C05: Light Telescopes
advertisement

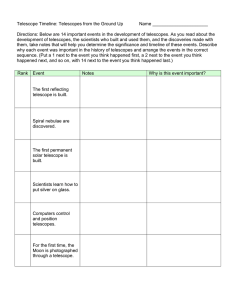
Light & Telescopes (Chapter 5) All of what we know and understand about the stars is the result of observation and analysis of light. Student Learning Objectives • Describe the properties of light • Identify types and properties of telescopes What are the properties of light? Electromagnetic waves carry information as well as energy. Light speed is constant in a vacuum (in space) • 3 x 108 m/s • 186,000 miles/sec • 670 million mph The energy we are now observing from objects in space was generated at some time in the past. Sun Proxima Centauri Sirius Andromeda Galaxy 8 min. 4.2 LY 8.6 LY 2.5 x 106 LY Practice: In a science fiction movie, when a spaceship explodes, we see and hear the explosion instantly. What are the mistakes in this scenario? Wave Properties Electromagnetic waves have a wavelength (l) and frequency (n). c = ln Electromagnetic radiation exhibits wave-particle duality. Photons No mass Pure energy Each photon of light carries energy. E = hc l E = hn The more photons, the higher the intensity. Electromagnetic Radiation l n E Gamma Rays X-Rays Ultraviolet Visible Infrared Radio http://www.chromoscope.net/ http://spaceplace.nasa.gov/ir-photo-album/en/ We interpret particular wavelengths of visible light as particular colors! Red 7000 Å Cooler Less Energy 5500 Å Blue 4000 Å Hotter More Energy ROY G BV Some of the Information in The Light • Energy output • Temperature • Chemical composition • Distance • Relative Motion Atmospheric Windows Practice 1) What is the speed of a radio wave? 2) Which wavelength is longer? a. 95.1 MHz b. 1220 MHz More Practice 3) Which star would be hotter, a blue star or a red star? 4) What affects the intensity of the light we receive from stars? What are the main features of optical telescopes? Reflection is a bounce (mirrors) Refraction is a change in velocity (lenses) Reflecting Telescope Reflecting telescopes utilize a mirror. Refracting Telescope Refracting telescopes utilize a lens. The objective or primary lens/mirror of the telescope is the most important part. Newtonian Reflector Mirror Refractor Issues All refractors produce chromatic aberration (“color deviation or distortion”). Interesting Note: A very long focal length will minimize chromatic aberration. This is why the early refracting telescopes (like Galileo’s) were made very long. Reflector Issues Reflectors may produce a fuzzy image due to spherical aberration (curvature distortion). Hubble Images Advanced optical telescopes use floppy mirror segments controlled by a computer. Why? Practice 1) What is the main purpose of a telescope? 2) Where are the telescopes that astronomers use? 3) Are there any telescopes that can be used during the day? Mauna Kea, Hawaii (Elevation 14,000 Feet) What are the functions of telescopes? Light Gathering Power Ability of the telescope to collect photons. LGP = (Diameter)2 Resolving Power Ability of the telescope to “see” fine detail, and distinguish individual objects from each other a = (2.06 x 105) l Diameter Larger D and Smaller l sharper images An image of two stars through a telescope with low angular resolution An image of two stars through a telescope with high angular resolution. Image Credit: Richard Bloch Magnifying Power Telescopes enlarge the image. Atmosphere & Light affect observations. Mars with naked eye Practice 1) Which telescope would allow you to see fainter objects? a. Small diameter telescope b. Large diameter telescope c. Either as long as there is good magnification 2) What are the advantages of space based telescopes? What is a radio telescope? A large parabolic dish gathers radio waves and reflects this energy to a central focus. Star formation regions SETI program Interferometers A single radio telescope has very poor angular resolution. An interferometer is a set of radio telescopes connected together. Constructive light Interference NRAO Detectors Photometers: count photons Measure Intensity CCD - Charge-Coupled Device: produce electronic images with millions of light detectors (pixels on a small silicon wafer) Measure Intensity per Pixel Camera! Spectrographs: use a grating to split light into individual wavelengths White Light → Rainbow Adaptive optics: is a computer program that corrects for bad seeing Removes blurring caused by atmosphere Sun's Visible Spectrum Image Credit: Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope Image Credit: Gemini Observatory Practice 1) What do people use everyday that has a CCD camera? 2) Optics are lenses and mirrors. How do adaptive optics differ from regular optics? 3) What are two tools that astronomers can use to produce the clearest image possible?