iran-it-future-english.ppt
advertisement

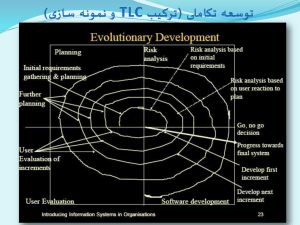
وضعیت مطلوب فاوا در ایران بسمت وضع مطلوب الکترونیک صنعت الکترونیک و سخت افزار Electronics Government Interest • Special interest in new technology industries, say Electronics. • Ministry of Industries and Mines is the main authority. • A commission of the cabinet members is the main coordinator. • The new strategy of the country is to change the focus to high-tech industries. Electronics Hardware • One Billion US$/Y being spent on Electronics related goods. • The main exporters to Iran are Koreans, Germans, French, and Japanese. • Swedish and German companies are mostly active in Telecommunication devices. • Electronics industry generates 0.5% of the GDP. Electronics Hardware (PC) • All parts excepts drives, and chips are produced (CKD) domestically. • Almost 1,000,000/Y sales of PCs. • Domestic brands dominate the PC market. • Demand for branded servers is high. • Yearly market value around $500 to $700 millions. • Average market growth of 30% • Peripherals market value: $100m, Growth rate: 30% Telecommunications Telecommunications Networking Internet Telecommunications, Networking, & Internet Governing body • Ministry of Post, Telegraph, and Telephone is the main governing body. • The name of the ministry is changing from PTT to ICT, reflecting the change of its focus. • There is a monopoly for major telecom infrastructure of the country. • Breaking the monopoly and privatization is a promised goal of the ministry. • Regulatory Authority (RA) under establishment. • 50 large and medium size communication companies. Telecommunications, Networking, & Internet Communication Networks • • • • • • • • • • • Nationwide Microwave links New 19,000 km Nationwide Fiber Loops Backbone. 13 Millions fixed telephone lines. 2.3 million GSM postpaid subscribers. One private pager operator in two main cities. 5 VSAT hubs. 14,000 VSATs. X.25 network in 150 cities (11,200 ports). One national post and parcel delivery (monopoly). Many countrywide, regional, and city delivery agencies. Two Remote Sensing centers. Telecommunications Backbone Fiber Loops Backbone Regional Digital Links Microwave Backbone Satellite Telecommunications International Fiber Optics Trans Asia Europe (TAE) or “Silk Road” connects China to Europe, passing through Iran Putting 33 Iranian cities directly on the Fiber Telecommunications International Fiber Optics Underwater Fiber Optics Line Connects Iranian city of Jask to Fujaira in the UAE, and then to FLAG Telecommunications, Networking, & Internet Telephone (Fixed) Lines • 13 Millions fixed telephone lines, with %12 annual growth, penetration ratio 20+ per 100 capita. • The number of subscribers will grow to 15 million in 3 years. • E1 lines available. • Huge demand for more lines by ISPs. • Planned rapid growth and expansion. Telecommunications, Networking, & Internet Mobile phones • Iran is using GSM mobiles. • 2.3 million lines in use, Penetration Rate (per 100 capita): 3.51% • Monopoly operator-TCI (two small ones: in Isfahan and the Kish free zone), • In 3 years the total number of lines will increase to 10 millions. • TCI will provide up to 5 million lines, 2 million of it in Prepaid. • 5 millions should be provided by private sector. • Limited roaming with some Persian Gulf countries, Saudi Arabia, and Austria. • SMS recently operational, no GPRS yet, no hot billing yet, WAP service available but not popular. Telecommunications, Networking, & Internet Data Lines • Available media: – Copper – Fiber – Satellite – Microwave • Demanding services: – HDSL, ADSL – E1 – Satellite • Huge investment done and planned by TCI on the country fiber backbone connecting almost all cities. • Utilization of 20,000 (2B+D) and 350 (30B+D) ISDN Ports • Problem in the last mile. • Problem in end to end broadband. Telecommunications, Networking, & Internet Internet • About 3,500,000 Internet Users • 200% Yearly Growth (highest in the region) • Total Internet bandwidth excluding receive only DVB-MPEG2. : – Incoming: 1 Gbps – Outgoing: 550 Mbps • Satellite Connection (EutelSat) popular • 1000 asymmetric/receive-only satellite Internet users (DVB-MPEG2). • One GIX (NAP) is starting operation, with limited local backbone. Telecommunications, Networking, & Internet Internet •50 tier one (16 official), and 500 tier two ISPs. •Soon there will be up to 60 tier one ISPs. •User connection: Mainly Dial-up •Broadband: Hardly available •Many working coffee-Nets •Normal Leased lines Internet bandwidth available: 64 kbps~2 Mbps •Wireless Spread Spectrum local loops are popular. Telecommunications, Networking, & Internet Networking LAN WAN VPN Telecommunications, Networking, & Internet Iranian Companies • About 100 companies active in Networking • Their business activity include: – Network equipment import – Network design and implementation – Cabling • Market Value around $100 millions • Growth rate: 25% Networking Vendors & brands • Most popular Network equipment are: – Cisco – 3COM – D-Link – And a dozen others • Cisco is the major brand having a dozen distributors. • 3COM is the next. Software Production Services Software Government Authorities • High Council of Informatics (HCI) – The highest authority headed by a deputy of the deputy of the president – A part of Management & Planning Organization (MPO) – Not very active now • Supreme Council of ICT (SCICT) – Mainly responsible for Internet related issues – Responsible for running National ICT Agenda of Iran (NICTA) • High-Tech Industries Center (HTIC) – Responsible for industrial aspects of Software Industry – A part of Ministry of Industries & Mines Software Government Support • Government considers software as a point of focus. • Support of domestic production. • Financial support of software companies. • Government guarantees Iranian companies in outsourcing contracts. • Government promotes foreign investments in this field. • Tehran Software and IT Park (TSITP) is planning. Software Market Sectors • Business & Financial Solutions • Manufacturing Information Systems • Office Automation • Graphic & Design solutions • Engineering • Scientific • CBT Software Iranian Companies • More than 500 registered software companies. • Many more unregistered groups (3000 small computer companies). • Many are based in Tehran, Isfahan, Mashad, Tabriz, Rasht, and Shiraz. • The largest has 400 full time employees. • Many companies are very good candidates for direct or indirect investments. Software Qualifications • Eight companies have received ISO9001 and TickIT certification. More on the way. • All use known Methodologies mainly structured, and Object Oriented methodologies are popular. • Frameworks such as .NET & J2EE are getting popular • All of them have tracks of successful projects. Software Legal Issues • • • • • • • • • • • Software copyright law is ruled. This law protects all software that is 1st announced inside Iran. Foreign softwares are protected just through countries bilateral protocols. Joining the international conventions in the copyright to cover full protection of all software products is foreseen. The congress has approved joining the WIPO. The mentality and act of Iranian software companies is to respect the copyright law especially for their partners. Electronic/Digital signature law, adopted by the parliament. New Internet access limitation regulation announced in October 2001. Sub-committees for editing legal/criminal aspects of IT and ECommerce are working. National ICT strategic plan covering also the legal issues is under edition. Plan to put local Certificate Authority (CA) in place. Software Market Value • Main Customers are: – Government – Industries – Businesses • Market value is around $200 millions, excluding NICTA • Market potential is around $500 millions • 180 Mainframe computers. Software Market Growth • Government and industries’ attention to IT have raised the demand for software. • Growth rate is anticipated to be more than 100% • Iranian software companies are seeking for partnership with software technology companies to exploit the domestic Market. Software Banking and Trading a Sample market • 14 main banks with total of 12000 branches for retail banking. • 1000 ATM machines. • SWIFT & SCADA, as part of EDI are in use. • No serious Iranian currency credit cards yet. • 4 types of cash cards (Debit card) with limited use, and not compatible. • 500 stores with card readers. • Electronic/Digital signature law, adopted by the parliament. • Plan to put local Certificate Authority (CA) in place. Software B2C in Iran a Sample market • B2C sites are growing in Iran, some are getting popular. • B2C is the only E-Commerce option in the next 5 years, but with the following problems : • • • • Lack of local Credit card. Problem in free foreign currency exchange. No extended services on mobile phones. Still little Internet at homes. Software B2B in Iran a Sample market No such B2B in even near future because of : • Old fashion ways of wholesale. • Lack of improved and modern container delivery. • Many obstacles, which prolongs the whole process of order and delivery. • Lack of legally accepted auto-bid/tender algorithms and procedures for the net. Iran registered computer companies human resource indices Employee’s field of study Percentages 19% 18% Telecomunication Software eng 12% Hardware eng 51% Related Fields Iran registered computer companies human resource indices Employee’s educational levels proportion 10% 37% 44% 9% Diploma AA BSc. MSc. & Phd The employee’s status of registered computer companies Based on degrees and field of study November 2002 6000 5000 4000 Base Major Related Miscelaneous Totals 3000 2000 1000 0 AA BS MS Phd 3500 3000 2500 Software 2000 Telecomunication 1500 Electeronics 1000 Total 500 0 AA BS MS PHD Iran registered computer companies human resource indices Proportion of educational level in Iran universities for ICT 7% 17% AA BSc. MSc. Phd 30% 46% Iran registered computer companies human resource indices 6000 ICT Graduated from 1992 to 2000 (Each Year) 5000 4000 3000 2000 1000 0 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 Iran registered computer companies human resource indices Gender of ICT Graduated 30% male Female 70% Salary of IT Experts • • • • • • • • • • • Project Manager Technical Manager QA Manager System Analyzer System Designer programmer Operator Network Expert ISP Expert Database Expert Hardware MIN. 625 375 375 375 375 250 100 250 250 250 250 MAX. 2500 1875 1875 1500 1250 1250 250 1250 1250 1250 750 (US Dollar/ month ) Iran’s 3rd Five-year development plan (1999-2004) •15 Millions (1.4 Million/Y) fixed telephone lines. • 10 Millions mobile phone users. TCI post paid: 3 Million. TCI pre-paid: 2 Million. Two new independent operators : 5 Millions. • 15 Millions Internet users. • International fiber optic links to Internet : (TAE ,FLAG, SE-ME-WE-3). Iran’s 3rd Five-year development plan (1999-2004) •Four national fiber optic backbone loops. • Telecom Deregulation: fixed phone operator. Mobile phone operator. Pager. Data communications. Improved Frequency regulatory body RA). Iran’s 3rd Five-year development plan (1999-2004) Iran trade point and information center services start. • National plan for schools Internet access. • A centralized budget of 80 Million USD/Y is to spend in IT. • ISDN. • Full coverage of SS7 signaling. • 40,000 VSATs. • To remove all none-tariff obstacles. • To raise the non-oil export national income. • To remove multi rate foreign currency exchange. TAKFA – the national Iranian National ICT Agenda (NICTA) • Iranian government has decided to heavily invest in ICT application in Iran. • NICTA is the approved framework. • 1% of the National budget is promoted to be spent for IT applications. Iranian Government Plans & Actions TAKFA’s Main Initiatives • • • • • • • Development of ICT in commerce (eCommerce, eBanking, etc.) Move toward eGovernment (work automation, eServices, eDemocracy, etc.) Application of ICT in schools and workforce development (at primary & secondary schools, and vocational training institute) Application of ICT in Higher Education (Medical, Engineering, Social Sciences, Arts, etc.) ICT Development in Social services (Social security, health, etc.) ICT Development in Cultural issues (Farsi writing and usage, Art, Culture, etc.) ICT SME development (Tech Parks, Incubators, etc.) Iranian Government Plans & Actions TAKFA’s Framework Infra structure Employment & Industry NICTA HRD, culture and social Commerce & economical services Gov. services Culture Electronic In government digital environment Iranian Government Plans & Actions The Past • ICT important but not a priority • Some sector IT master plans but, old and out dated • Rare specific budget allocation at national level • Several authorities with different and sometimes overlapping responsibilities • Not enough authority Iranian Government Plans & Actions The Present • The first national IT application plan is compiled • A big shock to the internal Market, a boom! • Its execution started a year ago • Could attract the notice of the top executive body of the government to IT • Still the problem of main Authority • More initiative rather than a “Plan” • Little capacity to assess and select the projects properly Iranian Government Plans & Actions Government Priorities • ICT centric development of the country • Creation of new jobs • Encouraging foreign investment and involvement • Promotion of non-oil exports • Development of high-tech industries تکفا برنامه توسعه کاربری فناوری اطالعات Iranian Government Plans & Actions TAKFA’s main Points • Allocating specific budget for ICT projects • Easing regulations to reflect ICT needs, and to ease awarding contracts. • Assigning a top country level authority. • Creating a hierarchy of ICT councils in all ministries. Iranian Government Plans & Actions TAKFA Budget (2002) Fiscal year 1381 (ending March 2003) • Direct Assignment of $85M for existing national ICT projects. • Allowing to use $60M of job creation budget to be spent in ICT projects • Promoting the use of 1% (around $900M) of development budget to be spent in ICT projects Iranian Government Plans & Actions TAKFA Budget (2003) • Direct Assignment of $130M for existing national ICT projects. • 2% (about $450M) of current budget MUST be spent in ICT projects • A total of $580M must be spent. • Use of $60M of job creation budget is allowed. • Ministries are promoted to spend more for ICT projects (from their own development budget). تخمین نتایج آتی تکفا -5-7تگر :تحليل گرهای رايانه ای (تکفا) الف -مفروضات اندازه پروژه كوچك متوسط بزرگ بسياربزرگ نفر/ماه خريد (ميليون تومان) توليد (ميليون تومان) 15 50 100 1000 20 100 450 1000 40 150 700 1500 طرح تكفا برنامه توسعه و كاربردي فناوري ارتباطات و اطالعات در ايران است كه طبق پيش بيني قرار است طي 5سال باهزينه اي حدود 700 ميليارد تومان پياده سازي شود. تذكر :اين جدول مقاديرپيش فرض را نشان مي دهد درنظريه كارشناس ي درج شده درسامانه اين مقاديربعنوان مقاديركمينه با توجه به اندازه پروژه بهنگام شده اند. ب -تحليل تجميعي اطالعات : -1انواع سامانه ها : الف -سامانه اطالعاتي %57 ب -طرح مطالعاتي %22 پ -تامين تجهيزات سخت افزار %16 ت -آموزش %5 -5منابع تهيه : الف -داخل %75 ب -خارج %25 -2تشخيص كارشناس ي گونه سامانه ها : الف -اختصاص ي %62 ب -عمومي %38 -6سهم قابل قبول فناوري اطالعات درسازمان ها (در رابطه با توان جذب) : الف -معمولي ( %5بودجه عمراني) %58 ب -زياد ( %10بودجه عمراني) %31 پ -كم ( %3بودجه عمراني ) %11 -3تخمين ميزان انواع براساس اندازه سامانه ها : الف -بزرگ %37 ب -متوسط %29 پ -بسيار بزرگ %27 ت -كوچك %7 -7برآورد هزينه تهيه : الف -كمينه 20ميليون تومان ب -بيشينه 75ميليارد تومان پ -ميانگين 5ميلياردو 57ميليون 390هزار تومان ت -جمع 581ميليارد و 600ميليون تومان -4نحوه تهيه : الف -خريد %28 ب -توليد %72 -8نفر/ماه تخميني توليد : الف -كمينه 15نفر/ماه ب -بيشينه 75000نفر/ماه پ -ميانگين 3863نفر/ماه ت -جمع 444.248نفر/ماه پ -طبقه بندي پروژه ها : تعدادو عناوين پروژه هاي طرح تكفا ( 115پروژه درهفت گروه ) شامل : عنوان هاي طرح راهبردي 25 ) 1پروژه درطرح راهبردي ( دولت الكترونيكي ) 16 )2پروژه درطرح راهبردي ( گسترش كاربرد فناوري ارتباطات اطالعات در آموزش و پرورش و توسعه مهارت ديجيتالي نيروي انساني كشور ) 6 )3پروژه درطرح راهبردي ( توسعه صنعت ICTازطريق پايه گذاري SMEدرپارك هاي تحقيقاتي ) 17 )4پروژه درطرح راهبردي ( گسترش كاربرد فناوري ارتباطات و اطالعات در اقتصاد ،بازرگاني و تجارت ) 13 )5پروژه درطرح راهبردي ( گسترش كاربرد فناوري ارتباطات و اطالعات در آموزش عالي و آموزش كشور پزشكي) 19 )6پروژه درطرح راهبردي ( گسترش كاربرد فناوري ارتباطات و اطالعات درتوسعه خدمات اجتماعي) 19 )7پروژه درطرح راهبردي ( گسترش كاربرد فناوري ارتباطات و اطالعات در قلمرو فرهنگ ،هنرو تقويت خط و زبان فارس ي درمحيط رايانه اي ) ت -نحوه دسترس ي شامل : 32 )1پروژه ( خريد ) 6پروژه داخلي با هزينه 22.600م-ت توسط 213.61نفر/ماه 26پروژه خارجي با هزينه 302.590م-ت توسط 161.255نفر/ماه 83 )2پروژه ( توليد ) 81پروژه داخلي با هزينه 253.410م-ت توسط 261.205نفر/ماه 2پروژه خارجي با هزينه 3.000م-ت توسط 427نفر/ماه ) 3دركل از 115پروژه 87پروژه داخلي با هزينه 276.010م-ت توسط 282.566نفر/ماه 28پروژه خارجي با هزينه 305.590م-ت توسط 161.682نفر/ماه ث -اجراي 115پروژه طرح تكفا خريد ( 32پروژه ) داخلي توليد ( 83پروژه ) خارجي خارجي داخلي 6پروژه باهزينه 22600م-ت 26پروژه باهزينه 302.590م-ت 2پروژه باهزينه 3000م-ت 81پروژه باهزينه 253.410م-ت توسط 21.361نفر/ماه توسط 161.255نفر/ماه توسط 427نفر/ماه توسط 261.205نفر/ماه 28پروژه با هزينه 305.590م-ت توسط 161.682نفر /ماه 87پروژه باهزينه 276.010م-ت توسط 282.566نفر/ماه 32پروژه خريد باهزينه 325.190م-ت توسط 182.616نفر/ماه 83پروژه باهزينه 256.410م-ت توسط 261.632نفر/ماه 115پروژه باهزينه 581.600م-ت توسط 444.248نفر/ماه ج -انواع پروژه هاي طرح تكفا : تعداد انواع سامانه نيروي انساني الزم (نفر/ماه) بودجه اجرا (م-ت) بودجه سازماني (م-ت) بودجه سهم فناوري اطالعات (م-ت) سامانه اطالعاتي 66 271.332 340.770 383.598 22.750 طرح مطالعاتي 25 11.970 40.780 98.796 7.405 تامين تجهيزات سخت افزار 18 158.483 193.650 92.170 6.928 آموزش 6 2.463 6.400 35.722 3.477 جمع 115 444.248 581.600 610.286 40.560 -5-7تگر :تحليل گرهای رايانه ای (نظام جامع اطالعات کشور) الف -مفروضات: اندازه پروژه كوچك متوسط بزرگ بسياربزرگ نفر/ماه 15 50 100 1000 خريد 20 100 450 1000 توليد (ميليون تومان) 40 150 700 1500 اندازه پروژه پروژه ملي كوچك پروژه ملي متوسط پروژه ملي بزرگ نفر/ماه 4200 7000 12500 خريد 5000 9000 15000 تذكر :اين جدول مقاديرپيش فرض را نشان مي دهد درنظريه كارشناس ي درج شده درسامانه اين مقاديربعنوان مقاديركمينه با توجه به اندازه پروژه بهنگام شده اند. توليد (ميليون تومان) 7000 12000 20000 ث -اجراي 291پروژه سازماني خريد ( 135پروژه ) داخلي توليد ( 156پروژه ) خارجي خارجي داخلي 84پروژه باهزينه94247م-ت 51پروژه باهزينه 147635م-ت 1پروژه باهزينه 15م-ت 155پروژه باهزينه221310م-ت توسط 75170نفر/ماه توسط.96610نفر/ماه توسط 15نفر/ماه توسط .113245نفر/ماه 52پروژه باهزينه 147650م-ت توسط96625نفر/ماه 239پروژه باهزينه315557م-ت توسط 188415نفر/ماه 135پروژه خريد باهزينه 241882م-ت توسط 171780نفر/ماه 156پروژه باهزينه 221325م-ت توسط 13260نفر/ماه 291پروژه باهزينه 463207م-ت توسط 285040نفر/ماه نتایج ادواری تکفا گزارش تکفا Iranian Government Plans & Actions The Consensus • Consensus on ICT based development of the country. • All Government and System sectors have priority for ICT • Foreign Investment and involvement is encouraged. Iranian Government Plans & Actions Projects defined • A total of 1650 projects are officially submitted to the SCICT • Total value: over $2.7B • Most for: – Consultancy – Concept development and feasibility study – Creating organizations’ Infrastructure – Completion of projects defined in the past – Human resource development Iranian Government Plans & Actions Players • Work should be done by the private sector. • Foreign Companies are invited to help. • All national projects MUST be awarded to consortiums of Iranian & Foreign Companies. • In each case one or more Iranian companies will be involved. • Tehran Software and IT Park will be a facilitator and prime gateway Iranian Government Plans & Actions Market Expansion كشورIT پيش بيني حجم بازار 16 14 12 10 8 ميليارد دالر 6 4 2 0 1381 خوش بينانه 1382 1383 سال بدبينانه 1384 1385 1386 • Spill over effect in different market sectors • Market Growth of up to 60% • An estimated 2003 market value of $2.5B Iranian Government Plans & Actions Market Expansion b$ Optimistic Pessimistic Year • Spill over effect in different market sectors • Market Growth of up to 60% • An estimated 2003 market value of $2.5B Tehran Software and IT Park project Four Phases of TSITP Project • Planning and Basic Design • Design Development and Plan Implementation • Construction and Commissioning • Operation and Maintenance Tehran Software and IT Park project • Planning Started on Oct. 2002 • In-house studies for Phase One is almost finished • Center, Park, Polis . . . • Workshops with some International Consulting Firms done • • Some ground sites are short-listed RFP for Selecting the Main Consulting Firm for the Strategic Planning and Basic Design phase, and a long term collaboration is prepared • An international Tender to select the Main Consulting Firm is on the way soon • A pilot project (Center) is on hand Why Iran? Iran’s general advantages • General advantages: •Very young generation nation. •Highly educated . •Continuous economic growth of %5. •Low wage software developer. •Expert in localizing foreign software. •Big Market •Big neighboring countries potential markets Iran’s general weaknesses • Oil export as main source of national income. • Decisions are still made not on the base of information. • Industries/Businesses are not improved, so have not presented the demand for data yet. • Government is the main contractor, not ready for E-Procurement. • Still some non-tariff obstacles. • Hard to change line of business (Legacy jobs). • Lack of broad band end to end communication infrastructure. • Old and noisy copper local loops. • Still PTT owned monopoly firms, with weak services. • Old fashion banking system. • Lack of credit validation and certificate authority bureaus (CA). • Very high bank loan and financing rates. Iranian Government Plans & Actions Our Market The world is experiencing recession, but we have: • A very rapidly growing market in all IT sectors. • Potential yearly value of $ 2.5 billions • Mainly unexploited by foreign companies. • A good place for investment and outsourcing. متولیان بخش فاوا در ایران • • • • • • مرکز آمارایران سازمان برنامه و بودجه کمیسیون ملی انفورماتیک شورای عالی انفورماتیک کشور شورای عالی اطالع رسانی وزارت ارتباطات و فناوری اطالعات انجمن های علمی و صنفی فاوا در ایران • • • • • انجمن انفورماتیک ایران انجمن کامپیوتر ایران انجمن صنفی شرکتهای انفورماتیک انجمن فناوری اطالعات و ارتباطات ایران انجمن ملی فناوری اطالعات