Grade 7 Pacing Guide Block 3
advertisement
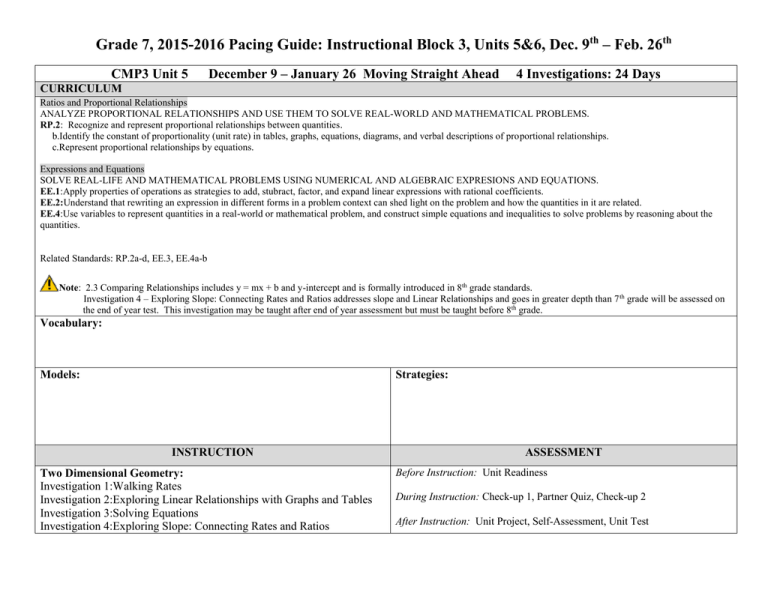
Grade 7, 2015-2016 Pacing Guide: Instructional Block 3, Units 5&6, Dec. 9th – Feb. 26th CMP3 Unit 5 December 9 – January 26 Moving Straight Ahead 4 Investigations: 24 Days CURRICULUM Ratios and Proportional Relationships ANALYZE PROPORTIONAL RELATIONSHIPS AND USE THEM TO SOLVE REAL-WORLD AND MATHEMATICAL PROBLEMS. RP.2: Recognize and represent proportional relationships between quantities. b.Identify the constant of proportionality (unit rate) in tables, graphs, equations, diagrams, and verbal descriptions of proportional relationships. c.Represent proportional relationships by equations. Expressions and Equations SOLVE REAL-LIFE AND MATHEMATICAL PROBLEMS USING NUMERICAL AND ALGEBRAIC EXPRESIONS AND EQUATIONS. EE.1:Apply properties of operations as strategies to add, stubract, factor, and expand linear expressions with rational coefficients. EE.2:Understand that rewriting an expression in different forms in a problem context can shed light on the problem and how the quantities in it are related. EE.4:Use variables to represent quantities in a real-world or mathematical problem, and construct simple equations and inequalities to solve problems by reasoning about the quantities. Related Standards: RP.2a-d, EE.3, EE.4a-b Note: 2.3 Comparing Relationships includes y = mx + b and y-intercept and is formally introduced in 8th grade standards. Investigation 4 – Exploring Slope: Connecting Rates and Ratios addresses slope and Linear Relationships and goes in greater depth than 7 th grade will be assessed on the end of year test. This investigation may be taught after end of year assessment but must be taught before 8th grade. Vocabulary: Models: Strategies: INSTRUCTION Two Dimensional Geometry: Investigation 1:Walking Rates Investigation 2:Exploring Linear Relationships with Graphs and Tables Investigation 3:Solving Equations Investigation 4:Exploring Slope: Connecting Rates and Ratios ASSESSMENT Before Instruction: Unit Readiness During Instruction: Check-up 1, Partner Quiz, Check-up 2 After Instruction: Unit Project, Self-Assessment, Unit Test CMP3 Unit 6 January 27 – February 26 What Do You Expect?, 5 Investigations: 22 Days CURRICULUM Statistics and Probability INVESTIGATE CHANCE PROCESSES AND DEVELOP, USE, AND EVALUATE PROBABILITY MODELS. SP.5: Understand that the probability of a chance event is a number between 0 and 1 that expresses the likelihood of the event occurring. Larger numbers indicate greater likelihood. A probability near 0 indicates an event that is neither unlikely nor likely, and a probability near 1 indicates a likely event. SP.6:Approximate the probability of a chance event by collecting data on the chance process that produces it and observing its long-run relative frequency, and predict the approximate relative frequency given the probability. SP.7:Develop a probability model and use it to find probabilities of events. Compare probabilities from a model to observed frequencies; if the agreement is not good, explain possible sources of the discrepancy. SP.8:Find probabilities of compound events using organized lists, tables, tree diagrams, and simulation. Related Standards: RP.2, RP.2a, RP.3, SP.7a-b, SP.8a-b Vocabulary: Models: Strategies: INSTRUCTION Integers and Rational Numbers: Investigation 1: A First Look At Chance Investigation 2: Experimental & Theoretical Probability Investigation 3: Making Decisions With Probability Investigation 4:Analyzing Compound Events Using An Area Model Investigation 5:Binomial Outcomes ASSESSMENT Before Instruction: Unit Readiness During Instruction: Partner Quiz, Check-up After Instruction: Unit Project, Self-Assessment, Unit Test, Interim 3 Assessment