Preceptors Pearls Two
advertisement

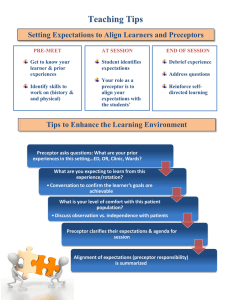
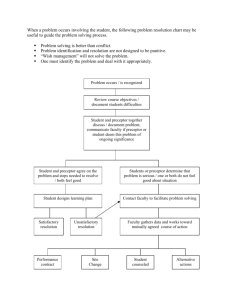
PRECEPTOR PEARLS II Sonoma State University Family Nurse Practitioner Program Dr. Wendy Smith and Dr. Mary Ellen Wilkosz Part II Tools and Practice Objectives- A Reminder of EB Learning Theory and Tools for Precepting • 1. Develop knowledge and understanding of the history and current status of the preceptor role. • 2. Develop an understanding of three learning theories/models that support the preceptor role and learning styles. Knowles ALT, Kolb’s Experiential Learning Theory, Benner’s Novice to Expert • 3. Have a clearer understanding of the: • Student and Program responsibilities • Preceptor and Clinical Faculty responsibilities • 4. Become familiar with Practice teaching and tools to augment clinical learning Tools to Facilitate FOCUS on Tools in Precepting • To Provide Quality Care • To Maintain Efficiency • To Provide Quality Education Group Activity #2 • Think of a preceptor you had, what are four attributes/qualities you can recall that made them an effective preceptor, or not so effective preceptor. Then lets share! Tools • Four (4) Specific clinical teaching strategies. 1. One Minute Precepting (5 micro skills) 2. SNAPPS- Learner Led Education 3. “Aunt Minnie” 4. Activated Demonstration Tool 1. “One minute preceptor” (OMP) • 5 key steps or “micro skills” • Getting a commitment (from student re situation – What does student want to do here? If I weren’t here what would you do?) • Probe for supporting evidence – What factors did you consider in making that decision? Where there other options you R/I, R/O • Teach general rules – the case at hand this is what the standard of care is, these are the principles – mini lecture, with advice for suggested reading. • Reinforce what was done right – provide case descriptive and behavior focused feedback. Focus first on what was done right • Correct mistakes – in reviewing case correct NOW. Focus on behaviors and decision making. Tool 2. SNAPPS- Learner led experience – Ask student! (Based on Cognitive learning and reflective Practice) • To Summarize, in 3 min or less -Relevant hx and physical • • • • • findings. Narrow the Diff Dx. or poss. interventions to 2 -3 most relevant and likely possibilities – PRIOR TO Preceptor Input. Analyze the Diff Dx by comparing and contrasting poss. explanations. Allows learner to verbalize thought process. Probe the Preceptor – learner asks about uncertainties, difficulties, or other approaches – Preceptor as Knowledge resource. Plan of Care - Attempts brief management plan or suggests specific interventions further refines with input Select a case-related issue for self-directed learning Tool 3. “Aunt Minnie” Value of Pattern Recognition “If the lady across street walks, talks, dresses like your Aunt Minnie she probably is your Aunt Minnie” • Technique employed by most clinicians for approach to common ambulatory problems. • 1. student evaluates patient then presents the CC and Dx • 2. student begins write-up and preceptor evaluates pt. • 3. the preceptor discusses case with student, • 4. the preceptor reviews and signs the medical record. Researchers found that instruction to students using familiarity driven pattern recognition combined with careful consideration of the presenting features led to improved dx accuracy. Tool 3. Activated Demos Teaching a skill A way to maximize the educational Value of a demonstration and provide learner with more than just a passive experience. 1. Preceptor selects pt to see, CC known. Preceptor assess Student’s relevant knowledge of case/condition. 2. Est. objs for exp and visit. What should student learn? 3. Preceptor provides clear guidance during skill demo, includes Preceptor/student discussion pre/during/post. 4. Student demonstrates skill, preceptor may interrupt and re-demo if not an evaluation/grading situation. 5. Discuss learning points and details of observation with student. 6. Set agenda for future learning opportunities. In Closing OMP has been evaluated the most extensively, and has been shown to improve diagnostic skills and disease specific teaching. Improvement in all areas of diagnostic process. SNAPPS less extensive eval, show promise for improving student case presentations, clinical reasoning and independ learning. “Aunt Minnie” – AKA Pattern Recognition - Studies show pattern recog can play a role in teaching and testing clinical reasoning so far (as of 2011) no formal eval of this teaching model pub. Activated Demo – Shows promise for preceptors to select learner focused teaching strategies but needs further evaluation and study. Other Tools/techniques • What have you used? • Any good Mnemonics? • OLDCARTS • PQRST • YOUR OWN AOLRAPPE • Toileted, DIAPPERS Where the Rubber Meets the Road! • Get to know your preceptee • Identify learning needs early on • Assess biases or values • Ask about other commitments • Be clear about expectations • Try some of these tools