Exam 2 study questions
advertisement

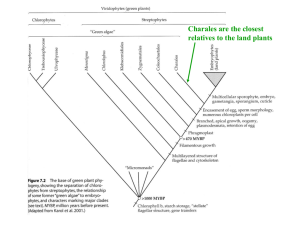
Review Questions for Exam 2 Label the following figures protonema gametophyte sporophyte archegonium antheridium sperm egg seta foot capsule fertilization meiosis rhizoids spore frond fiddlehead sori rhizome roots sporangium meiosis gametophyte sporophyte archegonium antheridium egg sperm spore fertilization 1 Sporophyte Microgametophytes Megagametophyte Pollen cone Ovulate cone Seed Ovule Meiosis (twice) Fertilization Embryo Pedicel Receptacle Pistil Stamen Sepal Petal Calyx Corolla Anther Filament Stigma Style Ovary Ovules 2 Flower Seed coat Embryo Endosperm Embryo sac Pollen grain Meiosis (twice) Double fertilization Ovule Micropyle Pollen tube Microspores Megaspores Shoot system Root system Primary root Secondary root Tertiary root Node Internode Axil Stem Leaf Petiole Axillary bud Terminal bud Blade Veins Flower 3 Name the phylum each one of these organisms belongs to: Liverwort____________________________________________ Horsetail_____________________________________________ Fern_________________________________________________ Selaginella __________________________________________ Ginkgo biloba__________________________________________ Douglas Fir____________________________________________ Lily_________________________________________________ Sago palm___________________________________________ Whisk fern_____________________________________________ Moss_________________________________________________ Name the dominant generation (sporophyte or gametophyte) for each: Liverwort____________________________________________ Horsetail_____________________________________________ Fern_________________________________________________ Selaginella __________________________________________ Ginkgo biloba__________________________________________ Douglas Fir____________________________________________ Lily_________________________________________________ Sago palm___________________________________________ Whisk fern_____________________________________________ Moss_________________________________________________ Describe each as homosporouos or heterosporous: Liverwort____________________________________________ Horsetail_____________________________________________ Fern_________________________________________________ Selaginella __________________________________________ Ginkgo biloba__________________________________________ Douglas Fir____________________________________________ Lily_________________________________________________ Sago palm___________________________________________ Whisk fern_____________________________________________ Moss_________________________________________________ Describe each as vascular or non-vascular: Liverwort____________________________________________ Horsetail_____________________________________________ Fern_________________________________________________ Selaginella __________________________________________ Ginkgo biloba__________________________________________ Douglas Fir____________________________________________ Lily_________________________________________________ Sago palm___________________________________________ Whisk fern_____________________________________________ Moss_________________________________________________ 4 Describe a dispersal mechanisms seen in flowering plants: Define meristem The sporophyte generation of a plant is________________ (haploid, diploid or triploid). Name the two types of gametangia: Name the two types of gametes: Name the structure which produces spores: Name the process in the alternation of generation life cycle which produces spores (type of cell division)__________________________. Name the group which is thought to be the ancestors of terrestrial plants___________________ What is meant by the term “localized growth”? Which plant phylum contains the greatest living biodiversity? Which plant exhibits dichotomous branching and describe this feature. Ovule _______________; ovary ______________; integument____________ Microspore_____________________; megaspore________________________ What are sporophylls? Name two classes which belong to the phylum anthophyta : Define pollination_______________________________ List two reasons why seeds are considered reproductively superior to spores : What does the term coevolution mean? List two alternative terms for microgametophyte________________ _______________ List two alternative terms for megagametophyte________________ _______________ What is the evolutionary significance of needles in conifers? 5 Define dioecious: Define deciduous: Define monoecious: Define evergreen: Define herbaceous: Define woody: List three benefits that flowering plants provide humans: The location of the production of microspores in a flowering plant:__________________ The location of the ovules in a flowering plant_____________________________ What is scarification?___________________________________________________ Monocots eudicots Root system type Leaf vein pattern Number of floral parts Vascular tissue in the steele Vascular bundles in stem List two examples of root adaptations: Roots hairs have vascular tissue. True or false Herbaceous tissues are produced by ______ growth; woody tissues are produced by _____growth. These woody tissues are the result of cell division by a(n)___________________ meristem. As a woody plant grows the epidermis is replaced by the ________________ which is produced by the _____________ cambium. Draw an arrow to the respective function and cell wall structure: Parenchyma flexible support very thin Collenchyma storage secondary cell wall present Sclerenchyma rigid support irregular thickness Name the types of different cells found in xylem tissue: Name the types of different cells found in phloem tissue: 6 Name the structures which cover or protect the following: Flower while developing_____________________ Root apical meristem________________________ Terminal bud______________________________ Sorus____________________________________ What plant organ(s) contains the endodermis tissue? What plant organ(s) contains the steele? What plant organ(s) contains the cortex? What plant organ(s) contains the mesophyll? What plant organ(s) contains vascular bundles? What plant organ(s) contains an epidermis with a cuticle? Name two leaf modifications discussed on class. Label each as monocot or eudicot; as root or stem and xylem and phloem 7 A biology student is walking along a forest trail and finds a 1 m tall plant that bears a pinecone-looking structure at its tallest point. When he touches this structure it emits a cloud of brownish dust. He examines these particles and finds that they are tiny single celled spheres. This student has probably found a____________________ a. immature pine tree b. liverwort gametophyte c. horsetail gametophyte d. club moss sporophyte The evolution of flowering plants is closely tied to the evolution of what group of animals? Assume the diploid number in a given plant is 16. How many chromosomes should be present in: Cells of a pollen grain_______________ Egg cell__________________________ Cells in the embryo of a seed______________ Cells in the endosperm of the seed______________ Cells found in the petals of the flower______________ Which plant cell types listed below would you expect to not find a nucleus? Parenchyma___ Collenchyma___ Tracheids___ Cork cells___ Sieve tube___ Sclerenchyma___ Companion cell___ Guard cell___ The portion of the root which gives rise to branch or lateral roots is the ______________. Which plant tissue contains the casparian strip? ___________________ growth is responsible for an increase in plant’s girth. List four unique characteristics of the Kingdom Plantae: 8