Reefs “Wave resistant organic frameworks”-can be coral, or other organisms
advertisement

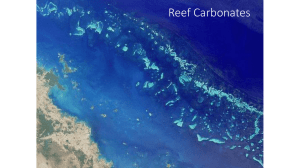
Reefs “Wave resistant organic frameworks”-can be coral, or other organisms Reefs today prefer clear, warm, normal salinity water Grow in response to the wave energy available Great Barrier Reef-large (2000 km) interconnected reef complex. 50-100 km from the coast due to the presence of a lot of terrigenous sediment along the continental coastline. Types of Reefs Algal mats Oyster reefs Worm reefs Coral-algal Reefs Hermatypic corals have symbiotic brown algae and live in the photic zone Also calcareous algae Reef classification Fringing reef Barrier Reef Atoll Reef Environments Windward Slope Windward Reef Flat Lagoon (with patch reefs) Leeward Reef Leeward Slope “Bucket Model” for reef development Reef Models and Sea Level “Catch up”, “Keep up”, and “Give up” or drowning