shortlifehistory
advertisement

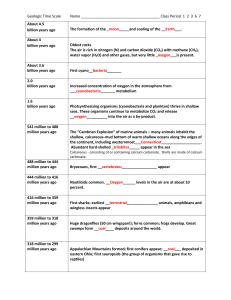
Precambrian Eukaryotes Acritarchs Ediacaran Vendian Acritarchs Cysts of unicellular eukaroytes, perhaps algae or egg cases of multicellular orgs. 1800 my through Devonian Ediacaran • 600 my-545 my • Soft-bodied • Many organisms of uncertain affinity Possible annelids, cnidarians (coral relatives) Probable cnidarian Possible mollusc? Total mysteries Vendian • “little shellies” • Right at Cambrian boundary Cambrian Trilobites: Extinct arthropods (like lobsters or shrimp but with calcite skeleton) Lingulate brachiopods Strange echinoderms Sponge reef • • • • • Middle Cambrian Excellent preservation of soft-bodied orgs. 5 kinds of arthropods (only 3 kinds today) First vertebrate Mysterious critters Burgess Shale Cambrian • • • • Smallish Skeletons (if any) of phosphate or thin CaCO3 Live on or near ocean floor Sponges, trilobites, early molluscs, echinoderms, lingulate brachiopods Ordovician Brachiopods (articulate) Bryozoans Crinoids (echinoderms) Cephalopods Corals Graptolites Ordovician invertebrates • More robust skeletons • Calcite skeletons • Taller, deeper (take up more ecological space) • The Paleozoic fauna appears: rhynchenelliform brachiopods, bryozoans, crinoids/blastoids, primitive cephalopods, graptolites, rugose/tabulate corals Middle-Late Paleozoic Middle-Late Paleozoic • Increasing height, increasing depth • Increasing diversity • New organisms – Eurypterids (giant sea scorpions) • Fish/amphibians Eurypterid Fish Jawless (bony plates on outside) Ostracoderms Armored: Acanthodians & Placoderms Chondrichthyes: Osteichthyes: Sarcopterygian: Lobe-finned fish Forerunners of quadrapeds Paleozoic What if… • You were at a Paleozoic banquet and were offered these creatures to eat: – – – – Brachiopod Bryozoan Crinoid Trilobite Which one would you rather eat? Why? • You were running the Paleozoic Ultimate Fighter show, and you had to design matchups between different Paleozoic creatures. Organize at least two matchups between two different kinds of creatures off the list. Who would be good opponents to match up? In each case, who would win and why? Mesozoic Life • Oceans - a whole new crew • The Modern Fauna – – – – Mollusks Crustaceans Echinoids Fish Bivalves Molluscs Gastropods Crustaceans Echinoids Mesozoic Life • Oceans - a whole new crew • The Modern Fauna – – – – Mollusks Crustaceans Echinoids Fish • Plus marine reptiles and ammonites Marine reptiles Ammonites Cenozoic Oceans • Like Mesozoic: Modern Fauna • Minus marine reptiles and ammonites • Plus whales and marine mammals Evolution of Tetrapods • • • • Arise from sarcopterygians (lobe-finned fish) Amphibianish creatures Reptiles (to birds) Mammals Tiktaalik - recent transitional find Amphibians Adaptations for life on land • • • • Breathe! Locomotion Avoid dessication Reproduction - amniotic egg allows longer development (no swimming larvae) – Leathery covering or eggshell – Larger size of egg – Larger yolk Adaptations for life on land: plants • Avoid dessication – thicker outsides • Reproduction – – Fancy fertilization methods, seeds – Marine plants release gametes into water • More complicated dispersal mechanisms for young Reptiles • Anapsids: turtles and their ancestors • Synapsids: pre-mammals & mammals Synapsids Therapsids: immediate forerunners of mammals Reptiles • Anapsids: turtles and their ancestors • Synapsids: pre-mammals & mammals • Diapsids: Rest of reptiles – – – – – Marine reptiles Snakes, lizards Pterosaurs Crocodilians Dinosaurs and birds Diapsids Pterosaurs Crocodiles Marine reptiles Marine reptiles Dinosaurs Diapsids Birds What were dinosaurs like? • At your table, address one of these questions: – How did dinosaurs stand? Were they capable of fast movement? – Were dinosaurs social animals? – Were dinos warm-blooded? • How do you know? What were dinosaurs like? • • • • Stood erect, not sprawling Some fast-moving Social behavior Maybe warm blooded Brontosaurus, 1953 Apatosaurus, 2007 Bone strength of ceratopsians could sustain a 35mph gallop T. rex had weak leg bones, delicate skull: Probably walking, not running Maybe scavenger? Maternal care Maiasaurs built nests in a large nesting colony, each a mom’s length apart. Nests have no broken egg shells in them, so mom cleaned them out. Babies may have been incapable of walking, like baby birds, so required care Herding Bone beds may represent mass mortality of a herd for example, trying to ford a river in flood, just like caribou and wildebeest disasters of recent years. Trackways Some trackways have little footprints on the inside, suggesting a herd structure like elephants, where the babies are protected by the adults on the outside Pack Hunting Popular idea, not much evidence: •One specimen of multiple raptors with prey •Large optic lobes, used in reptiles for higher brain functions Warm-bloodedness • • • • Predator-prey ratios Thermal inertia Haversian canals O-18 isotopic ratio Dino bone Tortoise bone O-18 to O-16 ratio varies with: •Season •Internal temperature Cold blooded animals have growth rings and large O-18 variability. Warm-blooded animals have no growth rings, uniform O18 levels