TAP 515-1: Smoothed out radioactive decay – =
advertisement
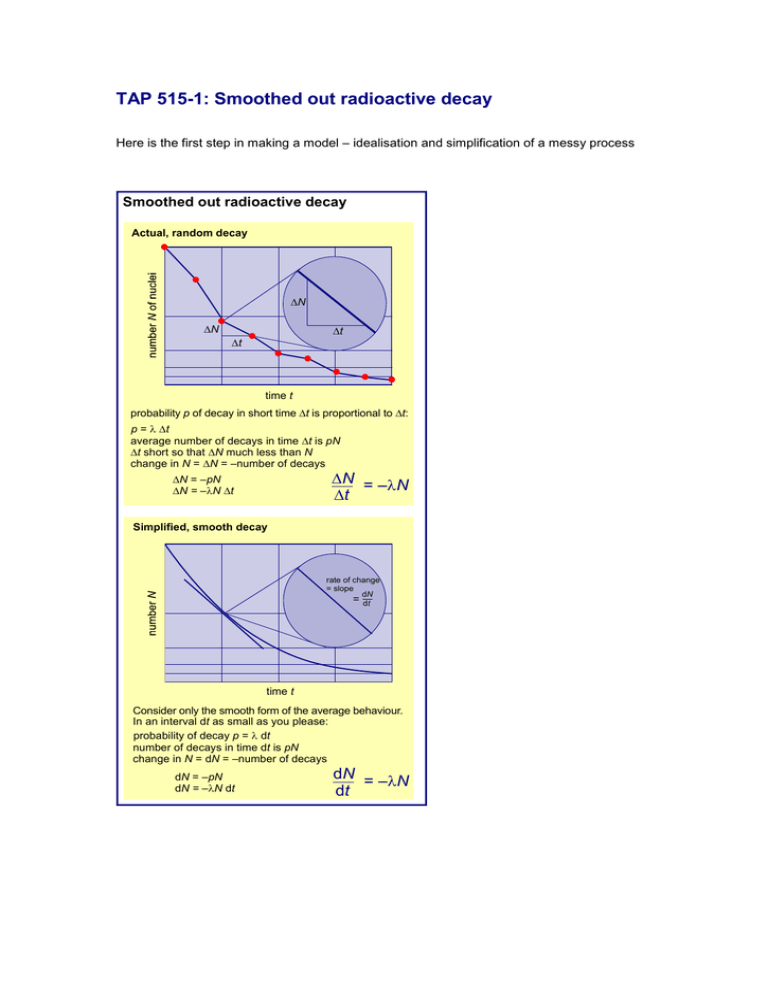
TAP 515-1: Smoothed out radioactive decay Here is the first step in making a model – idealisation and simplification of a messy process Smoothed out radioactive decay Actual, random decay N N t t time t probability p of decay in short time t is proportional to t: p = t average number of decays in time t is pN t short so that N much less than N change in N = N = –number of decays N = –N t N = –pN N = –N t Simplified, smooth decay rate of change = slope dN = dt time t Consider only the smooth form of the average behaviour. In an interval dt as small as you please: probability of decay p = dt number of decays in time dt is pN change in N = dN = –number of decays dN = –pN dN = –N dt dN = –N dt Practical advice The diagram could be used for an OHT External reference This activity is taken from Advancing Physics chapter 10, display material 10O