Name: BIOLOGY ... Classification:
advertisement

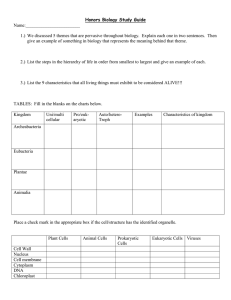
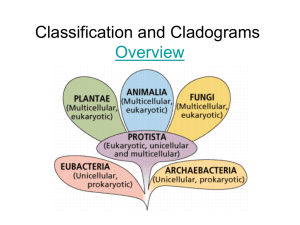
Name: ________________________________ BIOLOGY Date: ______ Classification: ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ Purpose of Classification 1. The reason is to logically organize the approximately 1.5 million species that we have on earth. 2. The classification of these species is based on their DNA component, development, reproduction, morphology and physiology. Carolus Linneaus - _____________________________________________________ Taxonomy _____________________________________________________________ Taxon ________________________________________________________________ Binomial Nomenclature 1. The system involves the assigning of a two-part scientific name to each species. o o o Uses______________ words scientific names always written in ____________________ two parts are the _____________________ and ____________________ 2. Why Latin?? Common names are not universal and meanings of words change over time o Mountain lion/puma/cougar (Puma concolor) o “Possums” in America are NOT possums in Australia (Didelphis virginiana versus Trichosurus vulpecula) Latin is universally understood, but does not favor any language or culture Latin is a “dead” language- it will not chang 3. Genus- ________________________________________________________________ Species in the same genus are thought to be closely related. Genus name is always ______________________ 4. A species descriptor is the second part of a scientific name. always _______________________ always follows genus name; never written alone 5. Both are underlined when written or in italics when typed. Examples: Homo sapiens, Drosophila melanogaster. Sometimes, the first name may be abbreviated (ex. Escherichia coli could be written as E. coli) The Science of Classification Hierarchical Classification Each level includes the level above it. Levels get increasingly specific from kingdom to species. Problem with the Linnaeus taxonomy system is it doesn’t account for molecular evidence. Linnaean system based only on ______________________________________ Name: ________________________________ BIOLOGY Date: ______ Modern Classification is based on __________________________________________ Cladograms/ Phylogenetic Trees 1. They are diagrams showing evolutionary relationships (family tree of species) 2. They are constructed by using morphology and DNA evidence 3. Important features used for the construction are derived and ancestral characteristics i. Derived characteristics-______________________________________ __________________________________________________________ ii. Ancestral characteristics- ____________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ Cladistics- methods to make an evolutionary tree – classification based on ____________________________________ – species placed in order that they descended from common ancestor Clade ________________________________________________________________ – Each species in a clade shares some traits with the __________________ – Each species in a clade has traits that have changed. Derived characters are traits shared in different degrees by clade members – basis of arranging species in____________________________ – more closely related species share more __________________________ – represented on cladogram as hash marks Dichotomous Keys _____________________________________________________ The 6 Kingdoms 1866 only two kingdoms (1) Animalia - consumers (2) Plantae – make their own food. (Photosynthetic) 1866 revised to also contain (3) Protista – single cell organism 1938 revised again to include Monera- (prokaryotes) 1959 – Fungi are not plants (4) Fungi- not photosynthetic 1977 – Kingdom Monera split (5) (Eu)bacteria (6) Archea Name: ________________________________ BIOLOGY Date: ______ Domains • Domains are above the kingdom level. – proposed by Carl Woese based on _____________studies of prokaryotes – domain model more clearly shows _________________________ diversity The 3 domains DOMAIN Archaea Bacteria KINGDOM Archaebacteria Eubacteria (Eukaryote or Prokaryote?) Eukarya Protista Fungi Plantae Prokaryote CELL WALL STRUCTURES No cell wall Unicellular or Multicellular? MODE OF NUTRITION unicellular multicelluar Autotroph/ Autotroph heterotroph (Autotroph or heterotroph?) MOVEMENT OF ORGANISM Animalia none REPRODUCTION (Asexual or sexual?) Extra Information EXAMPLES Mushrooms, yeasts Name: ________________________________ BIOLOGY Date: ______