Chapter 11 Chromosomes Two kinds of chromosomes
advertisement

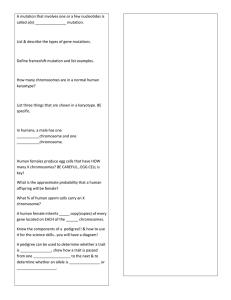
Chapter 11 Chromosomes Two kinds of chromosomes Autosomes Sex chromosomes Mammals have XY sex determination One or more Y chromosomes, develop into a male Birds have ZW, male has homologous sex chromosomes, female has non-homologous sex chromosome ZW Reptiles sex is determined by incubation temperate Karyotype Aneuploidy (unusual numbers of chromosome) XO Turner’s syndrome (shorter than usual, fertility problems) XXX (Trisomy X) very little effect XXY (Klinefelter’s Syndrome) XYY (supermale) Normal XX, you have dosage compensation Only one X is uncondensed during interphase Barr bodies (the second uncondensed X chromosome) Mosaicism (find this only in female mammals) Calico cat Sex-linked traits Sex-linked trait is found on the X chromosome Some examples: hemophilia, red-green colorblind Hemophilia is recessive, more often seen in males Woman who carries hemophilia Man who is not hemophiliac Crossed How many hemophiliac sons? 25% of all offspring normal sons? 25% of all offspring Hemophiliac daughters? 0% Normal daughters? 50% of offspring (half of these are carriers) Duplication Deletion Inversion Translocation If a man and woman have a child, and the woman makes a normal egg with one X chromosome, but the man has a non disjunction, producing one XY sperm, and one 0 sperm, what offspring might result? In chromosome 21, the woman has non disjunction, one egg has two C21s, the other has zero C21s. What kinds of offspring may result?