21. Urinary II - Physiology.doc
advertisement

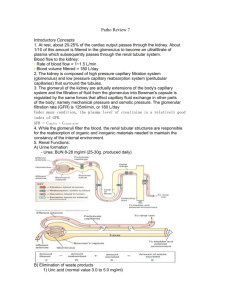
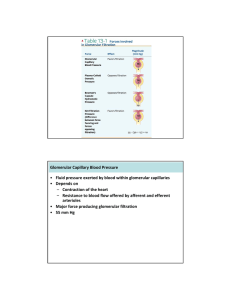
D’YOUVILLE COLLEGE BIOLOGY 108/508 - HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II LECTURE # 21 URINARY SYSTEM II RENAL PHYSIOLOGY - THE NEPHRON 1. Functions of Kidneys: • removal of nitrogenous wastes from blood • regulation of water, acid/base, and electrolyte balance • regulation of arterial pressure (renin/angiotensin system) • regulation of red cell production (erythropoietin mechanism) • role in activation of vitamin D hormone (calcium regulation) 2. Functions of the Nephron: glomerular filtration, tubular absorption, & tubular secretion (fig. 25 - 10) • Glomerular Filtration: glomerular membrane: consists of capillary endothelium (very leaky) + inner layer of squamous epithelium (features 'slit pore' between cells); permeability > 1000X that of normal capillaries (fig. 25 - 9) • glomerular pressure = 55 mm. Hg (usual is 35 mm.), stabilized by balanced vasoconstriction of afferent & efferent arterioles 1 • glomerular filtration (non-selective): approx. /5 of plasma flow (filtration fraction) yields glomerular filtration rate (GFR) = 125 ml./min. (180 l./day!) • filtrate resembles plasma minus proteins • Tubular Absorption: • selective process: sodium recovery (active transport) drives chloride transport (electrochemical drag); solute recovery provides osmotic gradient for water recovery; other substances (e.g. glucose, amino acids, vitamins) also recovered by active transport; urea recovered by diffusion (fig. 25 - 14) • 65 - 70% absorption in proximal tubule (obligatory water absorption) • distal tubule and collecting duct absorption hormonally regulated (facultative absorption) • 99+% of water filtered is normally recovered; 100% recovery of glucose, amino acids; 50% recovery of urea • 124 ml./min. (178.5 liters/day) normal tubular absorption rate (TA) results in urine output (UO = GFR - TA) of 1 ml./min. (1.5 liters/day) • absorbed materials return to blood in peritubular capillaries • Tubular Secretion: • active transport of additional substances into renal tubule • occurs mainly in proximal, distal and collecting tubules • potassium, hydrogen ion, uric acid, creatinine and ammonia are substances secreted into tubules 3. Renal Blood Flow -- Regulation of Glomerular Filtration Rate (fig. 25 -12): • major influence over GFR and therefore over UO (table illustration) • regulation of GFR via intrinsic (autoregulation -- adjustments within kidney) Bio 108 lec. 27 - p. 2 & extrinsic mechanisms: afferent vasoconstriction/vasodilation (autoregulation = myogenic response, JG apparatus response) promotes drop in GFR/rise in GFR; extrinsic adjustments alter systemic BP (sympathetic NS, renin-angiotensin system) • effect of autoregulation: 100% rise in arterial pressure results in only 15% rise in GFR