Topic Eight.AgeofRevolution.doc
advertisement

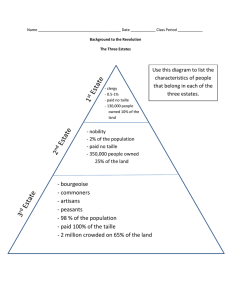
Topic Eight: The Age of Revolutions A. Background 1. Mercantilism a. India b. Spanish-America c. Colonial Wars 2. British supremacy a. “salutary neglect” b. “an empire on which the sun never sets” 3. French decline a. financial disaster B. The American Revolution 1. Pre-1763 British leadership a. local autonomy 2. Post-1763 British leadership a. problems with governance b. ineffective British government 3. British legislation a. Proclamation of 1763 b. Quebec Act (1774) c. Fiscal policies -Sugar Act (1764) - Stamp Act (1765) - Townsend Acts (1767) 4. The American Response a. trade boycotss b. Committees of Correspondence c. Sons of Liberty 5. Escalation, Peace and the Tea Act a. Boston Massacre b. Three years of peace c. Tea Act d. Intolerable Acts 6. War a. 1st Continental Congress (1774) b. Battle of Lexington and Concord c. Second Continental Congress (1775) d. Battle of Saratoga (1777) e. Battle of Yorktown (1781) 7. American Strengths and British Weaknesses a. As war continues past 1779, no way for British to win 8. Treaty of Paris (1783) a. United States given formal recognition by British b. pre-war debts valid c. triumph of Enlightenment ideals - especially embodied in the Constitution 9. Effects on Europe a. Dutch b. French c. challenges the European Royal System B. The French Revolution 1. Effects of the American Revolution on France a. proved that it could be done b. 9000 French take part c. Americans trying to maintain status quo, not overthrow institutions 2. France on the Eve of the Revolution a. Absolutist State, Middle Class has no access to political power b. No longer believe it was a reaction of the Middle Class, but a revolution against absolutism c. The Three Estates - 1st Estate, the Church, approx. 138k people - 2nd Estate, the Nobility, approx. 300k people - 3rd Estate, everyone else, approx. 27.5 million people d. Together the 1st and 2nd Estate owned about 50% of wealth but were exempt from taxation e. The 3rd Estate was everyone from the upper Middle Class to the poor and they bore the entire tax burden f. Frustration because no political voice, but educated enough to know Enlightenment philosophy g. Economic turmoil—inflation, feudal obligations (corvee), poor harvests, costly wars h. 25k prostitutes in Paris, 40k children abandoned/year i. When Louis XVI comes to the throne in 1774, has a mess to deal with j. Louis loans money to the Americans h. France hates his queen, Marie Antoinette 3. Louis attempts Reform a. Government is bankrupt – had practiced deficit spending for years b. But there is no way to effectively change the system c. Charles Alexandre de Calonne, Minister of Finance, 1786 - tries to institute a new taxation system d. Assembly of Notables called together in 1787 to approve new taxes e. This fails, forcing Louis to call a meeting of the Estates General f. 1200 representatives meet in May 1789 4. First Phase of the Revolution, the Estates General becomes the National Assembly a. 1st and 2nd Estate blocks any attempt at reform (voting was by estate, not by representative) b. Louis only wanted approval for new taxation scheme, but 3rd Estate wants sweeping political reform and changes c. June 17 the 3rd Estate, with sympathetic members of the 1st and 2nd Estate, declares itself the National Assembly, the new legislative body of France and the Revolution is on d. three days later take the Tennis Court Oath e. king is appalled and orders troops to Paris f. mob storms the Bastille on July 14 g. in countryside, Time of Fear, peasant uprisings h. these mobs motivate the National Assembly to quickly write a constitution i. August 27 issued the Declaration of the Rights of Man - natural rights of man are liberty, property, security and freedom from oppression j. issues a new constitution that made France into a constitutional monarchy - single chamber legislature, king has limited powers - govt. positions now elected - only enfranchised property owners - creates 83 departements, local officials also elected - promise to reform taxation system h. new constitution does not really address the issues which necessitated the Estates General in the first place…govt. debt and lack of food i. to raise money, Civil Constitution of the Clergy issued July 1790 - all Catholic officials work for the state - had to take an oath of loyalty - majority of church land confiscated j. but this angered the traditional rural population, the clergy and didn’t bring in much money k. Louis is alarmed at the new turn of events and tries to flee with his family in June of 1791 but is caught l. from now on the king will be under house arrest at the Tuileries Palace in Paris m. mistakes of the National Assembly - arrested the king, how can you have a constitutional monarchy - ignored the citizens of Paris (pop. 600k) - disqualified its members for elections under the new constitution 5. Second Phase, the Legislative Assembly, October 1791-August 1792 a. the new Legislative Assembly elected was more republican b. wanted to abolish the monarchy c. forces the king to declare war on Austria d. army is disorganized, had no competent officers e. also puts more financial pressure on France f. Sans-culottes (common citizens of Paris) call for an overthrow of the monarchy and the Legislative Assembly g. on August 10, 1792 they storm the Tuileries and the government falls h. what is left agrees to write a new constitution and the 2nd phase of the Revolution ends 6. Third Phase, the Republic, September 1792-August 1795 a. On September 20, 1792 the new National Convention declares an end to the monarchy and proclaims France a Republic b. On same day, French armies win a huge victory over Austria c. Give the government enough power to try and execute the king d. However, the government is split on the execution e. New government is now at war with all of Europe f. Also at war with France itself, counter-revolutionary movements all over the country g. Committee of Public Safety created and soon gains complete control h. The Reign of Terror begins led by Maximilien Robespierre i. Tribunals set up and executions begin j. Also, the Committee begins the Levee en Masse k. It begins price controls on bread, the other commodities l. Abolishes slavery, women could obtain divorces, education reform m. Protests against cultural programs, such as calendar reform and the “Cult of the Supreme Being” n. By July 1794, Robespierre is toppled from power and guillotined o. Thermidorian Reaction p. Churches reopened February 1795 q. New Constitution written in August, ushering in a new government 7. Fourth Phase, the Directory a. The new constitution called for a 2 house legislature and limited sufferage b. Also decreed that 2/3 of the National Convention must be seated in the new legislature, regardless of election outcomes c. A five man executive branch, called the Directory, is chosen d. When 1797 elections put a large number of royalists into the legislature, the Directory had them arrested or exiled e. France is now a dictatorship under the Directory f. The war is going well - 1795 Netherlands - 1796-97 Northern Italy - 1798 Switzerland, Rome and Naples g. Most of this due to the brilliance of a young general Napoleon Bonaparte h. Unable to solve the countries problems, the Directory calls Napoleon home to save them i. Instead, he institutes a coup against the Directory in November of 1799 and becomes virtual dictator of France j. Is the Revolution over? C. The Revolutions Spread 1. Haiti a. successful slave revolt under Toussaint l’Ouverture b. 1804 independent Republic of Haiti created 2. Spanish-America a. Spain weakened by Napoleon b. Simon Bolivar starts a revolution in South America c. Portugal loses Brazil d. Monroe Doctrine (1823) 3. Spain a. Revolt against Ferdinand VII in 1814 b. France puts him back on the throne c. Will lead to the Revolution of 1848 4. Greece a. under Ottoman rule b. in 1817 Serbia wins its independence c. 1820-21 Greek revolt d. Austria supports Ottomans, but Europe backs Greece e. 1830 Greece is independent