ME 481 Outline.doc
advertisement

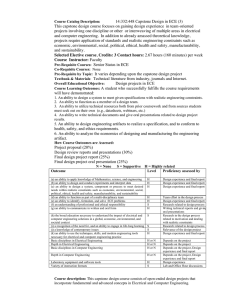
Course alpha, number, title ME 481 Mechanical Engineering Design Projects Required or elective Required Course (catalog) description Application of design concepts in mechanical engineering. Problem definition, design specifications. Modeling and analysis methods. Design optimization, economics, reliability. Manufacturing considerations in design. Capstone design projects. Prerequisite(s) (ME 410) and (ME 471) and completion of Tier I writing requirement. Textbook(s) and/or other required material Thompson, Creative Engineering Design, Okemos Class/Lab schedule: Total Credits: 3 Lecture/Recitation/Discussion Hours: 1 Lab Hours: 6 Topics covered a. Design Process b. Prob. Definition & Des. Qlty. c. Modeling and Analysis d. Design Optimization e. Reliability and Risk f. Legal Liability and Safety g. Engineering Economics h. Manufacturing Methods Course learning objectives 1. To participate in a small team solving an open-ended project. a. students evaluate numerous open-ended projects from industrial sponsors b. students form teams of their own choice comprising four members using a decision matrix approach 2. To work on a real-world inter-disciplinary design project. a. project has multiple solutions b. econoniics, manufacturing, marketing etc. considerations c. students select their semester-long project from a list of industrially-funded projects d. develop appropriate mathematical models of inter-disciplinary situations requiring a knowledge of the fundamental sciences and engineering judgement 3. To effectively participate in an industrial enterprise. a. This requires interacting with individuals from different disciplines. (manufacturing, electrical engineering, accounting etc.) b. This requires interacting with people in the non-engineering professions such as business, accounting, management etc. c. This requires interactions with individuals of different educational backgrounds on the shop floor, trades etc. d. This requires students to learn various relevant methods not taught in the current curriculum such as time-and motion studies, special manufacturing processes, failure mode and effects analysis etc. 4. To develop written and oral communication skills. a. posterboard presentations at the SDC (student design conference) b. written reports of an interim and final form c. communication with vendors by telephone and e-mail d. oral presentation in a conference setting at the SDC 5. To build and test prototypes to validate designs 6. To develop planning documents for a 15 week project. a. Gantt chart Verification of achieving the stated objectives:Note I above. Review the handout of industrial projects. 1 Students form four-person teams. Note 2 above. Review the industrial projects. Note 3 above. Review the written reports. Students deliver oral presentations at the site of the industrial sponsor. Note 4 above. Review the written reports and oral presentations at the SDC Note 5 above. Review the final report Presentations are made at the site of the industrial sponsor. Relationship of course to ME program outcomes The following measurement standard is used to evaluate the relationship between the course outcomes and the educational-program outcomes: 3 = Strong Emphasis, 2 = Some Emphasis, 1 = Little or No Emphasis. (a) an ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering—2 (b) an ability to design and conduct experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret data—3 (c) an ability to design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs—3 (d) an ability to function on multi-disciplinary teams—3 (e) an ability to identify, formulate, and solve engineering problems—3 (f) an understanding of professional and ethical responsibility—3 (g) an ability to communicate effectively—3 (h) the broad education necessary to understand the impact of engineering solutions in a global/societal context—1 (i) a recognition of the need for and the ability to engage in life-long learning—1 (j) a knowledge of contemporary issues—2 (k) an ability to use the techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for engineering practice—2 (l) design, build, and test in mechanical systems area—3 (m) design, build, and test in thermal/fluids area—3 (n) application of advanced mathematics—2 (o) capstone design experience—3 Contribution to professional component: 0% Engineering Science 100% Engineering Design Person(s) who prepared this description Brian Thompson Date of Preparation 2