Example 1
advertisement

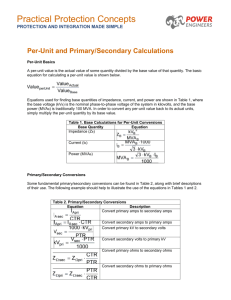
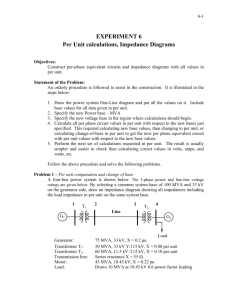
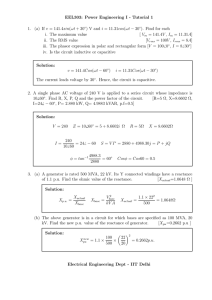
Examples: Example 1 Prepare a per-phase schematic of the system shown below in Figure B4.7 and show all impedances in per-unit on a 100 MVA, 154 kV base in the transmission line circuit. Necessary data for this problem are as follows G1: 50 MVA, 13.8 kV, X = 0.15 per-unit G2: 20 MVA, 14.4 kV, X = 0.15 per-unit T1: 60 MVA, 13.2/161 kV, X = 0.10 per-unit T2: 25 MVA, 13.2/161 kV, X = 0.10 per-unit Load: 25 MVA, 0.80 pf lag T1 T2 20 j80 G1 G2 10 j 40 10 j 40 Load Solution Base kV in the Transmission Line = 154 kV Base kV in G1 and G2 = 154 13 .2 12 .63 kV 161 Note: Once the Base kV is specified in the transmission line circuit, the Base kV in all other circuits is determined by the transformation ratio of the appropriate transformers. In this example T1 and T2 have the same transformation ratio. Hence the Base kV in G1 and G2 are equal. If the transformation ratios were not the same then the appropriate transformation ratios should be used to determine the base voltage. 2 G1 : X 0.15 100 13.8 0.3583 per unit 50 12.63 G2 : X 0.15 100 14.4 0.9755 per unit 20 12.63 2 2 2 2 2 100 161 100 13.2 T1 : X = 0.10 0.10 0.18216 per unit 60 154 60 12.63 100 161 100 13.2 T2 : X = 0.10 0.10 0.4372 per unit 25 154 25 12.63 Base Impedance in Transmissi on Line Circuit = Z T.Line (154x10 3 ) 2 237.16 100x10 6 20 j80 0.084 j 0.3373 per unit 237.16 Base Impedance in Load Circuit = (12.63x10 3 ) 2 1.595 100x10 6 10 j 40 6.269 j 25.075 per unit 1.595 Load = 25(0.8 + j0.6) = 20 + j15 MVA Z D. Line 2 Ru Vload (100 x10 6 ) 20 x10 6 (12.63 x10 3 ) 2 2 , Xu Vload (100 x10 6 ) 15 x10 6 (12.63 x10 3 ) 2 j 0 . 3583 G1 j 0 .18216 6.269 0 . 08 j 0 . 3373 j 25.075 j 25.075 j 0 .4372 6.269 Load Ru Xu j 0 .9755 G2