Snap shot of different approaches to Tree Building
advertisement

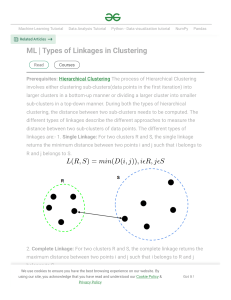
Snap shot of different approaches to Tree Building Similarity/Difference Methods that use clustering algorithms Repeatable – always results in the same “best” tree Less computationally intensive – suitable for large # of taxa UPGMA (EvoBeaker Dogs) Assumes equal rate of evolution – simple clustering algorithm (average distances) Neighbor-joining method Doesn’t assume equal rate of evolution – slightly more complex clustering algorithm Maximum parsimony Saves the shortest trees (there may be more than one) Maximum Likelihood Given a model of how evolution is thought to proceed and the data on hand, what is the most likely tree? Baysesian methods What is the probability of observing a hypothesize tree (or trees) given a model of evolution and the data on hand