Newton’s first law - inertia Chapter 2
advertisement

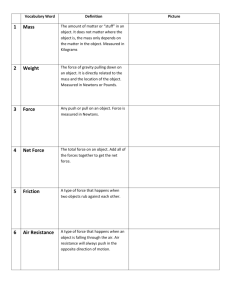
Chapter 2 Newton’s first law - inertia Goals • Understand vocabulary associated with forces, inertia, and equilibrium • Apply knowledge of these concepts to understand Newton’s first law • Apply Newton’s first law to solve equilibrium problems. Calif. Science Standards for motion • From California Science Standards, grade 2: – • Students know the way to change how something is moving is by giving it a push or a pull. The size of the change is related to the strength, or the amount of force, of the push or pull. And from grade 8: – – Students know the velocity of an object must be described by specifying both the direction and the speed of the object. Students know changes in velocity may be due to changes in speed, direction, or both. Newton changed the way people think • Isaac Newton (see page ___) discovered rules governing velocity, acceleration, force, etc. • He applied these ____________________ ____________(space) and on Earth. – First person to do this. – He theorized: Scientific ideas are “universal” • Things change for natural reasons – Ex: Motions change due to forces • Let’s start with some definitions and then his first law. • Matter = Vocabulary – ________________ • Mass = – _______________________ – Units are _____________________ • Force – – ____________. How many objects are involved in a force? – _____________________________________ – Units are ______________(or ________in British system) • Weight = – the __________________________________. What units? • Which objectS are involved in the force of gravity your pencil experiences after you let go? – Discuss with neighbor: what’s the second object for pencil falling down? Examples of forces • Let’s name some types of forces – _____________________ • • • • ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ – __________________(page ____) – ____________________ – ____________________ – ____________________ – ____________________ – ____________________ Newton’s first law (pages ____) • Everyday version: (slightly revised) – Objects in motion __________________ and – __________________________________ – __________________________________*. (Sometime written as “_________________ ___________________________________ • Called the “law of ______________” • Inertia = _________________________ – If moving, _____________________, etc. • *Net force will be defined later. Everyday Examples • Give examples from everyday life of: – Objects continuing at rest – Objects continuing in motion Heavy ball & strings demo • Page _____has a drawing. • What must happen to a string for the string to break? Which string will break if we suddenly hit the bottom string strongly? 0 1. Top 2. Bottom 3. Both at the same time 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 Debrief • Talk to your neighbors: – Did you get it right? – Why or why not? – Make sure you understand. Which string will break if we slowly push on the bottom string? 0 1. Top 2. Bottom 3. Both at the same time 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 Debrief • Talk to your neighbors: – Did you get it right? – Why or why not? – Make sure you understand. Net force (pages __________) • Objects can be pushed or pulled by _____ _______________________________. • These forces are combined as vectors and the result is the “net force.” – Vector = __________________________ _______________. Force examples … • Open to bottom of page ___ right now – After going over examples: replace the 5 N forces with 2 & 6 Newtons and re-do. – STUDENT: draw the diagrams to scale. Results of a Net force • _______ possibilities when an object experiences a net force: – Net force ___________ – Net force ___________________ • Net force _______________ – Called “__________________” – _______________applies. (__________________) • Net force _____________ – Newton’s Second law (covered later) Is it possible for an object to continue at rest under the influence of only one force? 1. Yes 2. No 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 Debrief • Talk to your neighbors: – Did you get it right? – Why or why not? – Make sure you understand. Equilibrium (pages _________) • When all forces balance/cancel out, the net force is ________. • “________________________” • Page ____ left margin example. What are the forces on the Sugar bag? Draw them, compare with neighbor. – Same question for the string. – Same question for the scale. – Same question for a book on table – Same question for a book with weight on table. More examples • Scaffold – make up a question. • Paradox of forces demo Debrief • Talk to your neighbors: – Did you get it right? – Why or why not? – Make sure you understand. Discussion questions • Inertia on airplane – let go of coin • Inertia on Earth – supersonic wind • (Both discussed on pages ___________) Homework • Pages 38-39 – Review Questions 10, 13, 17 – Exercises 6, 18, 26*, 27*. • *staging = wood plank that people are standing on Summary • Vocabulary • Forces – Definition, number of objects involved – Examples • Newton’s first law – Inertia – Equilibrium – Solve force problems.