Figure-7_07-COL.ppt
advertisement
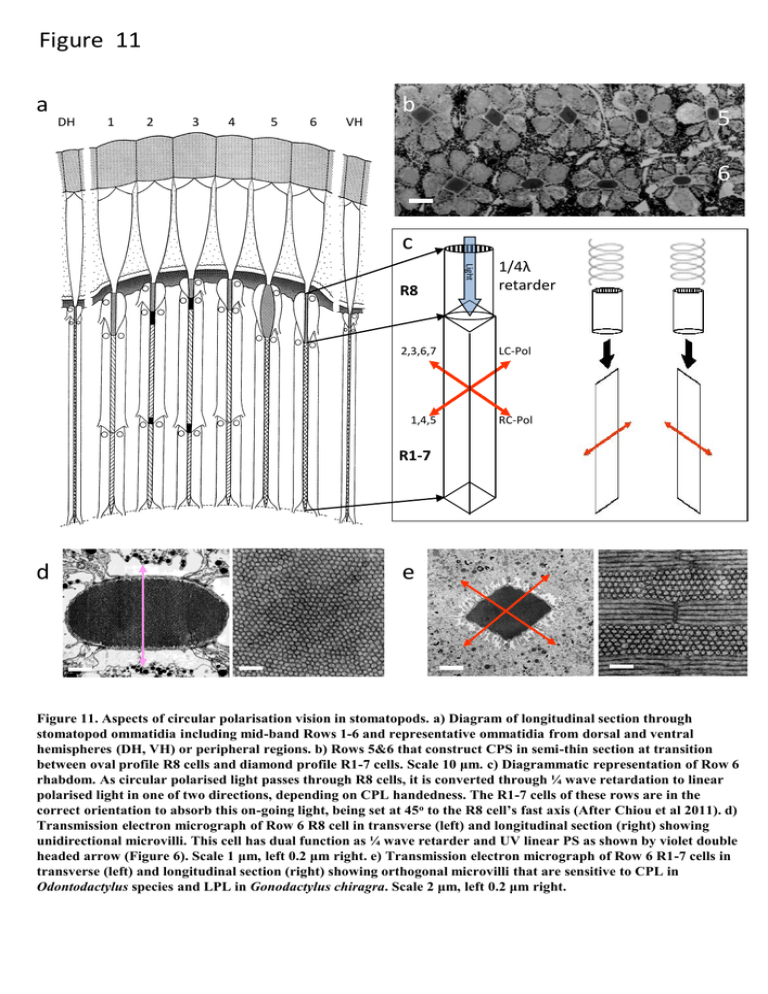
Figure 11 a DH 1 2 3 4 5 6 VH b 5 6 c 2,3,6,7 LC-Pol 1,4,5 RC-Pol Light R8 1/4λ retarder R1-7 d e Figure 11. Aspects of circular polarisation vision in stomatopods. a) Diagram of longitudinal section through stomatopod ommatidia including mid-band Rows 1-6 and representative ommatidia from dorsal and ventral hemispheres (DH, VH) or peripheral regions. b) Rows 5&6 that construct CPS in semi-thin section at transition between oval profile R8 cells and diamond profile R1-7 cells. Scale 10 μm. c) Diagrammatic representation of Row 6 rhabdom. As circular polarised light passes through R8 cells, it is converted through ¼ wave retardation to linear polarised light in one of two directions, depending on CPL handedness. The R1-7 cells of these rows are in the correct orientation to absorb this on-going light, being set at 45o to the R8 cell’s fast axis (After Chiou et al 2011). d) Transmission electron micrograph of Row 6 R8 cell in transverse (left) and longitudinal section (right) showing unidirectional microvilli. This cell has dual function as ¼ wave retarder and UV linear PS as shown by violet double headed arrow (Figure 6). Scale 1 μm, left 0.2 μm right. e) Transmission electron micrograph of Row 6 R1-7 cells in transverse (left) and longitudinal section (right) showing orthogonal microvilli that are sensitive to CPL in Odontodactylus species and LPL in Gonodactylus chiragra. Scale 2 μm, left 0.2 μm right.