Globalization Devolution

Global Challenges
Developed by
Joe Naumann
Whither Gaia?
1
Globalization – Empire Building
• Ancient times
– Alexander the Great
– Rome
• Middlel Ages
– Mongol
• 18 th -19 th Centuries
– British Empire
• 20 th Century
– Hitler (failed)
– Soviet Union (failed)
2
British Empire Was The Biggest
• Based on naval power
• Developed along with the growth of industry
– Markets
– Raw materials
– Protection of sea lanes
• “The sun never sets on the British Empire”
• Legacy
– English most widely spoken language
– Democratic ideals
3
British Empire & Others
4
19
th
Century Empire Dissolution
• Spanish and Portuguese (Americas)
• Causes
– Primary causative event – Napoleon’s conquest of Spain & Portugal
– Dissatisfied creoles (Spanish)
– Encouraged by the successful revolution in the United States in North America
– Encouraged by political philosophies expressed by Enlightenment writers
– Encouraged by the French Revolution
5
20
th
Century Empire Dissolution
• British, French, German, Italian, Belgian, Dutch
• Primary causative factors: World Wars I & II
• Improved communications
• Educated elites in the colonies took leadership roles
• Self-determination of peoples encouraged by United
Nations charter
• Costs increasing for economically burdened
European countries
• Retaining by force no longer feasible
6
Return of Hong Kong to China
• Last major part of the former British
Empire returned in 1997
7
Colonialism &
Neocolonialism
• Most less developed countries are former colonies
In a position to take advantage of the other
8
Two Paradoxical Forces
• The world is being shaped by two different and seemingly contradictory forces, both of which seem to be growing. Therein is the paradox – the tension within which we must live.
• A geographer brings that special, spatial, integrative point of view to the study of these transnational forces.
9
Forces in the Post-Cold-War World
• Globalism – The development of political and quasi-political organizations and structures that transcend the “nation-state.”
• Devolution – The breaking down into smaller, simpler parts as in ethnic strife leading to hostility and the breaking-up of multinational states and even states formerly thought to have become “nationstates.”
10
Globalism: The Positive Side
• the growing realization that all countries must work within the framework of a global economy.
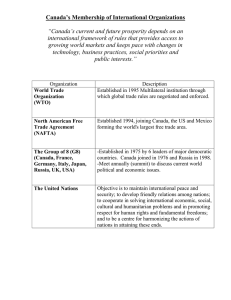
• Economic unions:
– NAFTA
– European Union
– Others
• International peace-keeping forces to prevent the spread of conflict.
• Russia consulting with and cooperating with
NATO????????????????
11
Globalism: The Negative Side
• Easier spread of ideas and diseases
– Terrorism – anti-Jewish & anti-American
– Diseases – AIDS, Ebola, Mad Cow, etc.
• Multi-national or Trans-national corporations
– the totality is not subject to the jurisdiction of any political unit.
• In 2001, the United States became committed to a “War on Terrorism.”
• Increased health concerns for citizens.
• Consumers seem to be having fewer real choices in the marketplace.
12
Devolution
• Striving of national or ethnic groups for sovereign political expression
• Parts of several multinational states may seek to unite as a separate political entity.
• Hostilities long thought dead have surfaced in the post Cold War world.
• When these threaten world security and trade, the US may become involved financially and/or militarily.
13
Global Economy
• No country on earth has, within its boundaries and jurisdiction, all the resources needed to operate as a developed country.
• The USA imports 100% of more than a dozen key mineral resources.
• Benefits:
– Greater economic diversity and job opportunities for countries.
– Better quality, lower cost consumer products.
14
Three Levels of Cooperation
• Free Trade Area – No internal tariffs
– Each country sets tariffs for nonmembers
• Customs Union – Eliminates internal tariffs & adopts a common external tariff policy
• Common Market –closest level of cooperation
– Eliminates internal tariff & sets common external
– Common laws relating to production
– May establish some common political institutions & may work toward eventual political union
– Many common political, economic, & social areas
15
Economic Unions
• The development after WW II of the European Union has improved living standards among members and given Europe the longest period of peace
• NAFTA has the potential to do that in the Western
Hemisphere – effort are being made to expand it.
• Initially there are some dislocations, but in the long-run member countries and their citizens benefit
16
EU Cooperation – potent force
• European Parliament – growing but limited power
• One huge market for goods, capital, labor
– Euro accepted by most but not all
• Transportation system at all levels
• Regional policy to assist poor agricultural areas and declining urban areas
• Social policy – laws for work, labor, visas, etc.
• Environmental policies
• Defense (really through NATO)
17
European Union Growth
18
European Union
• Promotes peace
• Has raised living standards
• Is probably the “model” economic union in the world today.
19
What is NATO Becoming?
20
NATO trying to keep the peace in
Kosovo
Click on the map to see the video
21
NAFTA begins in controversy
•
Click the picture to see the video
22
NAFTA (trade & investment only)
• Canada & USA
• Canada, USA, & Mexico
– More resistance in USA to Mexico joining
– Maquiladoras in northern Mexico
– Mexico may have developed real democracy
• Expansion
– Talks have been going on with Chile
– Andean & Middle American trade unions
– Talk of eventually the whole Western Hemisphere except for Cuba (Cuba will probably change after Castro dies)
23
NAFTA Trade
Flows
24
International Level
• League of Nations
• United Nations
25
UN Strengths
• Moral force in the world
• Forum for discussion & negotiation
– UN Convention on the Law of the
Sea
• Peace keeping forces in trouble spots
• Special agencies – improve social, medical, & educational conditions world wide
• World Court to settle disputes
26
UN Weaknesses
• Yearly income not guaranteed
– USA didn’t pay its assessment for years
• Permanent members with veto power in the security council
• No standing police force or military to enforce its resolutions
– countries censured, often ignore the resolutions
27
UN Encroachment on Sovereignty
Needed to Handle Some Problems
• States have limited jurisdiction on transnational corporations (multi-nationals)
• Globalization of justice
– Crimes against humanity – International War Crimes and
Genocide Tribunal established
• Human rights – Universal Declaration of Human
Rights
– Different cultures view individual rights and community rights differently
– Different views of individual’s social responsibility
28
More Encroachment
• Jurisdiction over open areas
– Arctic and Antarctic
– High Seas
– Airspace
– 1982 U.N. Convention on the Law of the Sea
– Endangered ocean species – regulating whaling
• Environmental problems don’t stop at borders
– Air pollution: acid rain, ozone depletion, global warming
– Water pollution – rivers, seas, & oceans
• International terrorism, i.e. N.Y. 9/11/2001
29
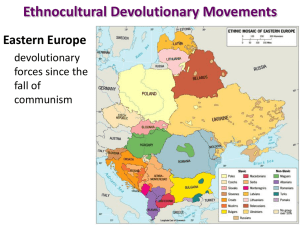
Devolution Movements are on the rise also
• Serious threats:
– Canada
– Spain
– United Kingdom – less serious except for N. Ireland.
– Russia -
– Afghanistan
• Recent examples:
– Former Yugoslavia
– Former Soviet Union
– Former Czechoslovakia
30
Factors that assist devolution
• Differences between the majority and a significant minority
– Language & religion – very emotional
– Economic development
• Historic animosity
• The minority is the dominant element in a somewhat compact region of the country
• Minority’s territory is more peripherally located than centrally located
• Minority is encouraged (financed) by another country
31 or foreign organizations
DEVOLUTION
• Sadly, terrorism is becoming a more frequently used tool by groups seeking “self-determination.”
32
Terrorism Factor
• Terrorism has struck on every continent except Australia
Ulster, N. Ireland Grozny, Chechnya Basque - Spain
33
Kashmir shelling Sri Lanka, truck bomb E. Timor victims
Cold War Europe
• Soviet Union split apart
• Eastern
European countries became truly free and sovereign.
34
Europe
• The potential abounds in
Europe and in other places too.
35
Successful Devolution
• Break up of colonial empires
• Partition of India/Pakistan
• Separation of Bangladesh from Pakistan
• East Timor (at least temporarily)
• Yugoslavia split 5 ways
• U.S.S.R. split into separate republics
• Czechoslovakia divided in two
• Philippine independence from USA
• Finland separated from Sweden & Russia
• United Arab Republic (short lived)
• Eritrea from Ethiopia
• Singapore from Malaysia
36
Failed attempts
• Biafra (Nigerian civil war)
• Chechnya from Russia (so far)
• Quebec (separation vote failed)
• Puerto Rico (separation vote failed)
• Katanga in Congo right after independence
• Ogodan province of Ethiopia
• USA civil war
• Philippines (so far)
• Sudan (so far)
• Basques in Spain (so far)
• Tamils in Sri Lanka (so far)
37
Kurdistan
Click on the map to see the video
• Perfect example of a stateless nation
38
Countries where the potential is real
• Russia
• Almost every African country
• Yugoslavia
• Italy
• Spain
• France
• Britain
• Brazil
• Mexico
• Indonesia
• China
• India
• Peru
• Colombia
• Cyprus
• Turkey
• Syria
• Iran
• Iraq
• Afghanistan
• New Zealand
• India
39
Sikhs in India
Click the picture of
Gandhi to see the video
•
What of the wisdom of Gandhi?
• What of Sikh separatism?
• What of Hindu Nationalism?
• How can they coexist?
40
European Paradox: Catalonia
• Catalonia is an example
• Desires separation from Spain but may settle for greater autonomy (Spanish government hopes so)
– It is the most industrially developed part of Spain
• BUT probably would want to remain in the European
Union
– Benefits from membership in the union – separation from the EU would hurt it economically
– One of the major industrial areas of the EU
41
Is the State Becoming Obsolete?
• There is some basis for saying yes to some type of global governance or cooperation
BUT – probably not in our lifetime
• Emotional factors, old jealousies, and old hatreds may prevent some global accommodation
• Differences in political and economic systems may be difficult to reconcile
42
We Will Play A Part in Determining the Future Shape and Destiny of
Gaia. What Parts Will We Play?
GAIA
43