measures of dispersion
advertisement

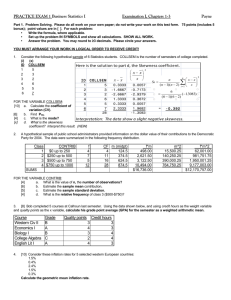
1 Consider the following three sets of data 50, 50, 50 Mean = 50 48, 50, 52 Mean = 50 1, 49, 100 Mean = 50 Measures of dispersion help us to study how spread or varied or scattered is the data. 2 Variance is the average of the sum of squares of deviations of observations from their mean. Variance = x i x 2 n Standard Deviation = Variance To compare two or more sets of data we calculate the Coefficient of Variation Coefficient of Variation = Standard Deviation x 100 Mean 3 Consider the following data representing the distribution of salaries of 3 companies A, B and C each having 76 employees: Class Mark Salary X (in Rs) Company A Company B Company C 250 200-300 3 3 3 350 300-400 8 8 9 450 400-500 16 15 13 550 500-600 22 23 23 650 600-700 16 18 20 750 700-800 8 6 5 850 800-900 3 2 2 950 900-1000 0 1 1 76 76 76 Total Number of employees 4 For the above data the following results are observed: Mean Salary (in Rs) S.D. (in Rs) C.V . S .D. 100 Mean Company A Company B Company C 550 550 550 140.49 140.49 140.49 25.54 25.54 25.54 In order to compare such types of data we use a measure called SKEWNESS. Skewness means lack of symmetry. 5 6 7 8 Skewness is measured with the help of COEFFICIENT OF SKEWNESS. If the value of coefficient of skewness is zero, the data is symmetric. If the value of coefficient of skewness is less than zero, the data is negatively skewed. If the value of coefficient of skewness is greater than zero, the data is positively skewed. 9 Consider the following data representing the distribution of salaries of 3 companies A, D and E each having 76 employees: Class Mark Salary X (in Rs) Company A Company D Company E 250 200-300 3 2 4 350 300-400 8 10 6 450 400-500 16 17 15 550 500-600 22 18 26 650 600-700 16 17 15 750 700-800 8 10 6 850 800-900 3 2 4 76 76 76 Total Number of employees 10 30 25 20 15 Company A Company D Company E 10 5 0 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 11 12 Kurtosis is measured by coefficient of kurtosis. Coefficient of Kurtosis characterizes the relative peakedness or flatness of data. Positive coefficient of kurtosis indicates a relatively peaked or leptokurtic data. Negative coefficient of kurtosis indicates a relatively flat or platykurtic data. Zero coefficient of kurtosis indicates mesokurtic data. 13