The Vitamins Chapter 10 & 11
advertisement

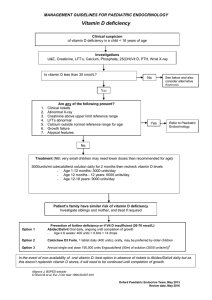
The Vitamins Chapter 10 & 11 The Water-Soluble Vitamins: B and C (there are 8 B Vitamins) The Fat-Soluble Vitamins: A, D, E, and K What are Vitamins? - small organic molecules - essential nutrients - required in very small quantities e.g. 5 g / day of Vit D 400 g / day of folate 14 g / day of biotin Compare this to the energy nutrients Energy Nutrients Assume a 2000 kcal / day diet % Carbs: % Lipids: % Proteins: ? ? ? Energy Nutrients Assume a 2000 kcal / day diet % Carbs: 55% x 2000 kcal = 1100 kcal % Lipids: 30% x 2000 kcal = 600 kcal % Proteins: 15% x 2000 kcal = 300 kcal 275 g Carbs, 67 g Lipids, 75 g Protein What do Vitamins look like? O H3C H3C N N N N O O CHOH CHOH OH O P O O CH2 CHOH O H H N H Riboflavin (Vit. B2) Pyridoxal phosphate (Vit. B6) CH2 OH CH3 HO O HOCH2 HO O OH Ascorbic Acid (Vit. C) What do Fat Soluble Vitamins look like? H3C CH3 CH3 CH3 OH CH3 Retinol (Vit. A) H3C CH3 H2C Pre-Vit. D HO What do Vitamins actually do? - they are co-factors or co-enzymes - they help proteins perform various functions within the body. e.g. - enzymes in energy metabolism - vision (Vit. A) Coenzyme Action The Water-Soluble Vitamins: B and C Metabolic pathways involving B Vitamins Getting Proper Levels of Vitamins If the guidelines of diet-planning are followed, individuals in the developed world should not have a problem. However, there are things to consider: 1) 2) 3) 4) Bioavailability Stability Solubility Toxicity Understanding Dose Levels vs Health Effects The B Vitamins - Thiamin - Riboflavin - Niacin - Biotin - Pantothenic acid - Pyridoxine - Folate - Cyanocobalamin Lets look at 2…… ©2001 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Thomson Learning™ is a trademark used herein under license. Thiamin Pork is the richest source of thiamin, but enriched or whole-grain products typically make the greatest contribution to a day’s intake because of the quantities eaten. Thiamin (TPP) - Vit B1 - involved in the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA - deficiency results in a condition known as beriberi - damage to nervous system, brain function, heart and muscles. ©2001 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Thomson Learning™ is a trademark used herein under license. Folate (Folic Acid) Leafy green vegetables, legumes, liver, and some fruits are naturally rich in folate. Folate (Folic acid) - involved in the synthesis of DNA, especially in newly formed cells - deficiency results in anemia and GI tract deterioration - in the developing fetus, neural tube defects have been linked to low folate levels Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) When dietitians say “vitamin C,” people think “oranges,” but these foods also are rich in vitamin C. Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) - deficiency results in scurvy - involved in the synthesis of collagen Ascorbic Acid (Vit. C) O H2N + O O H2N + OH O 2000 Vitamin C RDA (75 - 100 mg/day) Linus Pauling 90 75 Common cold And Heart Disease The Fat-Soluble Vitamins: A, D, E and K Forms of Vitamin A OH retinol H O retinal OH O retinoic acid -carotene Vitamin A Deficiency - 100 million children worldwide suffer from some form of Vit A deficiency - Infectious Disease - Measles kills 2 million children each year - Night Blindness and Xerophthalmia - Keratinization (RDA = 700 - 900 g / day) ©2001 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Thomson Learning ™ is a trademark used herein under license. The carotenoids in foods bring colors to meals ….. the retinoids in our eyes allow us to see them. Retinol’s Role in Vision 11-trans-retinal 11-cis-retinal light metarhodopsin-II N OPSIN rhodopsin N OPSIN retinal isomerism H O OPSIN light H O OPSIN Vitamin D Deficiency - rickets in children - osteomalacia in adults leading to osteoporosis (AI = 5 g / day) Vitamin D synthesis and activation Part from diet Part from biosynthesis ©2001 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Thomson Learning™ is a trademark used herein under license. Vitamin D synthesis and Latitude ©2001 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Thomson Learning™ is a trademark used herein under license. Vitamin D can be synthesized in the body with the help of sunlight or obtained from foods derived from animals. A deficiency causes rickets in childhood. Fortified Milk is an important food source. Vitamin E Deficiency: a-tocopherol - Primary deficiency is very rare - Secondary deficiency: (usually associated with a lack of fat absorption) - Erythrocyte hemolysis - Neuromuscular dysfunction (RDA = 15 mg / day) Free Radical Formation e- 2 H+ e- e- H+ . O O2 H2O2 2 . protein protein or lipids (PUFA) . OH + . OH or . lipids (PUFA) + H2O Anti-oxidant Protection Against Free Radicals . protein or protein + Vit. E lipids . (active) (PUFA) Vit. E . (inactive) + Vit. C or lipids (PUFA) Vit. E (active) + Vit. E . (inactive) + Vit. C Vitamin E Supplements Vitamin E has 3 stereogenic centres Therefore, when made synthetically: 2 x 2 x 2 = 8 different forms ONLY 1 is the NATURAL & ACTIVE form 1 / 8th Vitamin K Deficiency - Primary deficiency is rare because it is produced from bacteria in the GI. - Secondary deficiency: 1) altered fat absorption 2) drugs such as antibiotics kill or disrupt bacterial production of Vit. K (AI = 90 - 120 g / day) Vitamin K Deficiency - Hemorrhagic disease (uncontrolled bleeding) - Bone Health - i.e. osteoporosis (involved in the activation of 3 bone health related proteins) - Calcification of Arterial Plaques (increased risks of heart disease and arterial sclerosis) ©2001 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Thomson Learning™ is a trademark used herein under license. Notable food sources of vitamin K include: milk, eggs, brussels sprouts, collards, liver, cabbage, spinach, and broccoli. Phytochemicals in Disease Prevention Phytochemicals metabolites produced by plants e.g. 1) Antioxidant activity 2) Phytosterols Anti-oxidant Protection Against Free Radicals . protein or . lipids (PUFA) protein + Phyto chemical (active) or lipids (PUFA) . Phyto + chemical (inactive) Phytochemicals in Disease Prevention Broccoli Sprouts Red Wine: Resveratrol Apples: Flavonoids Garlic & Onions: Allicin (S) Flax: Lignan Tomatoes: Lycopene