Chapter 7 Rev.doc
advertisement

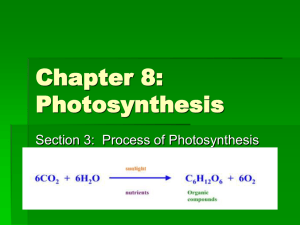
Chap 7 Review Questions(10) Give the formula for photosynthesis. For each reactant, indicate where the plant acquires it. For each product, note during what part of photosynthesis it is produced. Why is no glucose produced if a plant is kept in the dark, even though the sugar producing reactions are called lightindependent? Before photosynthesis evolved, ________ was rare in Earth's atmosphere. a. N2 b. CO2 c. O2 d. H2O e. air What structural feature of a leaf allows a leaf to obtain CO2 from the air? a. Stomata b. Epidermis c. Cuticle d. Mesophyll e. Chloroplast The vast majority of chloroplasts found in a leaf are located where? a. Vascular bundles b. Cuticle c. Epidermis d. Stroma e. Mesophyll Specifically, molecules of chlorophyll are located in membranes of sacs called: a. Cristae b. Thylakoids c. Stroma d. Grana e. Vesicles All of the following compounds are required (i.e. are necessary constitutents for chemical reactions) at some state of green plant photosynthesis, EXCEPT a. ATP b. NADP c. water d. oxygen e. carbon dioxide The cellular organelle of eukaryotic organisms which is responsible for photosynthetic activity is the: a. Nucleus b. Mitochondrion c. Chloroplast d. Endoplasmic reticulum e. Ribosome Energy is passed around different chlorophyll molecules until it reaches a specific chlorophyll molecule called the: a. Reaction center b. Photoelectric point c. Electron carrier molecule d. Accessory pigment e. Nucleus A pigment that absorbs red and blue light and reflects green light is: a. Phycocyanin b. Carotenoid c. Xanthophyll d. Melanin e. Chlorophyll Which statement is true regarding the light-dependent reactions? a. They rely on energy provided by glucose synthesis. b. Overall, they are exergonic because ATP is produced. c. Without water, the system would shut down. d. ATP and NADPH are needed. e. Without photosystem I, photosystem II could not occur. The replacement electrons for the reaction center of photosystem II come from: a. Photosystem I b. H2O c. Glucose d. O2 e. NADPH What is produced in photosystem II's electron transport system? a. NADPH b. ATP c. glucose d. O2 e. CO2 Light-dependent photosynthetic reactions produce: a. ATP, NADPH, O2 b. ATP, NADPH, CO2 c. Glucose, ATP, O2 d. Glucose, ATP, CO2 e. ATP, NADPH, H2O Where does the O2 released during photosynthesis come from? a. CO2 b. H2O c. ATP d. C6H12O6 e. RuBP During the process of photosynthesis, solar energy is converted into: a. Chemical energy b. Heat energy c. Thermal energy d. Mechanical energy e. Nuclear energy The light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis result in which of the following? a. Oxidation of CO2 b. Reduction of H2O c. Phosphorylation of ADP d. Oxidation of chlorophyll e. Oxidation of glucose What is the role of water in photosynthesis? a. to maintain turgor pressure b. to provide electrons c. to provide oxygen d. to provide H2 e. all of these Which of the following is a source of electrons used for reduction reactions by green plants? a. Glucose b. CO2 c. RuBP d. O2 e. H2O According to the chemiosmotic theory, during ATP synthesis, hydrogen ions cross the thylakoid membranes from the stroma by: a. Osmosis b. Facilitated diffusion c. Active transport d. Simple diffusion e. Phosphorylation The energy of the movement of electrons down their concentration gradient via electron transport within chloroplasts and mitochondria is used to generate molecules of: a. H2O b. CO2 c. C-H-O d. ATP e. O2 During photosynthesis, which chemical activity specifically results in the synthesis of molecules of ATP? a. Photosystem II b. Generation of NADPH c. Splitting of a water molecule d. Fixing of carbon e. Synthesis of O2 The NADPH required for carbon dioxide fixation is formed a. by the reduction of oxygen. b. by the hydrolysis of ATP. c. during the light reactions. d. only in C4 plants. e. in the mitochondria. The primary function of the light reactions of photosynthesis is a. to produce energy-rich glucose from carbon dioxide and water. b. to produce energy-rich ATP and NADPH. c. to produce NADPH used in respiration. d. to convert light energy to the chemical energy of lipids. e. to use the ATP to make glucose. In a. b. c. d. e. C3 photosynthesis, what fixes the carbon? RuBP PEP PGA PGAL ATP How many molecules of CO2 are fixed to form 1 molecule of glucose? a. 2 b. 3 c. 6 d. 9 e. 12 The term "cycle" is used to describe the light-independent reactions (Calvin-Bensen cycle) because... a. the same reactions occur every time. b. CO2 is fixed in every turn of the cycle. c. the process begins and ends with RuBP. d. glucose is synthesized during the process. e. the process depends on products from the light-dependent reactions. Where is glucose synthesized? a. Thylakoids b. Cytoplasm c. Matrix d. Stroma e. Intermembrane compartment Which of the following occurs during the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis? a. Water is converted into hydrogen and water. b. Carbon dioxide is converted into sugars. c. Chlorophyll acts as an enzyme only in the dark. d. Nothing occurs, the plant rests in the dark. e. None of the above. All of the following are part of the Calvin-Benson cycle except: a. Carbon Fixation b. Synthesis of G3P c. Generation of ATP d. Regeneration of RuBP e. All of the above are part of the cycle. Which of the following are required for the C3 cycle? a. CO2 b. RuBP enzyme c. ATP d. NADPH e. All of the above Which of the following provides O2 as an end product? a. Light-dependent reaction b. Light-independent reaction c. Cellular respiration d. Glycolysis e. Phosphorylation In the C3 cycle, where does the carbon come from to form glucose? a. from ATP and NADPH b. from chlorophyll c. from atmospheric CO2 d. from enzymes e. from water What happens to CO2 when it moves into the stroma? a. The CO2 gives up its O2. b. It immediately passes on to the thylakoids. c. It becomes a carbohydrate. d. The CO2 becomes a by-product of cellular respiration. e. It is converted to water. In the reduction of CO2 during C4 photosynthesis, which of the following initially combined with CO2? a. PGA b. RuBP c. PGAL d. NADH e. PEP Specifically, how is the energy derived from the breakdown of glucose initially used by cells? a. Phosphorylation of ADP b. Manufacture of proteins c. To drive photosynthesis d. Enzyme synthesis e. To synthesize simple sugars In to a. b. c. d. e. green plants, the primary function of the Calvin cycle is use ATP to release carbon dioxide. use NADPH to release carbon dioxide. split water and release oxygen. transport glucose out of the chloroplast. construct simple sugars from carbon dioxide. In C4 photosynthesis, where does the carbon come from to synthesize glucose? a. from ATP and NADPH b. from chlorophyll c. from enzymes d. from water e. from atmospheric CO2 In a. b. c. d. e. C4 photosynthesis, what initially fixes carbon? RuBP PEP PGA PGAL ATP Where does one expect to find the reactions of a C4 pathway occurring in a plant such as corn? a. Mesophyll cells b. Bundle-sheath cells c. Epidermal cells d. a and b e. b and c What kind of habitat does a C4 pathway plant favor? a. Hot and dry b. Cool and moist c. Totally aquatic d. Wet and cloudy e. Cool and dry Photorespiration is bad for a plant because... a. O2 is required. b. CO2 is synthesized. c. RuBP is degraded. d. glucose is synthesized. e. no ATP is produced. Where does the C4 cycle get its name? a. Only 4 carbons are used in the cycle b. It is a 4 step process c. 4 CO2 molecules are released d. The first product in the cycle has 4 carbons e. PEP is a 4-carbon molecule If C4 photosynthesis prevents photorespiration, why haven't all plants evolved to use the C4 pathway? a. All plants will evolve to be C4 in time. b. C4 produces some toxic byproducts. c. C4 is not advantageous in all climates. d. Only some plants use C4 photosynthesis. e. C4 is only advantageous in high oxygen habitats. When water supplies are plentiful for the plant a. the stomata remain open. b. the stomata will close. c. O2 uptake will increase. d. CO2 release will be possible. e. more water evaporation will occur. C3 plants are adapted to ________________ conditions, while C4 plants are adapted to _____________ environmental conditions. a. dry; wet b. wet; dry c. temperate; cool and rainy d. high light; low light e. drought; rainy List the three major reactants required for photosynthesis to occur and list a plant adaptation to provide for these reactants to come together to produce glucose. Light dependent reactions occur in the ____________________ and light independent reactions occur in the _________________ of the chloroplast of a typical mesophyll leaf cell. The cells in the ________________ layer of the leaf contain the majority of a leaf's chloroplasts. In the process of photosynthesis, _________ and __________ are required from the light dependent reactions to completely reduce carbon dioxide to glucose in the Calvin cycle. Which component of the Calvin-Benson cycle is recycled and why is this important for the light-independent reactions? Photosystem II generates _____________ and Photosystem I generates ______________, both of which are required by the light-dependent reactions. The combination of oxygen with RuPB during the lightindependent reactions, rather than carbon dioxide, is called __________. The carotenoids and other accessory pigments in the chloroplast help harvest light energy toward the reaction center chlorophyll molecules. a. True b. False