sources of Calcium Excellent sources include milk products – Skim milk, low-fat cheese, nonfat yogurt Other good sources include – Green leafy vegetables (kale, collard greens, broccoli, and cabbage are low in oxalates) – Others like orange juice, soy milk – Fish with edible bones (sardines, salmon) 12- Structure : calcium is a major structural element in bones and teeth. Cell signaling: – Constriction and relaxation of blood vessels. – Nerve impulse transmission. – Muscle contraction. – Secretion of hormones 3- Cofactors for enzymes and proteins: A-Hypercalcaemia (high serum calcium) 1-Hyperparathyrodism. 2-Carcinoma (Cancer) Metastatic To Bone 3-Sarcoidosis. 4-Multiple Myeloma B-Hypocalcaemia (low serum calcium) 1-Pseudohypoparathyrodism. 2-Vitamin D Deficiency. 3-Malabsorption. 4- Kidney Disease. stones, bones, abdominal groans and psychiatric moans (renal stones, peptic ulcers, pancreatitis, confusion, lethargy, weakness) Calcium ions react with reagent (ocresolphthalein-complexone) in an alkaline medium to form a purple colored complex. The absorbance of this complex is proportional to the concentration in the sample Requirements Requirements: Automatic pipettes Tips Cuvettes Spectrophotometer Reagent Specimen: Serum or plasma Preparation of Cuvettes Procedure Blank (only Reagent) Standard (Reagent+ Calcium St.) Sample (Reagent+Serum) Reagents Calcium Standard (μl) Sample # 1 (μl) Ca++ reagent (ml) Blank - Std. 20 S#1 - - - 20 1.0 1.0 1.0 Mix, wait 5 minutes at room temperature (RT). Zero the spectrophotometer with the blank at 570 nm. Read the absorbance for both of standard and the samples. Record your results for further calculation. The color is stable for at least 45 minutes. Calcium concentration (mg/dl)= Absorbance of Sample Absorbance of Standard X Standard Conc. Child 2.20-2.70 mmol/L (8.8-10.8 mg/dL) Adult 2.15-2.50 mmol/L (8.6-10.0 mg/dL) Conclusion Calcium is essential!!! An important mineral for human health Must meet adequate daily intake in order to maintain a healthy skeleton A very exciting area for research