Protein Synthesis Powerpoint Notes
advertisement

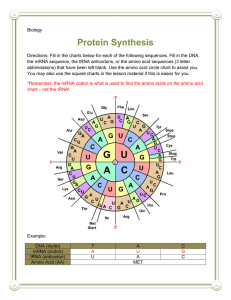
Protein Synthesis 1. Humans share most of the same protein families with ___________, flies, and plants 2. Hair grows by forming new cells at the base of the root. As they move upward through the skin they are cut off from their nutrient supply and start to form a hard protein called _______________ in a process called keratinization. As this occurs, the hair cells die. The dead cells and keratin form the shaft of the hair. 3. Fingernails grow about _______________ times as quickly as toenails 4. Each hair grows about __________/month and grows for up to ____ years. 5. The most expressive muscles are the facial muscles. We need ______ muscles to smile and ______ muscles to frown. 6. The most numerous are the skeletal muscles. When we walk for instance, we use _____ muscles. It is expected that students will be able to … 1. Demonstrate knowledge of the basic steps of protein synthesis, and identify the roles of DNA, mRNA, and ribosomes in the processes of transcription and translation. (p. 481-486) 2. Use the table of mRNA codons to determine the sequence of amino acids coded for by a specific DNA sequence (p. 481) 3. Give examples of 2 environmental mutagens that can cause mutations in humans. (p. 490) 4. Use examples to explain how mutations in DNA affect protein synthesis and may lead to genetic disorders (p. 490) VOCABULARY _____ Adenine _____ Anti-codons _____ Central Dogma _____ Code _____ Codon _____ Complementary Base _____ Cytosine _____ Elongation _____ Endoplasmic reticulum _____ Exocytosis _____ Gene _____ Gene mutation _____ Genetic code _____ Golgi body/Apparatus _____ Guanine _____ Helicase _____ Histones _____ Hydrolytic enzymes _____ Initiation _____ Initiation codon _____ Messenger RNA (mRNA) _____ Mutagen _____ Mutation _____ Peptide bonds _____ Peptidyl Transferase _____ Point mutation _____ Polypeptide _____ Polysome _____ Protein _____ Protein synthesis _____ Ribosomes _____ RNA Polymerase _____ Template _____ Terminator codon _____ Thymine _____ Transcription _____ Transfer RNA (tRNA) _____ Translation _____ Triplets _____ Uracil _____ Vesicle Proteins Have 2 Main Functions 1. Structural: proteins help make up all structures in living things Examples: a) ___________________ b) ___________________ c) ___________________ 2. Functional: other proteins help us to keep our bodies functioning properly and to digest our food. Examples: a) ___________________ b) ___________________ c) ___________________ d) ___________________ Protein structure is determined by the genetic code in your DNA. The section of DNA that codes for one protein is called a _______________. A gene is a section of DNA that determines the ____________________________ in a protein. Therefore, the _____________________________ and therefore, the _______________ of the protein it codes for. Central Dogma of Biology One _________ codes for one type of ____________ which does one ____________ in the cell. How Does Protein Synthesis Work? If the process of protein synthesis were a play, these would be the roles of all of the people involved The director who has the master plan =______________ The 3 assistant directors? _______, _______, _______ The cast (actors) = _________________ The stage = _________________ The stage crew (helpers) = ________________ Act One: ________________ (Trans = across, cription = to write) The coded message of a gene on DNA has ____________________ on how to make _________ particular ________________ that our bodies need. The instructions from a gene are copied from DNA to ________________ (__________) in the nucleus. Then, the mRNA moves through the _____________________ and into the cytoplasm where the proteins are made. The process of making mRNA is called ______________________ Watch the General Process Step 1: ________________ the DNA (starting at the promoter). Step 2: ______________________________ attach to form the mRNA strand Step 3: _______________ forms the RNA ______________ _______________ and checks for __________________ Step 4: The __________________ & leaves the nucleus, & the __________________ Act Two: __________________________ The mRNA code is made up of groups of _____________ ________ known as _________. Each codon codes for a specific ________________. Eg. AGC = Serine Eg. UGC = Cysteine CAU? ____________ GCC? ____________ See text figure 25.7 (page 481) CUU? ____________ UGA? ____________ AUG? ____________ AAA? ____________ Why a Triplet Code? It takes ____ nucleotides on the mRNA to code for _____. Why? We must code for ______ different amino acids and there are only __________ (nucleotides) in the alphabet. With a _____ nucleotide, there are only __ possible codes (41). For _____ nucleotides, there are only __ possible codes (42). However, for ______ nucleotides there are ____ possible codes (43), and that is enough to code for the 20 amino acids. Translation • The written code (codons) on mRNA is ‘_____________’ into a specific amino acid sequence by _____________ in the cytoplasm. • This is carried out with the help of relatively small _____________ _______ molecules. A tRNA molecule is a small piece of RNA that has a _________________________ attached to it. The tRNA also has a special sequence of 3 nucleotide bases known as an ____________. There is at least one type of tRNA for each of the 20 amino acids. As the correct _____________ are brought to the ribosome by the _________, they are joined together via __________________ to form the ___________ that the original DNA coded for. Please note that there is ______________________ for each amino acid: mRNA codons: tRNA anti-codons: U C U ______ G C C ______ The Steps of Translation: 1. The mRNA molecule moves ____________________ in the nuclear envelope and in to the cytoplasm. It joins with a ___________ and is translated one amino acid at a time. 2. ‘______________’: the first codon on any mRNA molecule is called the ‘____________’ codon. This codon is always ________, which codes for the amino acid _________. This is a message to ________ translation. 3. ‘_______________’: the ribosome’s job is to position the tRNA molecule onto the matching mRNA molecule. 4. ________________: The last codon on any mRNA molecule is called the ___________________, which is a message to ____________ translation. ________________: The last codon on any mRNA molecule is called the ___________________, which is a message to ____________ translation. CRACKING THE GENETIC CODE A BAD NIGHT AT THE THEATRE Question: What if something goes wrong during translation? Answer: ___________________ • • • A ____________ in the nucleotide sequence of DNA When the ________ (‘letters’) change, the _______________ are used to make the protein. The protein will _______ ______ to do its _____. There are 2 types of MUTATION: 1. ______________ mutations: a mutation of all or part of a chromosome. This usually involves ______________, and therefore, ________________. Example: Down’s syndrome. 2. _________ mutations: a mutation that occurs within a gene at some point along a chromosome. This mutation is only a change of 1 or a few ‘letters’ (nitrogenous bases). It usually only affects ___________, and therefore, _____________. Example: Sickle cell anemia.