humanbiolecture3.doc
advertisement

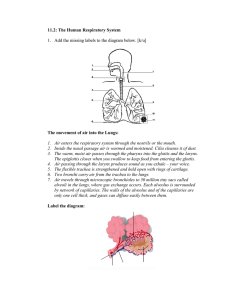
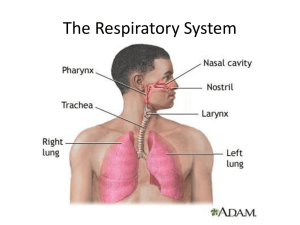
•Circulatory system – heart, blood vessels & blood •Supplies cells with nutrients from digestive system and removes wastes through the urinary system •Exchange of gases with respiratory system •Cardiovascular system – blood vessels and the heart have specific layers: endothelial lining, tunica media with muscles that determine blood pressure, tunica adventitia covering •Aneurysms are bulges of the vessel wall •In the skin are precapillary sphincters that affect the body temperature by opening or closing vessels that are closest to the outside •Capillaries exchange nutrients & wastes with tissue •Hydrostatic & osmotic pressures affect the flow and volume of blood that escapes and returns to capillaries in the tissues •Remaining fluid is carried away by lymph vessels •Veins have valves and rely on muscles that press against their walls to help force blood back to the heart •Varicose veins occur when valves become incompetent •The heart is located in the pericardial sac •Cardiac muscles that make up the myocardium contract •The heart has 2 atria & 2 ventricles separated by valves •Right heart controls the pulmonary circuit – pumping blood to the lungs for gas exchange •Left heart controls the systemic circuit – sending oxygenated blood to the rest of the body •Coronary arteries supply heart tissue •The pacemaker & autonomic nervous system determine rate •SA node, AV node, AV bundle, Purkinje fibers are involved •Systole & diastole (contraction & relaxation) cycle lasts 0.8 seconds •Lub – atrioventricular valves close; Dub – semilunar valves close •Electrocardigram measures electrical activity – records arrythmias •Blood pressure measures systolic & diastolic pressures using a sphygmomanometer •Hypertension & hypotension – Baroreceptors in the heart and some arteries monitor blood pressure •Sympathetic nervous system increases heart rate and blood pressure, exercise increases cardiac output •Angina pectoris is chest pain – often caused by myocardial infarcts – an area of heart tissue whose coronary artery is blocked •Congestive heart failure is ineffective pumping of blood, blood pools in veins – embolism is the flow of a large substance in the blood stream and causes strokes •Risk factors for cardiovascular disease include exposure to cigarette smoke, high blood cholesterol levels, sedentary lifestyle, diabetes, stress •The digestive system •Wall layers: •Mucosa submucosa muscularis serosa •Sphincters between organs •Raw material is broken down by: •Mechanical processing •Secretion of fluid, enzymes, acids, bile, mucus •Nutrients are absorbed across the mucosa into blood or lymph vessels •Undigested material is eliminated •Peristalsis propels food •segmentation mixes food •The mouth prepares food for swallowing •Teeth bite & chew & include incisors, cuspids, bicuspids (premolars) & molars covered with enamel, lined with dentin •Bacteria can dissolve enamel •The tongue tastes food & produces saliva, made of mucin, amylase, bicarbonate, lysozyme, which begin carbohydrate digestion •Parotid, submandibular, sublingual salivary glands •The pharynx & esophagus propel food to the stomach •Swallowing reflex: soft palate closes off nasal passages, larynx rises & epiglottis bends to close it, tongue pushes food back •Esophagus produces mucus & the lower esophageal sphincter opens to allow flow into the stomach •The stomach stores & digests with pepsin, hydrochloric acid, intrinsic factor, gastrin •Mixes food & begins digestion of proteins, absorbs alcohol and aspirin •The small intestine also digests food, and absorbs nutrients and water •Duodenum, jejunum, ileum have villi with microvilli to increase surface area •Pancreatic enzymes & bile help with digestion •Pancreas makes digestive enzymes & sodium bicarbonate and has islets of langerhans that make the hormones insulin & glucagon •The liver makes bile, stored in the gallbladder •Hepatic portal system processes digested proteins & carbohydrates that arrive through the hepatic portal vein •Stores vitamins A, D, E, K, iron, glucose •Makes plasma proteins & lipids •Inactivates chemicals & converts ammonia into urea •Destroys worn out red blood cells •The large intestine absorbs nutrients & water and its parts are the cecum, appendix, ascending, transverse, descending colon, & rectum •Bacteria digest leftover material, produce vitamin K •Internal & external anal sphincters •Proteins & carbohydrates are absorbed as amino acids & simple sugars, then diffuse into capillaries •Lipids are emulsified by bile & digested by pancreatic and intestinal lipase enzymes, making fatty acids & monoglycerides •Micelles pass through the intestinal mucosa and are recombined into triglycerides coated with proteins – chylomicrons •Enter lymphatic lacteals & go into regular circulation •Cholesterol attaches to lipoproteins – HDL bring it to the liver, LDL to body tissues •water absorbed by osmosis •Digestion is regulated by endocrine & nervous systems •External stimuli begin the digestive process •Stretch of stomach causes gastrin release, secretin & cholecystokinin are released by duodenum stretch, to make the pancreas & gall bladder secrete •Nutrients are stored until needed •Respiration is breathing and is divided into external, internal, and cellular respiration •Upper respiratory tract – nose, pharynx •Lower respiratory tract – larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs •URT – receptors for smell, filters, moistens, warms air •Nasal cavities lead to bony sinuses •Mucus traps particles •Auditory tubes connect with the pharynx •The larynx produces sound •Epiglottis protects larynx •Vocal cords surround the glottis within the thyroid cartilage •Trachea transports air to the bronchi •Bronchi branch into the lungs, branch further as bronchioles •Lungs are surrounded by the pleural membrane •Gas exchange occurs in alveoli - 300 million alveoli provide 800 square feet surface area for exchange •Surfactant reduces surface tension so alveoli won’t collapse •Capillaries bring blood to alveoli for gas exchange •Inhalation – diaphragm & ribs move out, increase space, so that air is sucked into the lungs •Expiration – often simple recoil of the muscles •Tidal volume - Inspiratory reserve - Expiratory reserve - Vital capacity - Residual volume are measurements of the amount of air •Sea level atmospheric pressure is 760 mm Hg •78% of the pressure comes from nitrogen, 21% from oxygen, 0.04% from carbon dioxide •Gas diffuses down its partial pressure gradient •Oxygen in air is 160 mm Hg •Deoxygenated blood is 40 mm Hg •Carbon dioxide 46 mm Hg •Diffusion occurs across capillary & alveolar wall •Hemoglobin transports 98% of •Carbon dioxide is usually transported as bicarbonate ion •Medulla of brain has a respiratory center, like a pacemaker, to make a person inspire for 2 seconds, expire fro 3 seconds by controlling the diaphragm •Chemical receptors in carotid and aorta monitor oxygen concentration and affect the respiratory center •Carbon dioxide concentration is monitored in cerebrospinal fluid •Asthma happens when there is an inflammatory reaction in the bronchi, causing increase of mucus & contraction of the bronchi muscles, making it hard for air to get to the alveoli •Emphysema & chronic bronchitis happen because of cigarette smoking – •Both make it difficult for gas exchange •Emphysema is when the alveoli become destroyed, chronic bronchitis with overproduction of mucus