Protists
advertisement

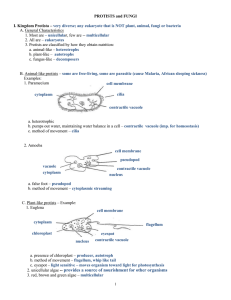
Protists Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Protista Protists are: Single-celled (unicellular) or simple multicellular, microscopic, eukaryotic (with a nucleus) organisms (Phytoflagellates): • Autotrophs (self- nourished) • Producers - produce their own food from light. Algae •Green Algae (7500sp) •Red Algae (5000sp) •Used in making ice cream •Brown Algae (1500sp) Euglena Flagellum •Uses its eyespot to sense sunlight •Moves by 2 flagella (1 Eyespot short and 1 long) •Contains chloroplasts to produce food for itself Chloroplasts Diatoms •Colorful - Many Shapes •Phytoplankton • Used to make toothpaste, insecticides and dynamite Dinoflagellates (whirling-whip) 2 Flagella; Cell Wall Red Tide Heterotrophs (other-nourished) that MOVE Protozoans Protists that move, but cannot make their own food Sarcodines • Pseudopods -extensions of the cell membrane and cytoplasm • Engulf food particles • Assist with movement Amoeba Radiolarian Ciliates • Have small, hair-like projections called cilia on the outside of their bodies • Provide movement • Act as sensors • Can help sweep in food Paramecium Zooflagellates • Protists that move using a flagellum • Live in water or within other organisms • Symbiotic relationship: Termites and wood roaches rely on a type of zooflagellate to digest the wood Heterotrophs that can’t move • Slime Molds – Cause of the great potato famine in Ireland; reproduce by spores • Sporozoans – parasites that feed on cells and body fluids of their host animal • Reproduce by producing spores Example: Plasmodium causes malaria, is transmitted by mosquitos