balance sheet
advertisement

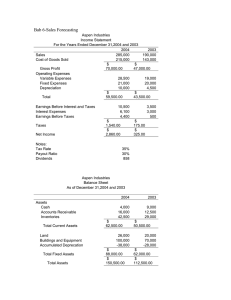
UNDERSTANDING BALANCE SHEET Balance Sheet 1. Asset structure and its financing 2.Efficient management of assets and liabilities 3.Prepared as on a given date in a specific format -generally vertical form 4.Two years comparative figures 5. Grouping and sub grouping of assets and liabilities Assets FIXED TANGIBLE INTANGIBLE CURRENT Fixed Assets are held by the enterprise for use in the production or supply of goods and services. Fixed assets are also called as long term assets Fixed assets provides facilities to produce and deliver goods and services. They are generally held by the business for a long time Tangible fixed Assets have physical existence viz: land, buildings,plant and machinery, furniture, equipments, motor vehicles etc. Intangible fixed assets have no physical existence they represent legal rights or economic benefits enjoyed by the company.viz patants, trademarks ‘goodwill, franchisee rights etc. Natural resources like oilwells,mines and forests are also fixed assets and they are treated as a category by itself due to their special nature. Current Assets :Such assets have the following characteristics: - It is held for sale in the ordinary course of the business. - It is expected to be realised in the normal operating cycle - It is cash or cash equivalent Operating cycle : a) more than 12 months b) less than 12 months Criteria of 12 months CURRENT ASSETS 1. Inventories 2. Debtors 3. Cash & Bank Balances ( Incl. Cash equivalents – treasury bills, equity shares held as investments ) LOANS & ADVANCES 4. Advances – staff advances, advances to suppliers 5. Advance Income Tax 6. Securities to various Govt. depts. 7. ICDs Fictitious Assets – no future economic benefit Miscellaneous expenditure like preliminary expenses, deferred revenue expenditure and profit and loss a/c dr balance. LIABILITIES Liabilities are those obligations which has to be paid in future. They may be due to present or past transactions. All expected future payments are not liabilities. Liabilities must arise from a completed transaction. If a company has entered into a 3 year contract to supply goods, the liability needs to be recorded only when the goods are supplied LIABILITIES LONG TERM SECURED UNSECURED CURRENT DEFINITE CONTINGENT ESTIMATED Secured liabilities 1. Debentures : Secured and unsecured Registered and unregistered Convertible and term Zero coupon ( deep discount bonds ) Callable Redeemable and Irredeemable Debentures issued at a premium Debentures issued at a discount Debenture issue expenses Conversion of debentures into equity Debenture Redemption Fund Mortgages payable – legal arrangement wherein a borrowing is secured by company’s immovable properties. Conditional mortgage / equitable mortgage Leases - legal agreement whereby the lessor conveys the right to use an asset for a specific period of time in return for a rent Operating lease Financial lease – FMV or PV of future lease payments whichever is less. Pensions and other post retirement benefits Deferred tax liability – Financial charge is less than tax charge Deferred tax asset – Financial charge is more than tax charge Accounting profit and taxable income Temporary and permanent differences Some questions ??? 1. Why is it important to distinguish between current liabilities and long term liabilities 2. If the market interest rate is higher than the coupon rate should debentures be issued at a premium, discount or at par Off balance Sheet financing 1. 2. 3. Transfer of receivables with recourse Product financing arrangement Derivatives 1. Details of Accounts Ltd. are given. Compute 1. COGS 2.Gross Profit 3. Operating expenses 4. Non operating expenses 5. Net operating profit 5. Net Profit 6. Retained earnings Turnover Materials consumed Processing charges Power & Fuel Excise duty Wages Managerial rem. Selling expenses 10.00 5.00 0.03 0.80 0.50 0.24 0.03 0.01 Loss on sale of assets Office expenses Interest on deb. Tax Proposed dividend 0.01 0.03 0.30 0.05 0.15 2. Share capital 2.00 (20000 shares of Rs.10/-) Debentures 1.00 Reserves & Surplus 3.00 Public deposits 0.25 Bank overdraft 0.05 Creditors 1.00 Accumulated depn. 1.00 Debtors 1.50 Inventory 0.50 Prepaid Expenses 0.02 Adv. from customers 0.05 Provision for tax 0.05 Outstanding expenses 0.01 Advance tax paid 0.05 Fixed Assets 3.00 Trade Investments 0.20 Mkt. Investments 0.02 Compute : 1. Net worth 2.Total capital employed 2. Net Fixed Assets 3. Current & Quick Assets 4. Current & Quick liabilities 3. The carrying cost of a machine as on 01.01.10 is Rs.100000. The company revalues the assets on that date at Rs.140000. What should be the accounting treatment in the books. 4. A Ltd. appoints B as his agent for selling goods for a commission of 5% on sales made. The agent made a sale of Rs.300000 during the year. What should be the amount of commission actually paid to the agent. ( TDS rate :5% + sc+e.cess ) Also discuss the accounting treatment in the books of accounts. 5. A Ltd. has investments of Rs.100000 in debentures carrying an interest rate of 12%. What should be the income recognised in the books of accounts. ( TDS rate 10% +sc+e.cess) 6. A Ltd. sells TV sets with a warranty of 1 year. In the year 2009-10 it sold 100000 units . The company estimates that 80% of the units shall have no defects. , 15% shall have minor defects ( costing Rs.500 each ) and 5% will have major defects ( costing Rs.10000 each ). Should it recognise the liability in the books of accounts. 7. The ED of a company wants your opinion on the following areas : 1. 2. 3. The prices of some of the machineries bought last year has gone up by 100 to 150 percent. The management wants to include the machineries at the market prices in the financial statements. One of the factory buildings was seriously damaged by the recent earthquake but it happened after the balance sheet date. Should a provision be made in the accounts for the same. The management proposes to discontinue the maintainence of fixed assets register due to a cost reduction programme in the company. 8. Whether the amount of long term debt payable in the next 12 months should be shown as current liability ? 9. How should interest accrued on loans not due be treated ? 10. A company’s records shows the following : a) Income Tax pending appeals – Rs.230500 b) Sales tax demand paid under protest – Rs. 278950 c) Counter claim by contractors – Rs. 85000 How should the above items be treated and disclosed in Accounts ? Classify the following accounts in financial statements into Tangible fixed assets, Intangible fixed assets, current assets , current liabilities, long term liabilities, equity, income, gains, losses , expenses 1.Receivables 2.Land, 3.Goodwill, 4.Bad debt, 5.Purchases, 6.Sales, 7.Real estate ( not used for business ) 8. Bad debt, 9.Rents & taxes, 10.Insurance premium paid in advance, 11.Insurance premium paid, 12.Insurance claim received,13 Freight inward,14 Freight outward,15. deposit with custom authority,16. Sales tax from sales,17. Bank charges,18. Depreciation,19. Share capital,20. Shares in Reliance Industries, 21.Excise duty paid,22. Advances from customers, 23.Advances to suppliers, 24.Copy right, 25.Cheques in hand, 26.Bills receivable, 27.Goods lying with customers for approval, 28.Staff welfare expenses, 29.Repairs and maintenance, 30.Interest paid, 31.Power & fuel, 32.Discount received from suppliers, 33,Discount allowed to customers, 34.Bank charges, 35.Cash credit form Bank of India, 36.Railway siding, 37.Travelling expenses, 38.Training expenses,39. Fixed deposit with Banks, 40.Loss by fire, 41.Profit on sale of assets, 42.Creditors, 43.Advances to employees, 44.Expenses of epoxy painting ( painting done every 5 years ), 45.Loan from IDBI, 46.Retained earnings, Plant & Machinery, 47.Provision for taxation ,48. Advance tax