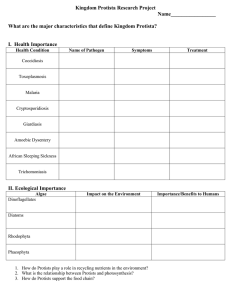
Protista Power Point

Kingdom Protista
Chapter 19
General Characteristics of
Protists
:
• ALL Eukaryotes that cannot be classified as a plant, animal, or fungus.
• They have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles;
• some are autotrophic, some are heterotrophic;
• some are multicellular, most are unicellular.
They are classified by the way they OBTAIN NUTRITION .
Three kinds of protists
• Animal-like (consume food)
• Plant-like (make their own food)
• Fungus-like (decomposer)
19.2 Animal-like Protists
TEKS 11C, 12A
KEY CONCEPT
Animal-like protists are single-celled heterotrophs that can move.
Animal-like Protists
• Called Protozoans- meaning “first animals”
• Examples:
– Zooflagellates
– Sarcodines
– Ciliates
– Sporozoans
Protozoans
• these are “Animal-like” protists that consume their food (heterotrophs)
• Unicellular
• characterized by modes of locomotion
(how they move)
– Cilia
– Flagella
– Pseudopod
Zooflagellates
Trichomonas
• Characteristics : move by flagella (one or two)
• Reproduction : mostly asexual by mitosis, some sexual reproduction- produce gametes that fuse
• Role/Function :
– Mostly free swimming
– Some are parasites
– Trypanosoma causes African Sleeping
Sickness, Giardia causes diarrhea
– Termites have a zooflagellate living inside them that helps them digest wood
Zooflagellates
nucleus flagella
Sarcodines
• Characteristics : move by pseudopodsextensions of cytoplasm
• Reproduction : asexually by mitosis
• Role/Function :
– free-swimming in aquatic environments
– Amebic dysentery (diarrhea)
Nucleus
Pseudopod
Ameba proteus
Ciliates
• Characteristics :
– use cilia for movement and feeding
– Have a macronucleus (active nucleus) and micronucleus (reserve copy)
• Reproduction : asexually by mitosis, can exchange material through conjugation (Figure
20-6 in book)
• Role/Function : free-living
Paramecium
Macronucleus
Micronucleus
Ciliates
Cilia
Sporozoans
• Characteristics : Do not move on their own
• Reproduction : complex reproduction with two phases- a sexual phase and asexual phase inside two different organisms!
• Role/Function :
– Parasitic
– Malaria is caused by the sporozoan Plasmodium
Sporozoans
Nucleus
19.3 Plantlike Protists
TEKS 8B, 8C, 11C
KEY CONCEPT
Algae are plantlike protists.
Plant-like (Algae)
• Unicellular
– Euglenophyta
– Chrysophyta
– Bacilliarophyta
(Diatoms)
– Pyrrophyta
(Dinoflagellates)
• Multicellular
– Rhodophyta
– Phaeophyta
– Chlorophyta
Unicellular Algae
• (describe their ecology/uses):
– autotrophic, capture sunlight with chlorophyll and other accessory pigments to make food
– base of many aquatic food chains
• Example : phytoplankton- floating photosynthetic organisms
Euglenophyta
• Characteristics : two flagella, no cell wall
• Reproduction : asexually by mitosis
• Role/Function :
– free-swimming
– can absorb material for food- recycling sewage
– can lead to algal blooms choking waters of nutrients
19.3 Plantlike Protists
TEKS 8B, 8C, 11C
• Euglenoids are a large group of plantlike protists.
– mostly photosynthetic
– some heterotrophic
– single-celled
– one or two flagella pellicle contractile vacuole nucleus flagellum chloroplast eye spot
Euglenophyta
Chloroplast
Flagellum
Nucleus
Chrysophyta
• Characteristics :
– cell walls sometimes of pectin
– Gold-colored chloroplasts
• Reproduction : asexually and sexually
• Role/Function : free-floating
• Known as “golden algae”
Diatoms
• Characteristics : secrete thin cell walls of silica
(main component of glass)
• Reproduction : asexually and sexually
• Role/Function :
– Free-floating, or
– live in soil
19.3 Plantlike Protists
TEKS 8B, 8C, 11C
• Diatoms are plantlike protists with glasslike shells.
– shells made of silica
– produce large amounts of oxygen
Pyrrophyta-Dinoflagellates
• Characteristics : have two flagella and thick cell wall
• Reproduction : asexually by mitosis
• Role/Function : responsible for red tides (algal bloom of dinoflagellates that secrete toxins that can cause illness paralysis, and death in fish and humans)
19.3 Plantlike Protists
TEKS 8B, 8C, 11C
• Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plantlike protists.
– have two flagella
– may be bioluminescent
– have stiff protective plates
– can cause red tide
Dinoflagellates
Dinoflagellates
Nucleus
Flagella
19.3 Plantlike Protists
TEKS 8B, 8C, 11C
• Multicellular algae are classified by their pigments.
– Green algae contain chlorophyll a and b.
– Brown algae contain chlorophyll c.
– Red algae contain chlorophyll a and phycoerythrin.
Multicellular Algae
• (describe their ecology/uses)-
– Autotrophic
– Multicellular
– some have specialized tissue
– seaweeds and kelp
– used in foods such as sushi, ice cream, salad dressing, candy, etc.
Red Algae (Rhodophyta)
• Characteristics : contain pigments- Chlorophyll a and Phycobilins (red)
• Reproduction : sexually
• Role/Function :
– Deeper sea, great at harvesting light
– Help form coral reefs
– Some used in foods and to make agar
Brown algae (Phaeophyta)
• Characteristics : contain pigments Chlorophyll a and c and Fucoxanthin (brown)
• Reproduction : sexually by mitosis and meiosis
• Role/Function :
– Form large habitats in aquatic ecosystems
– Used some in food
Volvox- colonial
Green algae (Chlorophyta)
• Characteristics :
– unicellular, colonial, or multicellular
– chlorophyll a and b
• Reproduction : sexually by mitosis and meiosis like true plants
• Role/Function : some form symbiotic relationships with other organisms
Spirogyramulticellular
Ulvamulticellular
19.3 Plantlike Protists
TEKS 8B, 8C, 11C
• Some algae produce sexually.
– Some species alternate generations.
– Sexual reproduction can be triggered by environmental stress.
Kaikoura, New Zealand
19.4 Funguslike Protists
TEKS 8B, 8C, 11C
KEY CONCEPT
Funguslike protists decompose organic matter.
• Slime Molds
• Water Molds
Fungus-like
19.4 Funguslike Protists
TEKS 8B, 8C, 11C
Slime molds and water molds are funguslike protists.
• Slime molds have both funguslike and animallike traits.
– decomposers, like fungi
– can move, like animals
Fungus-like
• (describe their ecology/uses):
– heterotrophic using external digestion to break down dead and decaying organic matter
Slime Molds
• Characteristics :
– cellular or acellular (masses with several nuclei)
– Unicellular but can gather and act multicellular
• Reproduction : sexually
• Role/Function : Forest floor or compostingrecycle organic matter
19.4 Funguslike Protists
TEKS 8B, 8C, 11C
• Slime molds can be plasmodial or cellular.
– Plasmodial slime molds are giant cells with many nuclei.
– Cellular slime molds contain independent cells.
Water Mold
• Characteristics :
– also called oomycetes (O-O-my-sets)
– Produce filaments called hyphae
• Reproduction : sexually and asexually
• Role/Function :
– dead decaying matter in aquatic environments
– some are plant parasites
– attack tomatoes and potatoes
19.4 Funguslike Protists
TEKS 8B, 8C, 11C
• Water molds are freshwater, funguslike protists.
– one type of water mold caused Great Potato Famine of Ireland in the 1800 ’ s
– made of branching strands of cells
– can be parasites of plants or fish