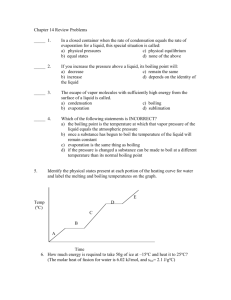
chapter11-PEX.doc
advertisement

Chapter 11 (Intermolecular Forces and Reading Graphs)
1. How many calories must be added to 20.0 g of ice at 10.0 oC to convert ice to steam
at 120.0 oC?
2. How many calories are required to change 10.0 g of water at 20.0 oC to 110.0 oC?
3. The Hf of Al is 2.58 Kcal/mole. How many calories are needed to melt 10.0 g of the
metal?
4. How many numbers are present in a unit of the following types? Explain each answer.
(a) simple cube
(b) body centered cube
(c) face centered cube
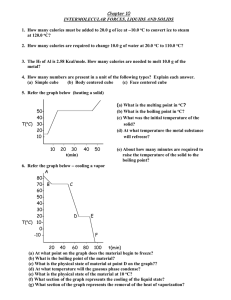
5. Referring to graph below heating a solid.
(a) What is the melting point in oC?
50(b) What is the boiling point in oC?
40(c) What was the initial temperature of the
o
T( C) 30solid?
20(d) At what temperature the metal substance
10 will refreeze?
l
10
l
l
l
30 40
t(min)
l
(e) About how many minutes are required to
raise the temperature of the solid to the
boiling point?
6. Referring to graph below Cooling a vapor.
A
8070- B
C
6050403020D
E
o
T( C) 100-10 F
l
20
l
l
l
50
l
20 40 60 80 100 t(min)
(a) At what point on the graph does the material begin to freeze?
(b) What is the boiling point of the material?
(c) What is the physical state of material at point D on the graph??
(d) At what temperature will the gaseous phase condense?
(e) What is the physical state of the material at 10 oC?
(f) What section of the graph represents the cooling of the liquid state?
1
(g) What section of the graph represents the removal of the heat of vaporization?
7. Referring to graph below phase diagram of compound.
A
2.52.0P(atm) 1.51.00.5-
l
0
C
l
60
B
l
80
l
l
l
T(oC)
120 160 200
(a) For this substance. in what physical state would it exist at 10 oC and 760 mm Hg?
(b) What is the pressure and temperature at the triple point?
(c) What are the critical temperature and pressure?
(d) What is the vapor pressure of the liquid phase at 100 oC?
(e) What is the maximum temperature to which the substance can be raised and still
undergo sublimation?
8. Referring to graph below vapor pressure of four liquids.
A B
1000800p
600(mmHg) 400200l
40
l
C
l
D
l
l
l
80 120 160 200 240
T(oC)
(a) At what temperature will "A" boil at normal pressure?
(b) What is the physical state of substance "B" at 600 torrs and 80 oC,?
(c) Which substance has the greatest intermolecular attraction? Explain.
(d) Which substance is most volatile?
(e) What must the external pressure be for substance "C" to boil at 40 oC?
(f) Which substance do you think would have the highest critical temperature.
9. Define the following terms:
a) Triple point
b) Critical temperature
e) Melting point f) Boiling point
2
c) Sublimation
g) Condensation
d) Evaporation
h) Deposition
i) Freezing point
j) Hydrogen bonding
Chapter 11- Intermolecular Forcesof Liquids and Solids
(Answers)
1. How many calories must be added to 20.0 g of ice at 10.0 oC to convert ice to steam
at 120.0 oC? (seg. = line segment, m.p. = melting point, b.p. = boiling point)
Seg. AB: heat ice to m.p. => mCpiceΔT = (20g)(2.09J/g-ºC)(10) = 418J
Seg. BC: melt ice w/heat of fusion => nHf = (1.11 mol)(6.01kJ/mol)x1000 = 6670J
Seg. CD: heat water to b.p. => mCpwaterΔT = (20g)( 4.18J/g-ºC)(100) = 8368J
Seg. DE: boil water w/heat of vaporization => nHv = (1.11mol)(40.67kJ/mol) = 45140J
Seg. EF: heat vapor to 120ºC=> mCpvapΔT = (20g)( 2.09J/g-ºC)(20) = 836J
Calories = (AB + BC + CD + DE + EF) ÷ 4.18 = 61432J ÷ 4.18 = 14,682.6 calories
2. How many calories are required to change 10.0 g of water at 20.0 oC to 110.0 oC?
Same as above; Only begin with seg. CD to EF.
Calories = (CD+DE+EF) ÷ 4.18 = (3347.2J + 22780J + 209J)÷ 4.18 = 6294.5 calories
3. The Hf of Al is 2.58 Kcal/mole. How many calories are needed to melt 10.0 g of the
metal? 10g Al => 0.37 mole
Calories = nHf = (0.37mol)(2.58 kcal/mole)(1000) = 955 calories.
4. How many numbers are present in a unit of the following types? Explain each answer.
(a) simple cube (1/8)atom/corner x 8 corners of cube = 1 atom
(b) body centered cube
{(1/8)atom x 8} + 1 centered atom = 2 atoms
(c) face centered cube {(1/8) x 8} + (1/2)atom x 6faces of cube)} = 4 atoms
5. Referring to graph below heating a solid.
(a) What is the melting point in oC? 15
(b) What is the boiling point in oC? 51
(c) What was the initial temperature of the
solid? 15
(d) At what temperature the metal substance
will refreeze? 15
5040o
T( C) 302010 l
10
l
20
l
l
30 40
t(min)
l
50
(e) About how many minutes are required to
raise the temperature of the solid to the
boiling point? 15 minutes
3
6. Referring to graph below Cooling a vapor.
A
8070- B
C
6050403020D
E
o
T( C) 100-10 F
l
20
l
40
l
l
l
60
80
100
t(min)
(a) At what point on the graph does the material begin to freeze? D
(b) What is the boiling point of the material? 71 oC
(c) What is the physical state of material at point D on the graph?? Liquid
(d) At what temperature will the gaseous phase condense? 71 oC
(e) What is the physical state of the material at 10 oC? Solid
(f) What section of the graph represents the cooling of the liquid state? CD
(g) What section of the graph is the removal of the heat of vaporization? BC
7. Referring to graph below phase diagram of compound.
2.52.0P(atm) 1.51.00.5-
A
l
0
l
60
B
C
l
80
l
l
l
T(oC)
120 160 200
(a) For this substance, what physical state is it in at 10 oC & 760 mm Hg? Solid
(b) What is the pressure and temperature at the triple point? 1atm, 60 oC
(c) What are the critical temperature and pressure? 120oC, 3.0atm
4
(d) What is the vapor pressure of the liquid phase at 100 oC? 1.5atm
(e) What is the maximum temperature to which the substance can be raised and still
undergo sublimation? 60 oC
8. Referring to graph below vapor pressure of four liquids.
A B
C
D
1000800p
600(mmHg) 400200l
40
l
l
l
l
l
80 120 160 200 240
T(oC)
(a) At what temperature will "A" boil at normal pressure? 49 oC
(b) What is the physical state of substance "B" at 600 torrs and 80 oC,? Gas
(c) Which substance has the greatest intermolecular attraction? Explain.
Substance D. It has the highest boiling point.
(d) Which substance is most volatile? Substance A
(e) What must the external pressure be for sub. "C" to boil at 40 oC? 80mmHg
(f) Which substance would have the highest critical temperature. Sub. D
9. Define the following terms:
a) Triple point Temp at which all 3 phases are in equilibrium.
b) Critical temperature Temp. above which sub. Cannot be liquefied, despite pressure.
c) Sublimation Substance changing directly from solid to gas state.
d) Evaporation Substance changing from liquid to gas state by heating.
e) Melting point Temp. at which solid and liquid states are in equilibrium.
f) Boiling point Temp. at which vapor pressure of liquid is in equilibrium w/atm press.
g) Condensation Same as f. Just in opposite direction.
h) Deposition Substance changing directly from gas to solid state.
i) Freezing point
Temp. at which solid and liquid states are in equilibrium.
J) Hydrogen bonding Intermolecular electrostatic attraction between H and O, or N,
or F of another molecule. The hydrogen has to be bonded to O, or N, or F in its own
molecule.
5