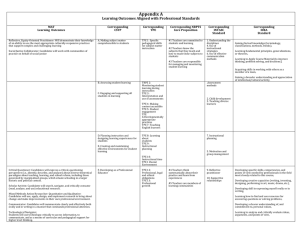
Preliminary Single Subject Biennial Report 2014
advertisement

Due Summer/Fall 2014) Academic Years 2012-2013 and 2013-14 Institution Michael D. Eisner College of Education CSU Northridge Date report is submitted November 15, 2014 Indigo due on September 15, 2014 Red and Yellow due November 15, 2014 Program documented in this report Single Subject Preliminary Credential Name of Program Single Subject Preliminary Credential Please identify all delivery options through Traditional, Intern, ACT (Accelerated which this program is offered Collaborative Teacher preparation program), Freshman Year Integrated (Traditional, Intern, Other) Program, Junior Year Integrated Program Credential awarded Single Subject Preliminary Credential Is this program offered at more than one site? No If yes, list all sites at which the program is offered Program Contact Julie Gainsburg Title Dept. Chair Phone # 818 677 2580 E-Mail Julie.gainsburg@csun.edu SECTION A – CREDENTIAL PROGRAM SPECIFIC INFORMATION PART I – Contextual Information The Single-Subject Program at California State University, Northridge (CSUN) offers Single-Subject credentials in Art; Business; English Language Arts; World Languages, including American Sign Language; Health Science; Home Economics; Music; Physical Education; Mathematics/Foundational Mathematics; Physical Education; Science (General/Specialization in Biology, Chemistry, Physical Science, Geosciences/Foundational); and Social Science. Our five Single-Subject Credential Program pathways are based on theoretical and scholarly understandings of teacher preparation and are aligned with the Unit’s Conceptual Framework [www.csun.edu/coe]. As a set, the pathways meet the varying needs of our candidates. Table 1 briefly describes the five pathways and shows enrollment and completion data for the three years reported. Program Changes Since 2011 Through Fall 2011, Candidates in the Traditional and Intern pathways have had the option of earning a BCLAD (Bilingual Cross-Cultural Language and Academic Development) Credential. Since Fall 2011, we have offered the Bilingual Authorization (BILA) via two routes: a “precredential” route, by which current single-subject credential candidates simultaneously earn the BILA, and a “post-credential” route, by which previously credentialed teachers (by CSUN or other institutions) add the BILA. BCLAD/BILA candidates are fluent in Spanish, Armenian, or Korean, as well as in the cultures associated with the language of emphasis. Details about the requirements and numbers of candidates in these two routes can be found in the attached BILA report. 2 Table 1: Program-Specific Candidate Information: Pathway Descriptions and Enrollment/Completion Data Program Pathway Note: All pathways include CLAD competencies. Traditional Single-Subject Credential Program (36 sem. units): A post-baccalaureate program for full- or part-time pre-service candidates. Qualified, fulltime candidates may complete the program in 2 semesters, but many take 3 or more semesters. 2012-2013 Candi- Comdates pleters 2013-14 Candi- Comdates pleters 71 54 Accelerated Collaborative Teacher (ACT) Preparation Program (36 sem. units): A 1year, field-based program for single-subject, multiple-subject, and education-specialist credential candidates. This post-baccalaureate, 5th-year program is offered in collaboration with Local District 2 of the Los Angeles Unified School District. Single-subject ACT candidates enroll in the same secondary education (SED) methods and field-experience courses and some of the same foundation classes as candidates in other SED pathways but enroll in special-education and equity/diversity classes with multiplesubject and special-education ACT candidates. 184 20 Single-Subject University Intern Program (36 sem. units): A 2-year, post-baccalaureate program for candidates hired and teaching fulltime in public secondary schools and who have met subject-matter competency and other requirements. CSUN has Intern Programs in cooperation with LAUSD and several other districts in the area. Traditional candidates may transfer to the Intern Program after completing one or more semesters of coursework and sometimes even after the initial field experience, SED 554. 10 8 Four-Year Integrated (FYI) Teacher Credential Program (124-125 sem. units): An undergraduate program admitting freshmen who enter CSUN prepared for college-level mathematics and writing classes. FYI enables an undergraduate to earn a B.A. Degree and a Preliminary Single-Subject credential in 4 years, in English or Math only. 6 3 Junior-Year Entry Integrated (JYI) Teacher Credential Program (Math - 69 sem. units; English - 73 sem. units following GE/lower-division course completion): An integrated undergraduate program admitting juniors, including community-college transfers. Entering students have completed all General Education requirements and lower-division English or Math courses required by the major. JYI enables an undergraduate to earn a B.A. Degree and a Preliminary Single-Subject Credential in English or Math in 4 years. 7 3 3 Since 2012, when the State Board of Education adopted the Common Core State Standards (CCSS) for K-12 instruction, our program faculty members have actively sought self-education and training in the CCSS and their implications for teacher education. Indeed, a few faculty members have been deeply involved in providing professional development and training for secondary teachers and teacher educators, locally and statewide. Credential-course instructors have been modifying their course material and assignments to help candidates address the CCSS with secondary pupils. Beginning in Spring 2014, this effort has become more formal, with same-course instructors collaborating on CCSS-aligned syllabus changes. Science credential courses have also begun to be modified to reflect the Next Generation Science Standards, adopted by the state in 2013. As there is much competition among teacher-education programs in the greater Los Angeles area, we continue to seek ways to make our pathways attractive to potential candidates, including through the use of technology. Currently, the SED offers a fully online section of SED 514, Computers in the Instructional Program, and hybrid sections of, SED 521, Literacy and Learning in Multiethnic Secondary Schools, SED 525ESL, Methods of Teaching English as a Second Language, SED 529, Teaching English Learners in Multiethnic Classrooms, and SED 514 4 PART II – Candidate Assessment/Performance and Program Effectiveness Information Transition Points and Key Assessments Table 2 shows our Transition Point Matrix with key assessment measures. Descriptions of some key measures follow Table 2. Table 2: Transition Point Matrix for All Single-Subject Credential Program Pathways Transition Point Transition Point 1 Entry to Program Transition Point 2 Entry to Clinical Practice Transition Point 3 Exit from First Clinical Experience Transition Point 4 Exit from Clinical Practice Measure 1) Undergrad GPA* > 2.67 overall or > 2.75 in last 60 units 2) Subject matter competency (CSET exam or Subject Matter Program) 3) Applicant Interview 4) Dispositions Self Survey at Beginning 1) GPA > 3.0 in credential program courses, with no grade below C 2) GPA >2.75 in all post-BA courses 3) Basic Skills (CBEST) Passed 4) Writing Proficiency (UDWPE score >10, or pass composition course, or score > 41 on CBEST) 1) Student Teaching Progress Report 1) Student Teaching Evaluation 2) Teacher Performance Assessment (PACT Teaching Event) 3) Dispositions Self Survey at Conclusion Transition Point 5 Exit from Program 1) GPA > 3.0 in program courses 2) GPA > 2.75 in all post-BA courses 3) CSU Exit Survey (Completers’ Perceptions) Transition Point 6 Follow-Up 1) CSU Follow-Up Survey (Completers’ Perceptions) 2) CSU Follow-Up Survey (Employers’ Perceptions) * GPA calculated on a 4-point scale, with A = 4.0, A- = 3.7, B+ = 3.3, B = 3.0, etc. 5 Applicant Interview All Single-Subject applicants participate in the Applicant Interview conducted by a full- or part-time faculty member. For the Traditional, FYI, and JYI Pathways, this is a small-group interview with 3-7 Multiple- and Single-Subject program applicants responding to the interviewer and to one another. For the Single-Subject ACT and Intern applicants, the respective program director conducts an individual interview and provides beginning advisement. The formal interview protocol comprises 6 general items for discussion by the applicants, and an individual writing task. Candidates’ responses are then rated on a 4-point scale for 7 rubric items. The majority of these items are dispositional, focusing on areas such as commitment to diversity, commitment to professional growth, character, and personality. Verbal skills are also rated. Standardized Examinations Candidates may demonstrate subject-matter competency at admission (Transition Point 1) with passing scores on the California Subject Examination for Teachers (CSET) in the subject area. Also required for program entry (Transition Point 1) is an attempt to meet the Basic Skills Requirement (BSR), usually by attempting all sections of the California Basic Skills Test (CBEST). To enter the initial clinical experience (Transition Point 2), candidates must pass all sections of the CBEST or meet the BSR in another way. Many candidates use a score of 41 or higher on the CBEST Writing Test to establish Writing Proficiency, another requirement at Transition Point 2. Teaching Performance Measures Student Teaching/Intern field-based assessments provide critical data at Transition Points 3 and 4. Traditional, ACT, FYI, and JYI Single-Subject Pathways. Candidates in these pathways complete two semesters of student teaching. In the first assignment, SED 554, they begin with structured observations and working with small groups of pupils, then assume responsibility for planning and teaching one class period daily at Week 6 or 7 through the remainder of the school’s semester or track. The final assessment for SED 554 is the Student Teaching Progress Report, organized by the 13 Teaching Performance Expectations (TPEs) in 6 Domains reflecting the California Standards for the Teaching Profession. The university supervisor and the cooperating teacher each submit a Progress Report (Transition Point 3). In the final SED 555 field experience, candidates plan and teach 3 class periods daily and are on site for an additional class period, for the school’s entire semester or track. The final assessment for this experience is the Student Teaching Evaluation, also organized by the 13 TPEs and their 6 Domains but with more items than the Progress Report. The university supervisor and the cooperating teacher(s) each submit a Student Teaching Evaluation near the end of the assignment (Transition Point 4). 6 Single-Subject University Intern Program. Intern candidates who are hired and teaching fulltime at a public school complete two beginning field experiences with the support of a university coach (or supervisor) and a school-based support provider in SED 593 and SED 594. Support providers do not complete the Progress Report, and the beginning field-experience performance assessment data for Interns includes only the SED 594 Intern Progress Report by the university supervisor (Transition Point 3). The final Intern field experience occurs in SED 555I, when both the university supervisor and cooperating teacher(s) complete the Intern Evaluation (Transition Point 4). The Student Teaching and Intern Progress Reports for SED 554 and SED 594 are identical evaluations. Similarly, the Student Teaching and Intern Evaluations for SED 555 and SED 555I are the same. This enables comparisons of performance across program pathways. Both the Progress Report and the Evaluation use a 5-level rubric, albeit with different sets of level descriptors. The Progress Report score levels are 1-2 (Initial Competency), 3-4 (Intermediate Competency), and 5 (Advanced Competency), while the Evaluation score levels are 1 (Unsatisfactory), 2 (Marginal), 3 (Satisfactory), 4 (Strong), and 5 (Outstanding). Required minimal scores for passing are established and clearly communicated to candidates, supervisors, and cooperating teachers. University supervisor workshops are held each January to address supervision issues and promote fair, unbiased, and reliable administration of these performance assessments. Activities based on videotapes and case studies are among those that have been used in past years. Cooperating teacher workshops are also held once or twice annually, and part of these meetings is typically devoted to exploring and clarifying these assessments. Our selected Single-Subject TPA, a key measure at Transition Point 4, is the Performance Assessment for California Teachers (PACT) Teaching Event. We have maintained a stable pool of about 33 assessors, drawn from full- and part-time faculty from the SED and related departments (e.g., Art) who work with the single-subject credential program as instructors and/or supervisors. All PACT Teaching Events are scored by this CSUN pool, except in rare cases where adjudication is needed in a subject with only two assessors. All CSUN assessors were initially trained and now annually recalibrate according to PACT specifications. Calibration is also maintained by assigning a minimum of 15% of the Teaching Events to be read by two (or more) assessors. When assessors of double-scored Teaching Events diverge on their scores to an extent that exceeds PACT calibration standards, these assessors discuss the discrepancies with the SED’s Lead Scorer of the subject to try to resolve the differences. Similarly, as per PACT policy, when an assessor fails to recalibrate on PACT’s annual benchmark, the SED’s Lead Scorer for the subject works with the assessor to try to resolve the discrepancies and clarify the rubrics. (If a Lead Scorer fails to recalibrate, he or she works with a trainer from SCALE.) Less than a third of our assessor pool did not initially recalibrate each of the years in this report: 8 did not recalibrate in 2012; 10 in 2013, and 7 in 2014. All were remediated as described. 7 Surveys Single-Subject candidates complete the Dispositions Survey in the first semester of enrollment (Transition Point 1) and near the end of their final field experience (Transition Point 4). Items address four dispositional areas: 1) Ethical behavior toward others, 2) High expectations for all, 3) Collaboration with peers and other professionals, and 4) Professional behavior. The survey has 17 items, with response selections ranging from 1 (Never) to 5 (Always). The CSU Exit Survey is a system-wide survey developed by the Chancellor’s Office of the California State University (CSU) and completed online by credential candidates at the end of their program (Transition Point 5). The CSU Exit Survey asks questions regarding candidates’ perceptions of their pre-service preparation and support, via items that clearly reflect state credential-program standards. Responses are submitted online, and scores for each item are reported as the percentages of respondents who felt Well Prepared, Adequately Prepared, Somewhat Prepared, or Not Prepared; 80% Well or Adequately Prepared has been set as the CSUN benchmark. The CSU Follow-Up Survey is also administered system-wide by the CSU to program completers/teachers one year after finishing the program (Transition Point 6) and by their supervisors/employers, allowing a comparison. Scores are reported as percentages of those who felt or believed the teachers to be Well Prepared, Adequately Prepared, Somewhat Prepared, or Not Prepared, again with 80% Well or Adequately Prepared as the CSUN benchmark. Items are similar to the CSU Exit Survey Items so that the Exit Survey and Follow-Up Survey responses from candidates can be compared. 8 Aggregated Data In this section we report the data from 5 measures from Transition Points 4 – 6 (Table 3) for the years 2011-2014. Table 3: Measures Yielding Data for This Report Transition Point Measure Transition Point 4 Exit from Clinical Practice Student Teaching Evaluation Teacher Performance Assessment (PACT Teaching Event) Transition Point 5 Exit from Program CSU Exit Survey (Completers’ Perceptions) Transition Point 6 Follow-Up CSU Follow-Up Survey (Completers’ Perceptions) CSU Follow-Up Survey (Employers’ Perceptions) Student Teaching Evaluation On the following pages, we provide the means for candidates’ scores on every item from the Student Teaching Evaluation, from both the university supervisor and cooperating teacher. Tables show the means for all five pathways for the school year 2011-12, followed by all tables for 2012-13 and then 2013-14. Please note that the 2013-14 tables are in a different format, with the items grouped by Domain. 9 Student Teaching Progress Report Single Subject Credential Traditional Fall 2012 and Spring 2013 Fall 2012 Supervising Teacher University supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2013 Supervising Teacher University supervisor Mean N Mean N 3.94 3.63 3.84 3.92 3.89 51 51 50 51 19 4.04 3.77 3.88 4.02 4.33 48 48 48 48 3 4.26 3.74 3.89 3.88 4.25 27 27 27 26 8 4.10 3.62 3.83 4.21 3.75 29 29 29 29 4 1.c, 1.d 3.67 3.65 3.61 3.76 3.64 51 51 49 50 50 3.73 3.79 3.69 3.72 3.57 48 48 48 46 44 3.93 3.85 3.88 3.85 3.70 27 27 26 26 27 3.86 3.66 3.69 3.61 3.60 29 29 29 28 25 1.b 3.78 51 3.72 46 3.74 27 3.83 29 1.b, 1.c 3.69 48 3.83 46 3.72 25 3.69 29 1.b. 1.c 3.52 50 3.71 38 3.59 27 3.82 22 1.b 3.78 51 3.91 47 3.96 27 3.86 29 1.b 3.67 51 3.75 48 3.81 27 3.93 29 1.b, 1.g 3.75 51 3.73 48 3.70 27 3.66 29 1.b 3.46 50 3.51 43 3.62 26 3.67 27 1.c 1.c 3.53 3.98 51 51 3.83 4.00 48 48 3.48 3.96 27 27 3.69 4.07 29 29 1.c 3.82 51 3.74 47 3.81 27 4.04 26 5.4 Maintains good rapport with students (TPE 11) 1.g 6.1 Maintains good rapport with faculty and staff (TPE 12) 1.g 6.2 Meets commitments and deadlines (TPE 12) 1.g 6.3 Meets professional, legal, and ethical obligations (TPE 12) 1.g 4.20 4.20 3.84 4.02 51 50 51 50 4.15 4.13 3.90 4.02 48 47 48 48 4.33 4.37 4.19 4.26 27 27 27 27 4.43 4.48 4.21 4.21 28 27 29 29 Teaching Performance Expectation NCATE Standard 1.1 Knows subject matter (TPE 1) 1.a 1.2 Demonstrates subject-specific pedagogical knowledge and skills (TPE 1) 1.b 1.3 Teaches to California academic content standards (TPE 1) 1.a, 1.b 1.4 Communicates effectively in oral and written English (TPE 1) 1.b 1.5 Communicates effectively in the BCLAD language (TPE 1, BCLAD only; leave blank for non-BCLAD candidates) 1.b 2.1 Monitors student learning during instruction (TPE 2) 1.d 2.2 Paces instruction appropriately and re-teaches content when necessary (TPE 2) 1.d 2.3 Uses multiple means of assessment (TPE 3) 1.d 2.4 Gives students meaningful feedback on assignments and assessments (TPE 3) 1.d 3.1 Learns about students prior knowledge, background, and interests, and plans lessons that draw on these (TPE 8) 3.2 Prepares complete and sequential lesson plans with a progression of learning tasks and assessments that build understanding of content (TPE 9) 3.3 Plans vocabulary, reading, writing, speaking, and listening instruction for content area learning (TPE 9) 3.4 Plans instruction that addresses academic language features of learning tasks and California English Language Development Standards (TPE 9) 4.1 Provides opportunities and time for students to practice and apply what they have learned (TPE 4) 4.2 Uses an effective mix of instructional activities to engage students in multiple learning modalities and to make content accessible (TPE 5) 4.3 Establishes and communicates developmentally appropriate and challenging academic expectations (TPE 6) 4.4 Differentiates instruction to meet the needs of students from diverse backgrounds, including English Learners and students with special needs (TPE 7) 5.1 Maximizes instructional time, managing classroom routines and transitions (TPE 10) 5.2 Creates a positive climate for learning and student discussion, maintaining clear expectations for academic and social behavior (TPE 11) 5.3 Creates an inclusive learning environment for students with diverse learning needs and backgrounds (TPE 11) 10 6.4 Reflects on, analyzes, and evaluates own teaching (TPE 13) 1.g 3.94 50 4.02 48 4.11 27 4.31 29 Notes: 1=Unsatisfactory, 2=Marginal, 3=Satisfactory, 4=Strong, 5=Outstanding 11 Student Teaching Progress Report Single Subject Credential Intern Fall 2012 and Spring 2013 Teaching Performance Expectation NCATE Standard Fall 2012 University supervisor Mean N Spring 2013 University supervisor Mean N - - 4.80 4.80 4.60 4.60 . 5 5 5 5 0 1.c, 1.d - - 4.60 4.80 4.60 4.00 4.00 5 5 5 3 5 1.b - - 4.40 5 1.b, 1.c - - 4.40 5 1.b. 1.c - - 4.20 5 1.b - - 4.80 5 1.b - - 4.80 5 1.b, 1.g - - 4.60 5 1.b - - 4.20 5 1.c 1.c - - 4.40 4.60 5 5 1.c - - 4.40 5 5.4 Maintains good rapport with students (TPE 11) 1.g 6.1 Maintains good rapport with faculty and staff (TPE 12) 1.g 6.2 Meets commitments and deadlines (TPE 12) 1.g 6.3 Meets professional, legal, and ethical obligations (TPE 12) 1.g - - 4.60 4.60 4.60 4.60 5 5 5 5 1.1 Knows subject matter (TPE 1) 1.a 1.2 Demonstrates subject-specific pedagogical knowledge and skills (TPE 1) 1.b 1.3 Teaches to California academic content standards (TPE 1) 1.a, 1.b 1.4 Communicates effectively in oral and written English (TPE 1) 1.b 1.5 Communicates effectively in the BCLAD language (TPE 1, BCLAD only; leave blank for non-BCLAD candidates) 1.b 2.1 Monitors student learning during instruction (TPE 2) 1.d 2.2 Paces instruction appropriately and re-teaches content when necessary (TPE 2) 1.d 2.3 Uses multiple means of assessment (TPE 3) 1.d 2.4 Gives students meaningful feedback on assignments and assessments (TPE 3) 1.d 3.1 Learns about students prior knowledge, background, and interests, and plans lessons that draw on these (TPE 8) 3.2 Prepares complete and sequential lesson plans with a progression of learning tasks and assessments that build understanding of content (TPE 9) 3.3 Plans vocabulary, reading, writing, speaking, and listening instruction for content area learning (TPE 9) 3.4 Plans instruction that addresses academic language features of learning tasks and California English Language Development Standards (TPE 9) 4.1 Provides opportunities and time for students to practice and apply what they have learned (TPE 4) 4.2 Uses an effective mix of instructional activities to engage students in multiple learning modalities and to make content accessible (TPE 5) 4.3 Establishes and communicates developmentally appropriate and challenging academic expectations (TPE 6) 4.4 Differentiates instruction to meet the needs of students from diverse backgrounds, including English Learners and students with special needs (TPE 7) 5.1 Maximizes instructional time, managing classroom routines and transitions (TPE 10) 5.2 Creates a positive climate for learning and student discussion, maintaining clear expectations for academic and social behavior (TPE 11) 5.3 Creates an inclusive learning environment for students with diverse learning needs and backgrounds (TPE 11) 12 6.4 Reflects on, analyzes, and evaluates own teaching (TPE 13) - 1.g - 4.80 5 Notes: 1=Unsatisfactory, 2=Marginal, 3=Satisfactory, 4=Strong, 5=Outstanding Student Teaching Progress Report Single Subject Credential ACT Fall 2012 Teaching Performance Expectation NCATE Standard Fall 2012 Supervising Teacher University supervisor Mean N Mean N 4.17 3.92 4.42 4.25 4.20 12 12 12 12 5 4.17 3.94 4.17 4.28 4.00 18 18 18 18 1 1.c, 1.d 4.25 3.83 3.83 4.00 3.67 12 12 12 12 12 3.89 4.00 3.59 3.61 3.56 18 18 17 18 16 1.b 4.08 12 4.28 18 1.b, 1.c 3.83 12 4.00 18 1.b. 1.c 4.00 11 3.61 18 1.b 4.17 12 4.17 18 1.b 4.17 12 4.28 18 1.b, 1.g 3.92 12 3.89 18 1.b 3.75 12 3.61 18 1.c 1.c 3.58 4.08 12 12 3.89 4.17 18 18 1.c 4.25 12 3.67 18 5.4 Maintains good rapport with students (TPE 11) 1.g 6.1 Maintains good rapport with faculty and staff (TPE 12) 1.g 4.33 4.55 12 11 4.39 4.28 18 18 1.1 Knows subject matter (TPE 1) 1.a 1.2 Demonstrates subject-specific pedagogical knowledge and skills (TPE 1) 1.b 1.3 Teaches to California academic content standards (TPE 1) 1.a, 1.b 1.4 Communicates effectively in oral and written English (TPE 1) 1.b 1.5 Communicates effectively in the BCLAD language (TPE 1, BCLAD only; leave blank for non-BCLAD candidates) 1.b 2.1 Monitors student learning during instruction (TPE 2) 1.d 2.2 Paces instruction appropriately and re-teaches content when necessary (TPE 2) 1.d 2.3 Uses multiple means of assessment (TPE 3) 1.d 2.4 Gives students meaningful feedback on assignments and assessments (TPE 3) 1.d 3.1 Learns about students prior knowledge, background, and interests, and plans lessons that draw on these (TPE 8) 3.2 Prepares complete and sequential lesson plans with a progression of learning tasks and assessments that build understanding of content (TPE 9) 3.3 Plans vocabulary, reading, writing, speaking, and listening instruction for content area learning (TPE 9) 3.4 Plans instruction that addresses academic language features of learning tasks and California English Language Development Standards (TPE 9) 4.1 Provides opportunities and time for students to practice and apply what they have learned (TPE 4) 4.2 Uses an effective mix of instructional activities to engage students in multiple learning modalities and to make content accessible (TPE 5) 4.3 Establishes and communicates developmentally appropriate and challenging academic expectations (TPE 6) 4.4 Differentiates instruction to meet the needs of students from diverse backgrounds, including English Learners and students with special needs (TPE 7) 5.1 Maximizes instructional time, managing classroom routines and transitions (TPE 10) 5.2 Creates a positive climate for learning and student discussion, maintaining clear expectations for academic and social behavior (TPE 11) 5.3 Creates an inclusive learning environment for students with diverse learning needs and backgrounds (TPE 11) 13 6.2 Meets commitments and deadlines (TPE 12) 1.g 6.3 Meets professional, legal, and ethical obligations (TPE 12) 1.g 6.4 Reflects on, analyzes, and evaluates own teaching (TPE 13) 1.g 4.27 4.27 4.25 11 11 12 4.06 4.22 4.17 18 18 18 Notes: 1=Unsatisfactory, 2=Marginal, 3=Satisfactory, 4=Strong, 5=Outstanding Student Teaching Progress Report Single Subject Credential FYI Fall 2012 Teaching Performance Expectation NCATE Standard 4.00 3.67 3.67 3.33 . 3 3 3 3 0 3.67 3.67 4.00 3.33 . 3 3 3 3 0 1.c, 1.d 3.33 3.00 3.33 3.33 3.67 3 3 3 3 3 3.00 3.00 3.33 3.00 3.33 3 3 3 3 3 1.b 3.00 3 3.33 3 1.b, 1.c 3.67 3 3.67 3 1.b. 1.c 3.67 3 3.67 3 1.b 3.67 3 4.00 3 1.b 3.67 3 3.67 3 1.b, 1.g 3.33 3 3.33 3 1.b 3.33 3 3.00 3 1.c 1.c 3.33 3.33 3 3 3.33 3.00 3 2 1.c 3.33 3 3.33 3 1.1 Knows subject matter (TPE 1) 1.a 1.2 Demonstrates subject-specific pedagogical knowledge and skills (TPE 1) 1.b 1.3 Teaches to California academic content standards (TPE 1) 1.a, 1.b 1.4 Communicates effectively in oral and written English (TPE 1) 1.b 1.5 Communicates effectively in the BCLAD language (TPE 1, BCLAD only; leave blank for non-BCLAD candidates) 1.b 2.1 Monitors student learning during instruction (TPE 2) 1.d 2.2 Paces instruction appropriately and re-teaches content when necessary (TPE 2) 1.d 2.3 Uses multiple means of assessment (TPE 3) 1.d 2.4 Gives students meaningful feedback on assignments and assessments (TPE 3) 1.d 3.1 Learns about students prior knowledge, background, and interests, and plans lessons that draw on these (TPE 8) 3.2 Prepares complete and sequential lesson plans with a progression of learning tasks and assessments that build understanding of content (TPE 9) 3.3 Plans vocabulary, reading, writing, speaking, and listening instruction for content area learning (TPE 9) 3.4 Plans instruction that addresses academic language features of learning tasks and California English Language Development Standards (TPE 9) 4.1 Provides opportunities and time for students to practice and apply what they have learned (TPE 4) 4.2 Uses an effective mix of instructional activities to engage students in multiple learning modalities and to make content accessible (TPE 5) 4.3 Establishes and communicates developmentally appropriate and challenging academic expectations (TPE 6) 4.4 Differentiates instruction to meet the needs of students from diverse backgrounds, including English Learners and students with special needs (TPE 7) 5.1 Maximizes instructional time, managing classroom routines and transitions (TPE 10) 5.2 Creates a positive climate for learning and student discussion, maintaining clear expectations for academic and social behavior (TPE 11) 5.3 Creates an inclusive learning environment for students with diverse learning needs and backgrounds (TPE 11) Fall 2012 Supervising Teacher University supervisor Mean N Mean N 14 5.4 Maintains good rapport with students (TPE 11) 1.g 6.1 Maintains good rapport with faculty and staff (TPE 12) 1.g 6.2 Meets commitments and deadlines (TPE 12) 1.g 6.3 Meets professional, legal, and ethical obligations (TPE 12) 1.g 6.4 Reflects on, analyzes, and evaluates own teaching (TPE 13) 1.g 4.33 3.67 3.00 3.67 3.67 3 3 3 3 3 4.00 4.33 3.33 4.00 4.00 3 3 3 3 3 Notes: 1=Unsatisfactory, 2=Marginal, 3=Satisfactory, 4=Strong, 5=Outstanding Student Teaching Progress Report Single Subject Credential JYI Fall 2012 Teaching Performance Expectation NCATE Standard Fall 2012 Supervising Teacher University supervisor Mean N Mean N 3.67 3.67 3.67 4.00 3.00 3 3 3 3 1 4.33 3.67 4.00 4.00 . 3 3 3 3 0 1.c, 1.d 4.00 4.00 3.67 3.67 3.33 3 3 3 3 3 3.33 3.67 4.33 4.00 4.00 3 3 3 3 3 1.b 4.00 3 3.67 3 1.b, 1.c 4.00 3 3.33 3 1.b. 1.c 3.67 3 3.67 3 1.b 4.00 3 3.67 3 1.b 4.00 3 4.00 3 1.b, 1.g 4.00 3 4.00 3 1.b 4.00 3 3.33 3 5.1 Maximizes instructional time, managing classroom routines and transitions (TPE 10) 1.c 5.2 Creates a positive climate for learning and student discussion, maintaining clear expectations for academic and social behavior (TPE 11) 1.c 3.33 4.33 3 3 3.33 4.00 3 3 1.1 Knows subject matter (TPE 1) 1.a 1.2 Demonstrates subject-specific pedagogical knowledge and skills (TPE 1) 1.b 1.3 Teaches to California academic content standards (TPE 1) 1.a, 1.b 1.4 Communicates effectively in oral and written English (TPE 1) 1.b 1.5 Communicates effectively in the BCLAD language (TPE 1, BCLAD only; leave blank for non-BCLAD candidates) 1.b 2.1 Monitors student learning during instruction (TPE 2) 1.d 2.2 Paces instruction appropriately and re-teaches content when necessary (TPE 2) 1.d 2.3 Uses multiple means of assessment (TPE 3) 1.d 2.4 Gives students meaningful feedback on assignments and assessments (TPE 3) 1.d 3.1 Learns about students prior knowledge, background, and interests, and plans lessons that draw on these (TPE 8) 3.2 Prepares complete and sequential lesson plans with a progression of learning tasks and assessments that build understanding of content (TPE 9) 3.3 Plans vocabulary, reading, writing, speaking, and listening instruction for content area learning (TPE 9) 3.4 Plans instruction that addresses academic language features of learning tasks and California English Language Development Standards (TPE 9) 4.1 Provides opportunities and time for students to practice and apply what they have learned (TPE 4) 4.2 Uses an effective mix of instructional activities to engage students in multiple learning modalities and to make content accessible (TPE 5) 4.3 Establishes and communicates developmentally appropriate and challenging academic expectations (TPE 6) 4.4 Differentiates instruction to meet the needs of students from diverse backgrounds, including English Learners and students with special needs (TPE 7) 15 5.3 Creates an inclusive learning environment for students with diverse learning needs and backgrounds (TPE 11) 1.c 4.00 3 4.33 3 5.4 Maintains good rapport with students (TPE 11) 1.g 6.1 Maintains good rapport with faculty and staff (TPE 12) 1.g 6.2 Meets commitments and deadlines (TPE 12) 1.g 6.3 Meets professional, legal, and ethical obligations (TPE 12) 1.g 6.4 Reflects on, analyzes, and evaluates own teaching (TPE 13) 1.g 4.00 5.00 4.67 5.00 3.67 3 3 3 3 3 4.33 4.33 4.33 4.67 4.00 3 3 3 3 3 Notes: 1=Unsatisfactory, 2=Marginal, 3=Satisfactory, 4=Strong, 5=Outstanding Student Teaching Progress Report Single Subject Credential Traditional Fall 2012 and Spring 2013 TPE Fall 2012 Teaching Performance Expectation TPE 1 Specific pedagogical skills for subject matter instruction TPE 2 Monitoring student learning during instruction TPE 3 Interpretation and use of assessments TPE 4 Making content accessible TPE 5 Student engagement TPE 6 Developmentally appropriate teaching practices TPE 7 Teaching English learners TPE 8 Learning about students TPE 9 Instructional planning TPE 10 Instructional time TPE 11 Social environment NCATE Standard(s) Supervising Teacher Spring 2013 University supervisor Supervising Teacher University supervisor Mean N Mean N Mean N Mean N 1.b 3.84 51 3.93 48 3.95 27 3.93 29 1.d 3.66 51 3.76 48 3.89 27 3.76 29 1.d 3.68 50 3.70 48 3.87 26 3.67 29 1.c 3.78 3.67 3.75 51 51 51 3.91 3.75 3.73 47 48 48 3.96 3.81 3.70 27 27 27 3.86 3.93 3.66 29 29 29 1.b 1.c, 1.d 1.b 1.c 1.c 3.46 3.64 3.66 3.53 4.00 50 50 51 51 51 3.51 3.57 3.71 3.83 3.97 43 44 47 48 48 3.62 3.70 3.69 3.48 4.04 26 27 27 27 27 3.67 3.60 3.72 3.69 4.11 27 25 29 29 29 1.b 1.b,1.c 16 TPE 12 Professional, legal, and ethical obligations TPE 13 Professional growth 1.g 4.01 51 4.01 48 4.27 27 4.29 29 1.g 3.94 50 4.02 48 4.11 27 4.31 29 Notes: 1=Initial Competence, 3=Intermediate Competence, 5=Advanced Competence 17 Student Teaching Progress Report Single Subject Credential Intern Fall 2012 and Spring 2013 TPE Teaching Performance Expectation TPE 1 Specific pedagogical skills for subject matter instruction TPE 2 Monitoring student learning during instruction TPE 3 Interpretation and use of assessments TPE 4 Making content accessible TPE 5 Student engagement TPE 6 Developmentally appropriate teaching practices TPE 7 Teaching English learners TPE 8 Learning about students TPE 9 Instructional planning TPE 10 Instructional time TPE 11 Social environment TPE 12 Professional, legal, and ethical obligations TPE 13 Professional growth NCATE Standard(s) 1.b 1.d 1.d 1.b 1.b,1.c 1.c 1.b 1.c, 1.d 1.b 1.c 1.c 1.g 1.g Fall 2012 Spring 2013 University supervisor University supervisor Mean N Mean N - - 4.70 4.70 4.50 4.80 4.80 4.60 4.20 4.00 4.33 4.40 4.53 4.60 4.80 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 Notes: 1=Initial Competence, 3=Intermediate Competence, 5=Advanced Competence 18 Student Teaching Progress Report Single Subject Credential ACT Fall 2012 TPE Fall 2012 Teaching Performance Expectation NCATE Standard(s) Supervising Teacher University supervisor Mean N Mean N TPE 1 Specific pedagogical skills for subject matter instruction TPE 2 Monitoring student learning during instruction TPE 3 Interpretation and use of assessments TPE 4 Making content accessible TPE 5 Student engagement 1.b 4.18 12 4.14 18 1.d 1.d 1.b 1.b,1.c TPE 6 Developmentally appropriate teaching practices TPE 7 Teaching English learners TPE 8 Learning about students 1.c 1.b 1.c, 1.d 4.04 3.92 4.17 4.17 3.92 3.75 3.67 3.96 3.58 4.22 4.40 4.25 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 3.94 3.61 4.17 4.28 3.89 3.61 3.56 3.96 3.89 4.07 4.19 4.17 18 18 18 18 18 18 16 18 18 18 18 18 TPE 9 Instructional planning TPE 10 Instructional time TPE 11 Social environment TPE 12 Professional, legal, and ethical obligations TPE 13 Professional growth 1.b 1.c 1.c 1.g 1.g Notes: 1=Initial Competence, 3=Intermediate Competence, 5=Advanced Competence 19 Student Teaching Progress Report Single Subject Credential FYI Fall 2012 TPE Fall 2012 Teaching Performance Expectation TPE 1 Specific pedagogical skills for subject matter instruction TPE 2 Monitoring student learning during instruction NCATE Standard(s) Supervising Teacher University supervisor Mean N Mean N 1.b 3.67 3 3.67 3 1.d 3.17 3 3.00 3 20 Student Teaching Evaluation – Part I Single Subject Credential: Intern Pathway Fall 2012 and Spring 2013 Teaching Performance Expectation 1.1 Knows subject matter (TPE 1) 1.2 Demonstrates subject-specific pedagogical knowledge and skills (TPE 1) 1.3 Teaches to California academic content standards (TPE 1) 1.4 Communicates effectively in oral and written English (TPE 1) 1.5 Communicates effectively in the BCLAD language (TPE 1, BCLAD only; leave blank for nonBCLAD candidates) 2.1 Monitors student learning by eliciting elaborated student responses to subject matter (TPE 2) 2.2 Responds to student questions and comments in ways that build understanding of subject matter (TPE 2) 2.3 Paces instruction appropriately and re-teaches content when necessary (TPE 2) 2.4 Uses multiple means of assessment (TPE 3) 2.5 Develops assessments that require students to show depth of understanding and skill (TPE 3) 2.6 Assesses students in both productive (talking/writing) and receptive (listening/reading) modalities (TPE 3) 2.7 Draws accurate conclusions from assessments about student and whole-class learning (TPE 3) 2.8 Uses the information from assessments to formulate next steps in instruction (TPE 3) 2.9 Communicates progress to students, giving them meaningful feedback on assignments (TPE 3) 2.10 Communicates course expectations and student progress to parents/guardians (TPE 3) 3.1 Learns about students' prior knowledge, background, and interests, and plans lessons that draw on these (TPE 8) 3.2 Learns the needs of students with special needs, including at-risk and gifted students, and uses this knowledge in planning (TPE 8) 3.3 Prepares complete and sequential lesson plans with a progression of learning tasks and assessments that build understanding of content (TPE 9) 3.4 Plans vocabulary, reading, writing, speaking, and listening instruction for content area learning (TPE 9) 3.5 Identifies academic language features of learning tasks, and plans supporting instruction (TPE 9) 3.6 Prepares lesson plans that address California English Language Development standards for English learners (TPE 9) 3.7 Plans for in-depth student discussion of content in whole class and small group formats (TPE 9) 3.8 Plans lessons and assessments that address multiple levels of cognitive demand (TPE 9) Fall 2012 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 1 1 1 1 1 5.00 5.00 5.00 4.00 . 1 1 1 1 0 5.00 4.67 4.67 5.00 4.00 3 3 3 3 1 4.75 4.50 4.50 4.50 . 4 4 4 4 0 5.00 5.00 1 1 4.00 4.00 1 1 4.00 5.00 3 3 4.50 4.75 4 4 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 1 1 1 1 3.00 4.00 4.00 4.00 1 1 1 1 4.67 4.67 4.67 4.33 3 3 3 3 4.75 4.25 4.25 4.00 4 4 4 4 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 1 1 1 1 1 4.00 4.00 4.00 4.00 4.00 1 1 1 1 1 4.67 4.33 4.67 4.67 4.33 3 3 3 3 3 4.00 4.75 4.50 4.50 4.50 4 4 4 4 4 5.00 1 4.00 1 4.67 3 4.50 4 5.00 1 5.00 1 5.00 3 4.25 4 5.00 1 5.00 1 4.67 3 4.00 4 5.00 5.00 1 1 4.00 5.00 1 1 4.33 4.67 3 3 4.00 4.00 4 3 5.00 5.00 1 1 4.00 4.00 1 1 4.33 4.33 3 3 4.50 4.25 4 4 Notes 1=Unsatisfactory, 2=Marginal, 3=Satisfactory, 4=Strong, 5=Outstanding 21 Student Teaching Evaluation – Part II Single Subject Credential: Intern Pathway Fall 2012 and Spring 2013 Teaching Performance Expectation 4.1 Communicates student learning objectives (TPE 4) 4.2 Promotes student practice and application of knowledge (TPE 4) 4.3 Integrates computer-based technology into instruction (TPE 4) 4.4 Uses an effective mix of instructional activities to engage students in multiple learning modalities (TPE 5) 4.5 Ensures meaningful and substantial participation of all students (TPE 5) 4.6 Establishes challenging academic expectations and fosters higher order thinking and problem-solving skills (TPE 6) 4.7 Connects curriculum to life outside school, including future higher education and career options (TPE 6) 4.8 Meets the instructional needs of students from diverse cultural backgrounds, demonstrating cultural awareness and sensitivity (TPE 7) 4.9 Meets the instructional needs of English Learners (TPE 7) 4.10 Meets the instructional needs of students with special needs (TPE 5) 4.11 Meets the instructional needs of students at risk of educational failure (TPE 5) 5.1 Maximizes instructional time, managing classroom routines and transitions (TPE 10) 5.2 Maintains classroom control and consistently enforces policies (TPE 10) 5.3 Learns about and uses school facilities and resources for instruction (TPE 10) 5.4 Creates a positive climate for learning and student discussion, maintaining clear expectations for academic and social behavior (TPE 11) 5.5 Creates an inclusive learning environment for students with diverse learning needs and backgrounds (TPE 11) 5.6 Maintains good rapport with students (TPE 11) 6.1 Maintains good rapport with faculty and staff (TPE 12) 6.2 Maintains good rapport with students' families (TPE 12) 6.3 Meets commitments and deadlines (TPE 12) 6.4 Meets professional, legal, and ethical obligations (TPE 12) 6.5 Reflects on, analyzes, and evaluates own teaching (TPE 13) 6.6 Implements changes based on self-reflection and constructive suggestions from others (TPE 13) Fall 2012 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 1 1 1 1 5.00 5.00 3.00 5.00 1 1 1 1 4.00 4.67 4.00 4.33 3 3 3 3 4.25 4.25 4.33 4.25 4 4 3 4 5.00 5.00 1 1 4.00 5.00 1 1 4.00 4.67 3 3 4.50 4.00 4 4 5.00 1 4.00 1 4.67 3 4.50 4 5.00 1 4.00 1 5.00 3 4.25 4 5.00 5.00 5.00 1 1 1 4.00 4.00 4.00 1 1 1 4.33 4.00 4.00 3 3 3 4.00 4.25 4.50 3 4 4 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 1 1 1 1 5.00 5.00 4.00 5.00 1 1 1 1 4.00 4.67 4.67 5.00 3 3 3 3 4.25 4.50 4.25 4.50 4 4 4 4 5.00 1 5.00 1 5.00 3 4.50 4 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 5.00 5.00 4.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 4.75 5.00 4.75 4.75 4.75 4.50 4.75 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 Notes 1=Unsatisfactory, 2=Marginal, 3=Satisfactory, 4=Strong, 5=Outstanding 22 Student Teaching Evaluation – Part I Single Subject Credential: ACT Pathway Spring 2013 Teaching Performance Expectation 1.1 Knows subject matter (TPE 1) 1.2 Demonstrates subject-specific pedagogical knowledge and skills (TPE 1) 1.3 Teaches to California academic content standards (TPE 1) 1.4 Communicates effectively in oral and written English (TPE 1) 1.5 Communicates effectively in the BCLAD language (TPE 1, BCLAD only; leave blank for nonBCLAD candidates) 2.1 Monitors student learning by eliciting elaborated student responses to subject matter (TPE 2) 2.2 Responds to student questions and comments in ways that build understanding of subject matter (TPE 2) 2.3 Paces instruction appropriately and re-teaches content when necessary (TPE 2) 2.4 Uses multiple means of assessment (TPE 3) 2.5 Develops assessments that require students to show depth of understanding and skill (TPE 3) 2.6 Assesses students in both productive (talking/writing) and receptive (listening/reading) modalities (TPE 3) 2.7 Draws accurate conclusions from assessments about student and whole-class learning (TPE 3) 2.8 Uses the information from assessments to formulate next steps in instruction (TPE 3) 2.9 Communicates progress to students, giving them meaningful feedback on assignments (TPE 3) 2.10 Communicates course expectations and student progress to parents/guardians (TPE 3) 3.1 Learns about students' prior knowledge, background, and interests, and plans lessons that draw on these (TPE 8) 3.2 Learns the needs of students with special needs, including at-risk and gifted students, and uses this knowledge in planning (TPE 8) 3.3 Prepares complete and sequential lesson plans with a progression of learning tasks and assessments that build understanding of content (TPE 9) 3.4 Plans vocabulary, reading, writing, speaking, and listening instruction for content area learning (TPE 9) 3.5 Identifies academic language features of learning tasks, and plans supporting instruction (TPE 9) 3.6 Prepares lesson plans that address California English Language Development standards for English learners (TPE 9) 3.7 Plans for in-depth student discussion of content in whole class and small group formats (TPE 9) 3.8 Plans lessons and assessments that address multiple levels of cognitive demand (TPE 9) Spring 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 4.40 4.10 4.35 4.15 4.25 20 20 20 20 12 4.44 4.28 4.28 4.22 4.00 18 18 18 18 4 4.05 4.15 20 20 4.22 4.39 18 18 3.95 4.30 3.95 4.05 20 20 20 20 4.11 4.11 4.06 4.06 18 18 18 18 4.15 4.15 4.15 4.11 4.15 20 20 20 18 20 4.11 4.11 4.17 3.94 4.06 18 18 18 16 18 4.21 19 3.94 18 4.00 20 4.33 18 4.20 20 4.44 18 4.00 20 4.00 18 3.95 19 3.94 16 4.20 20 4.17 18 4.00 20 4.00 18 Notes 1=Unsatisfactory, 2=Marginal, 3=Satisfactory, 4=Strong, 5=Outstanding 23 Student Teaching Evaluation – Part II Single Subject Credential: ACT Pathway Spring 2013 Teaching Performance Expectation 4.1 Communicates student learning objectives (TPE 4) 4.2 Promotes student practice and application of knowledge (TPE 4) 4.3 Integrates computer-based technology into instruction (TPE 4) 4.4 Uses an effective mix of instructional activities to engage students in multiple learning modalities (TPE 5) 4.5 Ensures meaningful and substantial participation of all students (TPE 5) 4.6 Establishes challenging academic expectations and fosters higher order thinking and problemsolving skills (TPE 6) 4.7 Connects curriculum to life outside school, including future higher education and career options (TPE 6) 4.8 Meets the instructional needs of students from diverse cultural backgrounds, demonstrating cultural awareness and sensitivity (TPE 7) 4.9 Meets the instructional needs of English Learners (TPE 7) 4.10 Meets the instructional needs of students with special needs (TPE 5) 4.11 Meets the instructional needs of students at risk of educational failure (TPE 5) 5.1 Maximizes instructional time, managing classroom routines and transitions (TPE 10) 5.2 Maintains classroom control and consistently enforces policies (TPE 10) 5.3 Learns about and uses school facilities and resources for instruction (TPE 10) 5.4 Creates a positive climate for learning and student discussion, maintaining clear expectations for academic and social behavior (TPE 11) 5.5 Creates an inclusive learning environment for students with diverse learning needs and backgrounds (TPE 11) 5.6 Maintains good rapport with students (TPE 11) 6.1 Maintains good rapport with faculty and staff (TPE 12) 6.2 Maintains good rapport with students' families (TPE 12) 6.3 Meets commitments and deadlines (TPE 12) 6.4 Meets professional, legal, and ethical obligations (TPE 12) 6.5 Reflects on, analyzes, and evaluates own teaching (TPE 13) 6.6 Implements changes based on self-reflection and constructive suggestions from others (TPE 13) Spring 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 4.20 4.20 4.35 4.25 20 20 20 20 4.22 4.11 4.33 4.22 18 18 18 18 3.95 4.05 20 20 4.00 4.11 18 18 4.20 20 4.00 18 4.20 20 4.06 18 4.00 4.10 4.05 20 20 20 3.88 3.93 3.94 16 14 16 4.00 3.90 4.25 4.25 20 20 20 20 4.33 4.39 4.28 4.44 18 18 18 18 4.30 20 4.22 18 4.50 4.60 4.26 4.40 4.63 4.40 4.50 20 20 19 20 19 20 20 4.44 4.61 4.56 4.56 4.61 4.61 4.50 18 18 16 18 18 18 18 Notes 1=Unsatisfactory, 2=Marginal, 3=Satisfactory, 4=Strong, 5=Outstanding 24 Student Teaching Evaluation – Part I Single Subject Credential: FYI Pathway Spring 2013 Teaching Performance Expectation 1.1 Knows subject matter (TPE 1) 1.2 Demonstrates subject-specific pedagogical knowledge and skills (TPE 1) 1.3 Teaches to California academic content standards (TPE 1) 1.4 Communicates effectively in oral and written English (TPE 1) 1.5 Communicates effectively in the BCLAD language (TPE 1, BCLAD only; leave blank for nonBCLAD candidates) 2.1 Monitors student learning by eliciting elaborated student responses to subject matter (TPE 2) 2.2 Responds to student questions and comments in ways that build understanding of subject matter (TPE 2) 2.3 Paces instruction appropriately and re-teaches content when necessary (TPE 2) 2.4 Uses multiple means of assessment (TPE 3) 2.5 Develops assessments that require students to show depth of understanding and skill (TPE 3) 2.6 Assesses students in both productive (talking/writing) and receptive (listening/reading) modalities (TPE 3) 2.7 Draws accurate conclusions from assessments about student and whole-class learning (TPE 3) 2.8 Uses the information from assessments to formulate next steps in instruction (TPE 3) 2.9 Communicates progress to students, giving them meaningful feedback on assignments (TPE 3) 2.10 Communicates course expectations and student progress to parents/guardians (TPE 3) 3.1 Learns about students' prior knowledge, background, and interests, and plans lessons that draw on these (TPE 8) 3.2 Learns the needs of students with special needs, including at-risk and gifted students, and uses this knowledge in planning (TPE 8) 3.3 Prepares complete and sequential lesson plans with a progression of learning tasks and assessments that build understanding of content (TPE 9) 3.4 Plans vocabulary, reading, writing, speaking, and listening instruction for content area learning (TPE 9) 3.5 Identifies academic language features of learning tasks, and plans supporting instruction (TPE 9) 3.6 Prepares lesson plans that address California English Language Development standards for English learners (TPE 9) 3.7 Plans for in-depth student discussion of content in whole class and small group formats (TPE 9) 3.8 Plans lessons and assessments that address multiple levels of cognitive demand (TPE 9) Spring 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 4.00 3.80 3.80 3.80 4.00 5 5 5 5 2 4.00 3.50 4.00 4.00 . 2 2 2 2 0 3.40 3.20 5 5 3.50 3.50 2 2 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.40 5 5 5 5 3.50 3.50 3.50 3.50 2 2 2 2 3.40 3.40 3.80 3.33 3.60 5 5 5 3 5 3.50 3.50 3.50 5.00 4.00 2 2 2 1 2 3.60 5 3.50 2 3.60 5 3.50 2 3.80 5 3.50 2 3.40 5 3.50 2 3.60 5 3.50 2 3.60 5 4.00 2 3.60 5 3.50 2 Notes 1=Unsatisfactory, 2=Marginal, 3=Satisfactory, 4=Strong, 5=Outstanding 25 Student Teaching Evaluation – Part II Single Subject Credential: FYI Pathway Spring 2013 Teaching Performance Expectation 4.1 Communicates student learning objectives (TPE 4) 4.2 Promotes student practice and application of knowledge (TPE 4) 4.3 Integrates computer-based technology into instruction (TPE 4) 4.4 Uses an effective mix of instructional activities to engage students in multiple learning modalities (TPE 5) 4.5 Ensures meaningful and substantial participation of all students (TPE 5) 4.6 Establishes challenging academic expectations and fosters higher order thinking and problemsolving skills (TPE 6) 4.7 Connects curriculum to life outside school, including future higher education and career options (TPE 6) 4.8 Meets the instructional needs of students from diverse cultural backgrounds, demonstrating cultural awareness and sensitivity (TPE 7) 4.9 Meets the instructional needs of English Learners (TPE 7) 4.10 Meets the instructional needs of students with special needs (TPE 5) 4.11 Meets the instructional needs of students at risk of educational failure (TPE 5) 5.1 Maximizes instructional time, managing classroom routines and transitions (TPE 10) 5.2 Maintains classroom control and consistently enforces policies (TPE 10) 5.3 Learns about and uses school facilities and resources for instruction (TPE 10) 5.4 Creates a positive climate for learning and student discussion, maintaining clear expectations for academic and social behavior (TPE 11) 5.5 Creates an inclusive learning environment for students with diverse learning needs and backgrounds (TPE 11) 5.6 Maintains good rapport with students (TPE 11) 6.1 Maintains good rapport with faculty and staff (TPE 12) 6.2 Maintains good rapport with students' families (TPE 12) 6.3 Meets commitments and deadlines (TPE 12) 6.4 Meets professional, legal, and ethical obligations (TPE 12) 6.5 Reflects on, analyzes, and evaluates own teaching (TPE 13) 6.6 Implements changes based on self-reflection and constructive suggestions from others (TPE 13) Spring 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 3.80 4.00 3.75 3.80 5 5 4 5 4.00 4.00 4.00 4.00 2 2 2 2 3.60 3.40 5 5 3.50 4.00 2 2 3.40 5 3.50 2 4.20 5 4.00 2 4.33 3.80 3.75 3 5 4 3.50 3.50 3.50 2 2 2 3.60 3.20 4.00 4.20 5 5 4 5 3.50 3.50 4.00 4.50 2 2 2 2 3.80 5 3.50 2 4.40 4.75 4.00 3.60 4.00 4.00 4.20 5 4 3 5 5 5 5 4.00 4.00 5.00 3.50 4.00 3.50 4.00 2 2 1 2 2 2 2 Notes 1=Unsatisfactory, 2=Marginal, 3=Satisfactory, 4=Strong, 5=Outstanding 26 Student Teaching Evaluation – Part I Single Subject Credential: JYI Pathway Spring 2013 Teaching Performance Expectation 1.1 Knows subject matter (TPE 1) 1.2 Demonstrates subject-specific pedagogical knowledge and skills (TPE 1) 1.3 Teaches to California academic content standards (TPE 1) 1.4 Communicates effectively in oral and written English (TPE 1) 1.5 Communicates effectively in the BCLAD language (TPE 1, BCLAD only; leave blank for nonBCLAD candidates) 2.1 Monitors student learning by eliciting elaborated student responses to subject matter (TPE 2) 2.2 Responds to student questions and comments in ways that build understanding of subject matter (TPE 2) 2.3 Paces instruction appropriately and re-teaches content when necessary (TPE 2) 2.4 Uses multiple means of assessment (TPE 3) 2.5 Develops assessments that require students to show depth of understanding and skill (TPE 3) 2.6 Assesses students in both productive (talking/writing) and receptive (listening/reading) modalities (TPE 3) 2.7 Draws accurate conclusions from assessments about student and whole-class learning (TPE 3) 2.8 Uses the information from assessments to formulate next steps in instruction (TPE 3) 2.9 Communicates progress to students, giving them meaningful feedback on assignments (TPE 3) 2.10 Communicates course expectations and student progress to parents/guardians (TPE 3) 3.1 Learns about students' prior knowledge, background, and interests, and plans lessons that draw on these (TPE 8) 3.2 Learns the needs of students with special needs, including at-risk and gifted students, and uses this knowledge in planning (TPE 8) 3.3 Prepares complete and sequential lesson plans with a progression of learning tasks and assessments that build understanding of content (TPE 9) 3.4 Plans vocabulary, reading, writing, speaking, and listening instruction for content area learning (TPE 9) 3.5 Identifies academic language features of learning tasks, and plans supporting instruction (TPE 9) 3.6 Prepares lesson plans that address California English Language Development standards for English learners (TPE 9) 3.7 Plans for in-depth student discussion of content in whole class and small group formats (TPE 9) 3.8 Plans lessons and assessments that address multiple levels of cognitive demand (TPE 9) Spring 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 4.50 4.25 4.75 4.50 5.00 4 4 4 4 1 4.33 4.00 4.33 5.00 4.00 3 3 3 3 1 4.25 4.50 4 4 3.67 4.00 3 3 4.50 4.25 4.25 4.50 4 4 4 4 4.33 4.33 4.00 4.00 3 3 3 3 4.50 4.50 5.00 4.50 4.50 4 4 4 4 4 4.00 4.33 4.00 4.00 3.67 3 3 3 3 3 4.75 4 4.00 3 4.50 4 4.33 3 4.50 4 4.00 3 4.50 4 3.67 3 4.50 4 3.67 3 4.25 4 4.67 3 4.25 4 4.33 3 Notes: 1=Unsatisfactory, 2=Marginal, 3=Satisfactory, 4=Strong, 5=Outstanding 27 Student Teaching Evaluation – Part II Single Subject Credential: JYI Pathway Spring 2013 Teaching Performance Expectation 4.1 Communicates student learning objectives (TPE 4) 4.2 Promotes student practice and application of knowledge (TPE 4) 4.3 Integrates computer-based technology into instruction (TPE 4) 4.4 Uses an effective mix of instructional activities to engage students in multiple learning modalities (TPE 5) 4.5 Ensures meaningful and substantial participation of all students (TPE 5) 4.6 Establishes challenging academic expectations and fosters higher order thinking and problemsolving skills (TPE 6) 4.7 Connects curriculum to life outside school, including future higher education and career options (TPE 6) 4.8 Meets the instructional needs of students from diverse cultural backgrounds, demonstrating cultural awareness and sensitivity (TPE 7) 4.9 Meets the instructional needs of English Learners (TPE 7) 4.10 Meets the instructional needs of students with special needs (TPE 5) 4.11 Meets the instructional needs of students at risk of educational failure (TPE 5) 5.1 Maximizes instructional time, managing classroom routines and transitions (TPE 10) 5.2 Maintains classroom control and consistently enforces policies (TPE 10) 5.3 Learns about and uses school facilities and resources for instruction (TPE 10) 5.4 Creates a positive climate for learning and student discussion, maintaining clear expectations for academic and social behavior (TPE 11) 5.5 Creates an inclusive learning environment for students with diverse learning needs and backgrounds (TPE 11) 5.6 Maintains good rapport with students (TPE 11) 6.1 Maintains good rapport with faculty and staff (TPE 12) 6.2 Maintains good rapport with students' families (TPE 12) 6.3 Meets commitments and deadlines (TPE 12) 6.4 Meets professional, legal, and ethical obligations (TPE 12) 6.5 Reflects on, analyzes, and evaluates own teaching (TPE 13) 6.6 Implements changes based on self-reflection and constructive suggestions from others (TPE 13) Spring 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 4.75 4.50 4.75 4.50 4 4 4 4 4.33 4.33 4.33 4.00 3 3 3 3 4.50 4.50 4 4 4.00 4.00 3 3 4.25 4 3.67 3 4.50 4 4.00 3 4.25 4.25 4.25 4 4 4 3.67 3.67 4.00 3 3 3 4.25 4.25 5.00 5.00 4 4 4 4 4.33 4.67 4.67 5.00 3 3 3 3 4.25 4 4.33 3 5.00 5.00 4.50 5.00 5.00 4.50 4.50 3 4 4 4 4 4 4 4.33 4.67 4.33 4.67 5.00 4.67 4.33 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Notes: 1=Unsatisfactory, 2=Marginal, 3=Satisfactory, 4=Strong, 5=Outstanding 28 Single Subject Credential Second Semester (SED 555) Student Teaching Evaluation Domain A: Making Subject Matter Comprehensible to Students Fall 2013 and Spring 2014 Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 1.1 Knows subject matter (TPE 1) 4.2727 22 4.6250 8 4.2833 60 4.2982 57 1.2 Demonstrates subject-specific pedagogical knowledge and skills (TPE 1) 4.4091 22 4.2500 8 4.1333 60 4.1053 57 1.3 Teaches to California academic content standards (TPE 1) 4.5909 22 4.5000 8 4.3167 60 4.2281 57 1.4 Communicates effectively in oral and written English (TPE 1) 4.0000 22 4.6250 8 4.3667 60 4.3509 57 1.5 Communicates effectively in the BCLAD language (TPE 1, BCLAD only; leave blank for non-BCLAD candidates) 2.6818 22 1.7500 8 2.2833 60 .7018 57 Traditional ACT Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 1.1 Knows subject matter (TPE 1) 4.1154 26 4.4737 19 1.2 Demonstrates subject-specific pedagogical knowledge and skills (TPE 1) 4.0385 26 4.3158 19 1.3 Teaches to California academic content standards (TPE 1) 4.2308 26 4.4737 19 1.4 Communicates effectively in oral and written English (TPE 1) 4.3846 26 4.5789 19 1.5 Communicates effectively in the BCLAD language (TPE 1, BCLAD only; leave blank for non-BCLAD candidates) 1.0000 26 .8947 19 Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 1.1 Knows subject matter (TPE 1) 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 4.5000 4 1.2 Demonstrates subject-specific pedagogical knowledge and skills (TPE 1) 5.0000 2 4.5000 2 4.5000 2 4.7500 4 1.3 Teaches to California academic content standards (TPE 1) 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 4.5000 2 4.7500 4 1.4 Communicates effectively in oral and written English (TPE 1) 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 4.5000 4 1.5 Communicates effectively in the BCLAD language (TPE 1, BCLAD only; leave blank for non-BCLAD candidates) 2.5000 2 .0000 2 .0000 2 1.2500 4 Intern Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 1.1 Knows subject matter (TPE 1) 5.0000 1 4.1429 7 3.8750 8 1.2 Demonstrates subject-specific pedagogical knowledge and skills (TPE 1) 3.0000 1 4.1429 7 3.8750 8 1.3 Teaches to California academic content standards (TPE 1) 5.0000 1 4.4286 7 4.2500 8 1.4 Communicates effectively in oral and written English (TPE 1) 5.0000 1 4.1429 7 4.1250 8 1.5 Communicates effectively in the BCLAD language (TPE 1, BCLAD only; leave blank for non-BCLAD candidates) 0.0000 1 1.0000 7 .0000 8 FYI/JYI 29 Single Subject Credential Second Semester (SED 555) Student Teaching Evaluation Domain B: Assessing Student Learning Fall 2013 and Spring 2014 Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 4.3636 22 4.1250 8 3.9167 60 3.5088 57 4.5000 22 4.2500 8 4.2500 60 4.0702 57 2.3 Paces instruction appropriately and re-teaches content when necessary (TPE 2) 4.5000 22 4.1250 8 3.9500 60 4.0175 57 2.4 Uses multiple means of assessment (TPE 3) 4.5000 22 3.7500 8 4.0667 60 3.9649 57 4.4091 22 4.1250 8 3.9167 60 3.9123 57 4.4545 22 4.2500 8 4.1000 60 3.9649 57 4.3636 22 4.3750 8 4.0500 60 3.7368 57 4.2273 22 4.1250 8 4.0667 60 3.7719 57 4.3182 22 4.2500 8 4.1500 60 3.9474 57 3.8182 22 3.6250 8 3.5667 60 2.9298 57 Traditional 2.1 Monitors student learning by eliciting elaborated student responses to subject matter (TPE 2) 2.2 Responds to student questions and comments in ways that build understanding of subject matter (TPE 2) 2.5 Develops assessments that require students to show depth of understanding and skill (TPE 3) 2.6 Assesses students in both productive (talking/writing) and receptive (listening/reading) modalities (TPE 3) 2.7 Draws accurate conclusions from assessments about student and whole-class learning (TPE 3) 2.8 Uses the information from assessments to formulate next steps in instruction (TPE 3) 2.9 Communicates progress to students, giving them meaningful feedback on assignments (TPE 3) 2.10 Communicates course expectations and student progress to parents/guardians (TPE 3) ACT 2.1 Monitors student learning by eliciting elaborated student responses to subject matter (TPE 2) 2.2 Responds to student questions and comments in ways that build understanding of subject matter (TPE 2) Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 3.9615 26 4.0000 19 4.1154 26 4.1579 19 2.3 Paces instruction appropriately and re-teaches content when necessary (TPE 2) 3.7692 26 3.9474 19 2.4 Uses multiple means of assessment (TPE 3) 4.0385 26 4.2105 19 4.0385 26 4.1579 19 4.0385 26 4.1053 19 3.8846 26 4.0526 19 3.9231 26 4.0000 19 4.0385 26 3.8421 19 3.7692 26 3.1053 19 2.5 Develops assessments that require students to show depth of understanding and skill (TPE 3) 2.6 Assesses students in both productive (talking/writing) and receptive (listening/reading) modalities (TPE 3) 2.7 Draws accurate conclusions from assessments about student and whole-class learning (TPE 3) 2.8 Uses the information from assessments to formulate next steps in instruction (TPE 3) 2.9 Communicates progress to students, giving them meaningful feedback on assignments (TPE 3) 2.10 Communicates course expectations and student progress to parents/guardians (TPE 3) 30 Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 5.0000 2 4.0000 2 5.0000 2 4.0000 4 5.0000 2 4.0000 2 4.5000 2 4.5000 4 2.3 Paces instruction appropriately and re-teaches content when necessary (TPE 2) 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 4.5000 2 4.2500 4 2.4 Uses multiple means of assessment (TPE 3) 5.0000 2 4.5000 2 4.5000 2 4.2500 4 5.0000 2 4.5000 2 4.0000 2 4.2500 4 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 4.5000 2 4.0000 4 5.0000 2 4.5000 2 4.0000 2 4.5000 4 2.5000 2 5.0000 2 4.0000 2 4.7500 4 5.0000 2 4.5000 2 2.0000 2 4.2500 4 5.0000 2 4.5000 2 2.5000 2 4.2500 4 Intern 2.1 Monitors student learning by eliciting elaborated student responses to subject matter (TPE 2) 2.2 Responds to student questions and comments in ways that build understanding of subject matter (TPE 2) 2.5 Develops assessments that require students to show depth of understanding and skill (TPE 3) 2.6 Assesses students in both productive (talking/writing) and receptive (listening/reading) modalities (TPE 3) 2.7 Draws accurate conclusions from assessments about student and whole-class learning (TPE 3) 2.8 Uses the information from assessments to formulate next steps in instruction (TPE 3) 2.9 Communicates progress to students, giving them meaningful feedback on assignments (TPE 3) 2.10 Communicates course expectations and student progress to parents/guardians (TPE 3) Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 4.000 1 3.8571 7 3.6250 8 4.000 1 4.1429 7 3.8750 8 2.3 Paces instruction appropriately and re-teaches content when necessary (TPE 2) 3.000 1 3.5714 7 3.6250 8 2.4 Uses multiple means of assessment (TPE 3) 4.000 1 3.7143 7 3.8750 8 5.000 1 3.7143 7 3.6250 8 5.000 1 4.1429 7 3.7500 8 3.000 1 3.5714 7 3.1250 8 4.000 1 3.4286 7 3.1250 8 4.000 1 3.5714 7 3.000 1 2.1429 7 FYI/JYI 2.1 Monitors student learning by eliciting elaborated student responses to subject matter (TPE 2) 2.2 Responds to student questions and comments in ways that build understanding of subject matter (TPE 2) 2.5 Develops assessments that require students to show depth of understanding and skill (TPE 3) 2.6 Assesses students in both productive (talking/writing) and receptive (listening/reading) modalities (TPE 3) 2.7 Draws accurate conclusions from assessments about student and whole-class learning (TPE 3) 2.8 Uses the information from assessments to formulate next steps in instruction (TPE 3) 2.9 Communicates progress to students, giving them meaningful feedback on assignments (TPE 3) 2.10 Communicates course expectations and student progress to parents/guardians (TPE 3) 3.6250 2.7500 8 8 31 Single Subject Credential Second Semester (SED 555) Student Teaching Evaluation Domain C: Engaging and Supporting Students in Learning Fall 2013 and Spring 2014 Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 4.1 Communicates student learning objectives (TPE 4) 4.4091 22 4.1250 8 4.0167 60 4.0702 57 4.2 Promotes student practice and application of knowledge (TPE 4) 4.5000 22 4.2500 8 4.1500 60 4.1053 57 4.3 Integrates computer-båased technology into instruction (TPE 4) 4.6364 22 3.7500 8 3.6000 60 3.5439 57 4.4 Uses an effective mix of instructional activities to engage students in multiple learning modalities (TPE 5) 4.3182 22 4.2500 8 4.2000 60 3.9649 57 4.5 Ensures meaningful and substantial participation of all students (TPE 5) 4.3182 22 4.2500 8 4.1333 60 3.9474 57 4.4091 22 4.3750 8 3.8333 60 3.9123 57 4.3636 22 4.0000 8 4.0167 60 3.7193 57 Traditional 4.6 Establishes challenging academic expectations and fosters higher order thinking and problem-solving skills (TPE 6) 4.7 Connects curriculum to life outside school, including future higher education and career options (TPE 6) 4.8 Meets the instructional needs of students from diverse cultural backgrounds, demonstrating cultural awareness and sensitivity (TPE 7) 4.0455 22 4.2500 8 4.2333 60 3.8596 57 4.9 Meets the instructional needs of English Learners (TPE 7) 3.2273 22 4.2500 8 3.4500 60 3.0351 57 4.10 Meets the instructional needs of students with special needs (TPE 5) 3.8182 22 3.6250 8 3.8167 60 3.7018 57 4.11 Meets the instructional needs of students at risk of educational failure (TPE 5) 4.2727 22 4.0000 8 3.8167 60 3.5965 57 ACT Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 4.1 Communicates student learning objectives (TPE 4) 3.8077 26 4.2105 19 4.2 Promotes student practice and application of knowledge (TPE 4) 3.9615 26 4.1579 19 4.3 Integrates computer-based technology into instruction (TPE 4) 3.7308 26 4.0000 19 4.4 Uses an effective mix of instructional activities to engage students in multiple learning modalities (TPE 5) 4.0000 26 4.2632 19 4.5 Ensures meaningful and substantial participation of all students (TPE 5) 3.6154 26 4.0000 19 3.8846 26 4.1579 19 3.8077 26 3.6316 19 4.6 Establishes challenging academic expectations and fosters higher order thinking and problem-solving skills (TPE 6) 4.7 Connects curriculum to life outside school, including future higher education and career options (TPE 6) 4.8 Meets the instructional needs of students from diverse cultural backgrounds, demonstrating cultural awareness and sensitivity (TPE 7) 3.9231 26 3.7368 19 4.9 Meets the instructional needs of English Learners (TPE 7) 2.9615 26 3.0526 19 4.10 Meets the instructional needs of students with special needs (TPE 5) 3.3077 26 3.4211 19 4.11 Meets the instructional needs of students at risk of educational failure (TPE 5) 3.4231 26 3.3684 19 32 Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 4.1 Communicates student learning objectives (TPE 4) 5.0000 2 4.0000 2 4.0000 2 4.5000 4 4.2 Promotes student practice and application of knowledge (TPE 4) 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 4.5000 2 3.7500 4 4.3 Integrates computer-based technology into instruction (TPE 4) 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 2.0000 2 4.0000 4 4.4 Uses an effective mix of instructional activities to engage students in multiple learning modalities (TPE 5) 4.5000 2 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 4.7500 4 4.5 Ensures meaningful and substantial participation of all students (TPE 5) 5.0000 2 4.5000 2 4.0000 2 4.0000 4 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 3.5000 2 4.7500 4 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 4.5000 2 4.5000 4 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 3.2500 4 4.9 Meets the instructional needs of English Learners (TPE 7) 2.5000 2 2.5000 2 2.0000 2 4.0000 4 4.10 Meets the instructional needs of students with special needs (TPE 5) 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 2.0000 2 3.7500 4 4.11 Meets the instructional needs of students at risk of educational failure (TPE 5) 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 1.5000 2 3.7500 4 Intern 4.6 Establishes challenging academic expectations and fosters higher order thinking and problem-solving skills (TPE 6) 4.7 Connects curriculum to life outside school, including future higher education and career options (TPE 6) 4.8 Meets the instructional needs of students from diverse cultural backgrounds, demonstrating cultural awareness and sensitivity (TPE 7) Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 4.1 Communicates student learning objectives (TPE 4) 5.000 1 4.1429 7 3.7500 8 4.2 Promotes student practice and application of knowledge (TPE 4) 3.000 1 4.1429 7 4.1250 8 4.3 Integrates computer-based technology into instruction (TPE 4) 4.000 1 3.0000 7 3.1250 8 4.4 Uses an effective mix of instructional activities to engage students in multiple learning modalities (TPE 5) 5.000 1 4.1429 7 3.6250 8 4.5 Ensures meaningful and substantial participation of all students (TPE 5) 3.000 1 3.8571 7 3.7500 8 4.000 1 3.8571 7 3.3750 8 4.000 1 3.5714 7 3.2500 8 5.000 1 3.8571 7 3.1250 8 4.9 Meets the instructional needs of English Learners (TPE 7) 3.000 1 2.4286 7 2.6250 8 4.10 Meets the instructional needs of students with special needs (TPE 5) 4.000 1 3.0000 7 2.3750 8 4.11 Meets the instructional needs of students at risk of educational failure (TPE 5) 2.000 1 3.0000 7 2.3750 8 FYI/JYI 4.6 Establishes challenging academic expectations and fosters higher order thinking and problem-solving skills (TPE 6) 4.7 Connects curriculum to life outside school, including future higher education and career options (TPE 6) 4.8 Meets the instructional needs of students from diverse cultural backgrounds, demonstrating cultural awareness and sensitivity (TPE 7) 33 Single Subject Credential Second Semester (SED 555) Student Teaching Evaluation Domain D: Planning Instruction and Designing Learning Experiences For Students Fall 2013 and Spring 2014 Traditional 3.1 Learns about students' prior knowledge, background, and interests, and plans lessons that draw on these (TPE 8) 3.2 Learns the needs of students with special needs, including at-risk and gifted students, and uses this knowledge in planning (TPE 8) 3.3 Prepares complete and sequential lesson plans with a progression of learning tasks and assessments that build understanding of content (TPE 9) 3.4 Plans vocabulary, reading, writing, speaking, and listening instruction for content area learning (TPE 9) 3.5 Identifies academic language features of learning tasks, and plans supporting instruction (TPE 9) 3.6 Prepares lesson plans that address California English Language Development standards for English learners (TPE 9) 3.7 Plans for in-depth student discussion of content in whole class and small group formats (TPE 9) 3.8 Plans lessons and assessments that address multiple levels of cognitive demand (TPE 9) ACT 3.1 Learns about students' prior knowledge, background, and interests, and plans lessons that draw on these (TPE 8) 3.2 Learns the needs of students with special needs, including at-risk and gifted students, and uses this knowledge in planning (TPE 8) 3.3 Prepares complete and sequential lesson plans with a progression of learning tasks and assessments that build understanding of content (TPE 9) 3.4 Plans vocabulary, reading, writing, speaking, and listening instruction for content area learning (TPE 9) 3.5 Identifies academic language features of learning tasks, and plans supporting instruction (TPE 9) 3.6 Prepares lesson plans that address California English Language Development standards for English learners (TPE 9) 3.7 Plans for in-depth student discussion of content in whole class and small group formats (TPE 9) 3.8 Plans lessons and assessments that address multiple levels of cognitive demand (TPE 9) Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 4.1818 22 4.0000 8 3.8500 60 3.8421 57 4.1364 22 4.1250 8 3.9833 60 3.8772 57 4.4091 22 4.3750 8 4.1667 60 3.9825 57 4.3636 22 4.3750 8 3.9825 60 4.0333 57 4.3182 22 4.1250 8 4.0167 60 3.8070 57 3.2273 22 4.3750 8 3.3333 60 3.4211 57 4.0455 22 4.1250 8 3.8500 60 3.6316 57 4.1818 22 4.3750 8 3.8772 60 3.9000 57 Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 3.8846 26 3.6316 19 3.7308 26 3.6316 19 3.8077 26 4.2105 19 3.8462 26 4.0000 19 3.7692 26 3.7895 19 3.3462 26 2.7895 19 3.8077 26 4.0526 19 3.9231 26 4.0000 19 34 Intern 3.1 Learns about students' prior knowledge, background, and interests, and plans lessons that draw on these (TPE 8) 3.2 Learns the needs of students with special needs, including at-risk and gifted students, and uses this knowledge in planning (TPE 8) 3.3 Prepares complete and sequential lesson plans with a progression of learning tasks and assessments that build understanding of content (TPE 9) 3.4 Plans vocabulary, reading, writing, speaking, and listening instruction for content area learning (TPE 9) 3.5 Identifies academic language features of learning tasks, and plans supporting instruction (TPE 9) 3.6 Prepares lesson plans that address California English Language Development standards for English learners (TPE 9) 3.7 Plans for in-depth student discussion of content in whole class and small group formats (TPE 9) 3.8 Plans lessons and assessments that address multiple levels of cognitive demand (TPE 9) FYI/JYI 3.1 Learns about students' prior knowledge, background, and interests, and plans lessons that draw on these (TPE 8) 3.2 Learns the needs of students with special needs, including at-risk and gifted students, and uses this knowledge in planning (TPE 8) 3.3 Prepares complete and sequential lesson plans with a progression of learning tasks and assessments that build understanding of content (TPE 9) 3.4 Plans vocabulary, reading, writing, speaking, and listening instruction for content area learning (TPE 9) 3.5 Identifies academic language features of learning tasks, and plans supporting instruction (TPE 9) 3.6 Prepares lesson plans that address California English Language Development standards for English learners (TPE 9) 3.7 Plans for in-depth student discussion of content in whole class and small group formats (TPE 9) 3.8 Plans lessons and assessments that address multiple levels of cognitive demand (TPE 9) Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 5.0000 2 4.5000 2 4.0000 2 4.0000 4 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 4.0000 4 5.0000 2 4.5000 2 4.5000 2 4.5000 4 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 4.7500 4 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 4.5000 2 4.5000 4 2.5000 2 4.5000 2 2.0000 2 3.7500 4 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 3.5000 2 4.5000 4 4.5000 2 5.0000 2 4.0000 2 4.7500 4 Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 3.000 1 3.0000 7 3.1250 8 5.000 1 3.2857 7 3.0000 8 3.000 1 3.5714 7 3.6250 8 5.000 1 4.1429 7 4.0000 8 4.000 1 4.0000 7 3.1250 8 3.000 1 2.2857 7 3.1250 8 5.000 1 4.2857 7 3.8750 8 4.000 1 4.1429 7 3.6250 8 35 Single Subject Credential Second Semester (SED 555) Student Teaching Evaluation Domain E: Creating and Maintaining Effective Environments for Student Learning Fall 2013 and Spring 2014 Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 5.1 Maximizes instructional time, managing classroom routines and transitions (TPE 10) 4.1818 22 4.5000 8 3.9000 60 4.0175 57 5.2 Maintains classroom control and consistently enforces policies (TPE 10) 3.8636 22 4.1250 8 3.8500 60 4.0526 57 5.3 Learns about and uses school facilities and resources for instruction (TPE 10) 4.3182 22 3.8750 8 4.2000 60 4.1579 57 4.4545 22 4.6250 8 4.2500 60 4.1754 57 4.2727 22 4.7500 8 4.2000 60 4.1228 57 4.6364 22 4.7500 8 4.4500 60 4.3158 57 Traditional 5.4 Creates a positive climate for learning and student discussion, maintaining clear expectations for academic and social behavior (TPE 11) 5.5 Creates an inclusive learning environment for students with diverse learning needs and backgrounds (TPE 11) 5.6 Maintains good rapport with students (TPE 11) ACT Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 5.1 Maximizes instructional time, managing classroom routines and transitions (TPE 10) 3.5769 26 4.2105 19 5.2 Maintains classroom control and consistently enforces policies (TPE 10) 3.4231 26 4.3158 19 5.3 Learns about and uses school facilities and resources for instruction (TPE 10) 4.0385 26 3.6316 19 3.8077 26 4.3684 19 3.8846 26 3.8947 19 4.0000 26 4.1579 19 5.4 Creates a positive climate for learning and student discussion, maintaining clear expectations for academic and social behavior (TPE 11) 5.5 Creates an inclusive learning environment for students with diverse learning needs and backgrounds (TPE 11) 5.6 Maintains good rapport with students (TPE 11) Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 5.1 Maximizes instructional time, managing classroom routines and transitions (TPE 10) 4.5000 2 4.0000 2 3.5000 2 4.5000 4 5.2 Maintains classroom control and consistently enforces policies (TPE 10) 5.0000 2 4.5000 2 3.5000 2 4.5000 4 5.3 Learns about and uses school facilities and resources for instruction (TPE 10) 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 3.5000 2 4.2500 4 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 4.5000 2 4.7500 4 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 4.5000 2 4.2500 4 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 4.5000 2 4.5000 4 Intern 5.4 Creates a positive climate for learning and student discussion, maintaining clear expectations for academic and social behavior (TPE 11) 5.5 Creates an inclusive learning environment for students with diverse learning needs and backgrounds (TPE 11) 5.6 Maintains good rapport with students (TPE 11) 36 Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 5.1 Maximizes instructional time, managing classroom routines and transitions (TPE 10) 4.000 1 3.4286 7 3.7500 8 5.2 Maintains classroom control and consistently enforces policies (TPE 10) 3.000 1 3.4286 7 3.7500 8 5.3 Learns about and uses school facilities and resources for instruction (TPE 10) 4.000 1 3.4286 7 4.0000 8 4.000 1 4.1429 7 4.0000 8 4.000 1 4.0000 7 3.5000 8 5.000 1 4.5714 7 4.2500 8 FYI/JYI 5.4 Creates a positive climate for learning and student discussion, maintaining clear expectations for academic and social behavior (TPE 11) 5.5 Creates an inclusive learning environment for students with diverse learning needs and backgrounds (TPE 11) 5.6 Maintains good rapport with students (TPE 11) 37 Single Subject Credential Second Semester (SED 555) Student Teaching Evaluation Domain F: Developing as a Professional Educator Fall 2013 and Spring 2014 Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 6.1 Maintains good rapport with faculty and staff (TPE 12) 4.7273 22 4.0000 8 4.4500 60 4.2632 57 6.2 Maintains good rapport with students' families (TPE 12) 3.8182 22 3.2500 8 3.8167 60 2.9474 57 6.3 Meets commitments and deadlines (TPE 12) 4.5455 22 4.5000 8 4.2000 60 4.2281 57 6.4 Meets professional, legal, and ethical obligations (TPE 12) 4.5455 22 4.1250 8 4.2833 60 4.2281 57 6.5 Reflects on, analyzes, and evaluates own teaching (TPE 13) 4.5455 22 4.6250 8 4.3167 60 4.2281 57 6.6 Implements changes based on self-reflection and constructive suggestions from others (TPE 13) 4.5000 22 4.6250 8 4.2667 60 4.4386 57 Traditional ACT Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 6.1 Maintains good rapport with faculty and staff (TPE 12) 4.3846 26 4.2632 19 6.2 Maintains good rapport with students' families (TPE 12) 3.6154 26 2.8947 19 6.3 Meets commitments and deadlines (TPE 12) 4.0385 26 4.4737 19 6.4 Meets professional, legal, and ethical obligations (TPE 12) 4.4231 26 4.5789 19 6.5 Reflects on, analyzes, and evaluates own teaching (TPE 13) 4.2308 26 4.5789 19 6.6 Implements changes based on self-reflection and constructive suggestions from others (TPE 13) 4.1538 26 4.5263 19 Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 6.1 Maintains good rapport with faculty and staff (TPE 12) 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 4.5000 2 5.0000 4 6.2 Maintains good rapport with students' families (TPE 12) 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 .0000 2 3.2500 4 6.3 Meets commitments and deadlines (TPE 12) 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 4.5000 2 4.2500 4 6.4 Meets professional, legal, and ethical obligations (TPE 12) 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 4.5000 4 6.5 Reflects on, analyzes, and evaluates own teaching (TPE 13) 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 4.5000 2 4.0000 4 6.6 Implements changes based on self-reflection and constructive suggestions from others (TPE 13) 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 5.0000 2 4.2500 4 Intern 38 Fall 2013 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N Spring 2014 Cooperating Teacher University Supervisor Mean N Mean N 6.1 Maintains good rapport with faculty and staff (TPE 12) 4.000 1 3.8571 7 4.5000 8 6.2 Maintains good rapport with students' families (TPE 12) 4.000 1 3.2857 7 2.2500 8 6.3 Meets commitments and deadlines (TPE 12) 4.000 1 4.1429 7 3.8750 8 6.4 Meets professional, legal, and ethical obligations (TPE 12) 5.000 1 4.2857 7 4.1250 8 6.5 Reflects on, analyzes, and evaluates own teaching (TPE 13) 5.000 1 4.0000 7 4.1250 8 6.6 Implements changes based on self-reflection and constructive suggestions from others (TPE 13) 5.000 1 4.7143 7 4.2500 8 FYI/JYI 39 Teacher Performance Assessment (PACT Teaching Event) On the following pages are tables providing the means for rubrics from the PACT Teaching Event, our state-required Teacher Performance Assessment, for the three school years. Please note that these tables combine data from all pathways. Performance Assessment for California Teachers (PACT) Teaching Event Single Subject Credential Fall 2012 and Spring 2013 Fall 2012 Spring 2013 Rubric Mean N Mean N Establishing a balanced instructional focus 2.64 56 2.79 77 Making content accessible 2.52 56 2.53 78 Designing assessments 2.48 56 2.57 77 Engaging students in learning 2.30 56 2.31 77 Monitoring student learning 2.20 56 2.26 77 Analyzing student work from an assessment 2.26 57 2.37 78 Using assessment to inform instructional decisions 2.18 57 2.23 79 Providing feedback 2.32 57 2.33 78 Monitoring student progress 2.41 56 2.28 78 Reflecting on learning using theoretical research 2.45 56 2.31 77 Understanding Language Demands 2.05 55 2.25 76 Supporting academic language development 2.20 55 2.18 76 Notes: 1=Unsatisfactory, 2=Satisfactory (passing), 3=Strong, 4=Exemplary 40 CSU Exit Survey (Program Completers’ Perceptions) 41 CSU Exit Survey – Teacher Preparation: Part I Single Subject Credential: Traditional Pathway 2012-2013 Completers N Well prepared Adequately prepared Somewhat prepared Not at all prepared ...to prepare lesson plans and make prior arrangements for students' class activities. 58 74% 17% 5% 2% ...to organize and manage a class or a group of students for instructional activities 58 69% 21% 5% 2% ...to organize and manage student behavior and discipline satisfactorily. 58 52% 33% 12% 2% ...to use an effective mix of teaching strategies and instructional activities. 58 64% 28% 5% 2% ...to meet the instructional needs of students who are English language learners. 58 38% 48% 10% 2% ...to meet the instructional needs of students from diverse cultural backgrounds. 58 47% 38% 12% 2% ...to meet the instructional needs of students with special learning needs. 57 32% 49% 18% 2% ...to understand how personal, family and community conditions often affect learning. 58 57% 33% 7% 2% ...to learn about my students' interests and motivations, and how to teach accordingly. 58 64% 26% 7% 2% ...to get students involved in engaging activities and to sustain on-task behavior. 58 59% 29% 9% 2% ...to use computer-based technology to help students learn subjects of the curriculum. 58 62% 28% 7% 2% ...to use computer-based technology for instruction, research, and record keeping.. 58 66% 28% 3% 2% ...to monitor student progress by using formal and informal assessment methods. 58 60% 29% 7% 2% ...to assess pupil progress by analyzing a variety of evidence including exam scores. 58 53% 38% 5% 2% ...to adjust my teaching strategies so all pupils have chances to understand and learn. 58 53% 38% 5% 2% ...to adhere to principles of educational equity in the teaching of all students. 58 69% 22% 5% 2% ...to use class time efficiently by relying on daily routines and planned transitions. 58 67% 21% 9% 2% ...to know about resources in the school & community for at-risk students and families. 58 41% 33% 21% 3% ...to communicate effectively with the parents or guardians of my students. 58 47% 29% 19% 2% ...to work collaboratively on school issues with other teachers in our school. 58 53% 24% 17% 2% ...to think about problems that occur in teaching and to try-out various solutions. 58 57% 31% 9% 2% ...to understand my professional, legal, and ethical obligations. 58 64% 24% 9% 2% ...to evaluate and reflect and seek out assistance that leads to professional growth. 58 74% 19% 3% 2% As a new teacher, I am ... 42 CSU Exit Survey – Teacher Preparation: Part II Single Subject Credential: Traditional Pathway 2012-2013 Completers N Well prepared Adequately prepared Somewhat prepared Not at all prepared ...to know and understand the subject(s) in which I earned my teaching credential(s). 58 79% 19% 0% 2% ...to teach my primary subject according to State Academic Standards in my grade(s) 58 76% 22% 2% 0% ...to contribute to students' reading skills including comprehension in my subject area. 58 55% 40% 5% 0% ...to use textbooks and other materials that are aligned with State Standards in my area. 58 67% 26% 7% 0% ...to recognize adolescence as a period of intense pressure for students to be like peers 58 67% 29% 2% 2% ...to anticipate and address issues of drug, alcohol and tobacco use by my students. 58 41% 34% 17% 7% ...to anticipate and address possession of weapons and threats of violence at school. 58 41% 24% 24% 10% ...to anticipate and address the needs of students who are at risk of dropping out. 58 43% 31% 22% 3% ...to understand adolescent development, human learning and the purposes of schools 58 57% 38% 3% 2% ...to assist individual students in areas of their instructional needs in my subject area. 58 71% 22% 5% 2% ...to establish academic expectations that are intellectually challenging for students. 58 72% 22% 5% 0% ...to provide opportunities for students to develop advanced problem-solving skills. 57 58% 37% 4% 2% ...to communicate my course goals and requirements to students and parents. 58 72% 22% 3% 2% ...to develop fair criteria for course grades and to explain these to students and parents. 57 72% 19% 9% 0% ...to help students realize the connections between my subject and life beyond school. 58 64% 33% 3% 0% ...to help students realize the impact of academic choices on life- and career-options. 58 69% 24% 7% 0% ...to encourage/enable students to assume increasing responsibility for their learning. 58 72% 24% 3% 0% ...to encourage/enable students to learn behaviors that contribute to future success. 58 72% 22% 3% 2% As a new teacher, I am ... 43 CSU Exit Survey – Instructional Preparation Single Subject Credential: Traditional Pathway 2012-2013 Completers Instruction in your Teaching Credential Program Instruction in how children and adolescents grow and develop. Instruction in the implications of human learning and motivation. Instruction in school purposes, organization, issues and history. Instruction in methods of classroom teaching and management. Instruction in the teaching of English language learners (ELL). Instruction in cultural diversity and multicultural education. Instruction in teaching students with special learning needs. Instruction in using computer technology for classroom instruction. Instruction in ways of teaching English classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Language Other than English classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Mathematics classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Music classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Art classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Physical Education classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Science (Biological Sciences) classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Science (Physics) classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Science (Chemistry) classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Science (Geosciences) classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Health Science classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Social Science classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Agriculture classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Business classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Home Economics classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Industrial and Technology classes in grades 7-12. N Well prepared Adequately prepared Somewhat prepared Not at all prepared 56 55 55 55 56 57 57 56 57 57 57 57 57 57 56 57 57 57 57 57 57 57 57 57 52% 51% 33% 65% 50% 51% 44% 61% 21% 2% 19% 7% 0% 2% 7% 4% 2% 2% 0% 7% 0% 0% 0% 0% 36% 36% 51% 27% 29% 32% 35% 23% 4% 2% 5% 4% 0% 0% 2% 4% 4% 2% 0% 5% 0% 0% 0% 0% 7% 7% 11% 2% 16% 12% 16% 9% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 4% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 0% 0% 0% 0% 5% 5% 5% 5% 5% 5% 5% 7% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 44 CSU Exit Survey – Value and Helpfulness of Program Single Subject Credential: Traditional Pathway 2012-2013 Completers N Very valuable Somewhat valuable Little Value No value My supervised teaching experiences in K-12 schools. 57 86% 14% 0% 0% My fieldwork (e.g., school visits, observations, school-based course assignments, etc.) and observations prior to supervised teaching. 57 65% 28% 5% 2% Discussions sponsored by the university during student teaching. 48 54% 27% 13% 6% Guidance and assistance from field supervisor(s) from the campus. 56 79% 13% 9% 0% Guidance and assistance from supervising teacher(s) in K-12 schools. 56 86% 11% 2% 2% Information and support provided in initial program orientation. 55 47% 22% 24% 7% Information, support, and solutions provided by the credentials office 56 36% 25% 29% 11% Information, support and advice provided by faculty advisor(s) 56 64% 23% 9% 4% Information provided in written materials (e.g., handbook, catalogues, website) 57 49% 26% 16% 9% Rate the value of these elements of your credential program: 45 CSU Exit Survey – Teacher Preparation: Part I Single Subject Credential: Intern Pathway 2012-2013 Completers As a new teacher, I am ... ...to prepare lesson plans and make prior arrangements for students' class activities. ...to organize and manage a class or a group of students for instructional activities ...to organize and manage student behavior and discipline satisfactorily. ...to use an effective mix of teaching strategies and instructional activities. ...to meet the instructional needs of students who are English language learners. ...to meet the instructional needs of students from diverse cultural backgrounds. ...to meet the instructional needs of students with special learning needs. ...to understand how personal, family and community conditions often affect learning. ...to learn about my students' interests and motivations, and how to teach accordingly. ...to get students involved in engaging activities and to sustain on-task behavior. ...to use computer-based technology to help students learn subjects of the curriculum. ...to use computer-based technology for instruction, research, and record keeping.. ...to monitor student progress by using formal and informal assessment methods. ...to assess pupil progress by analyzing a variety of evidence including exam scores. ...to adjust my teaching strategies so all pupils have chances to understand and learn. ...to adhere to principles of educational equity in the teaching of all students. ...to use class time efficiently by relying on daily routines and planned transitions. ...to know about resources in the school & community for at-risk students and families. ...to communicate effectively with the parents or guardians of my students. ...to work collaboratively on school issues with other teachers in our school. ...to think about problems that occur in teaching and to try-out various solutions. ...to understand my professional, legal, and ethical obligations. ...to evaluate and reflect and seek out assistance that leads to professional growth. N Well prepared Adequately prepared Somewhat prepared Not at all prepared 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 100% 33% 50% 100% 50% 50% 17% 50% 83% 67% 67% 67% 83% 83% 83% 67% 67% 67% 50% 83% 83% 67% 100% 0% 67% 50% 0% 33% 50% 50% 50% 17% 33% 33% 33% 17% 17% 17% 33% 33% 33% 33% 17% 0% 33% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 17% 0% 33% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 17% 0% 17% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 46 CSU Exit Survey – Teacher Preparation: Part II Single Subject Credential: Intern Pathway 2012-2013 Completers As a new teacher, I am ... ...to know and understand the subject(s) in which I earned my teaching credential(s). ...to teach my primary subject according to State Academic Standards in my grade(s) ...to contribute to students' reading skills including comprehension in my subject area. ...to use textbooks and other materials that are aligned with State Standards in my area. ...to recognize adolescence as a period of intense pressure for students to be like peers ...to anticipate and address issues of drug, alcohol and tobacco use by my students. ...to anticipate and address possession of weapons and threats of violence at school. ...to anticipate and address the needs of students who are at risk of dropping out. ...to understand adolescent development, human learning and the purposes of schools ...to assist individual students in areas of their instructional needs in my subject area. ...to establish academic expectations that are intellectually challenging for students. ...to provide opportunities for students to develop advanced problem-solving skills. ...to communicate my course goals and requirements to students and parents. ...to develop fair criteria for course grades and to explain these to students and parents. ...to help students realize the connections between my subject and life beyond school. ...to help students realize the impact of academic choices on life- and career-options. ...to encourage/enable students to assume increasing responsibility for their learning. ...to encourage/enable students to learn behaviors that contribute to future success. N Well prepared Adequately prepared Somewhat prepared Not at all prepared 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 67% 67% 50% 50% 67% 50% 33% 50% 50% 50% 50% 83% 67% 50% 83% 83% 83% 83% 33% 33% 50% 50% 33% 33% 67% 50% 50% 50% 50% 17% 33% 50% 17% 17% 17% 17% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 17% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 47 CSU Exit Survey – Instructional Preparation Single Subject Credential: Intern Pathway 2012-2013 Completers Instruction in your Teaching Credential Program Instruction in how children and adolescents grow and develop. Instruction in the implications of human learning and motivation. Instruction in school purposes, organization, issues and history. Instruction in methods of classroom teaching and management. Instruction in the teaching of English language learners (ELL). Instruction in cultural diversity and multicultural education. Instruction in teaching students with special learning needs. Instruction in using computer technology for classroom instruction. Instruction in ways of teaching English classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Language Other than English classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Mathematics classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Music classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Art classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Physical Education classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Science (Biological Sciences) classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Science (Physics) classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Science (Chemistry) classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Science (Geosciences) classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Health Science classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Social Science classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Agriculture classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Business classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Home Economics classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Industrial and Technology classes in grades 7-12. N Well prepared Adequately prepared Somewhat prepared Not at all prepared 6 6 6 6 6 5 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 50% 33% 33% 50% 50% 40% 50% 50% 0% 0% 33% 0% 0% 17% 33% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 50% 50% 50% 50% 33% 20% 33% 50% 17% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 17% 17% 0% 0% 20% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 17% 20% 17% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 48 CSU Exit Survey – Value and Helpfulness of Program Single Subject Credential: Intern Pathway 2012-2013 Completers N Very valuable Somewhat valuable Little Value No value My supervised teaching experiences in K-12 schools. 6 67% 17% 17% 0% My fieldwork (e.g., school visits, observations, school-based course assignments, etc.) and observations prior to supervised teaching. 6 67% 17% 17% 0% Discussions sponsored by the university during student teaching. 6 67% 17% 17% 0% Guidance and assistance from field supervisor(s) from the campus. 6 67% 17% 17% 0% Guidance and assistance from supervising teacher(s) in K-12 schools. 6 67% 33% 0% 0% Information and support provided in initial program orientation. 6 50% 0% 50% 0% Information, support, and solutions provided by the credentials office 6 33% 0% 33% 33% Information, support and advice provided by faculty advisor(s) 6 50% 0% 50% 0% Information provided in written materials (e.g., handbook, catalogues, website) 6 50% 33% 17% 0% Rate the value of these elements of your credential program: 49 CSU Exit Survey – Teacher Preparation: Part I Single Subject Credential: ACT Pathway 2012-2013 Completers As a new teacher, I am ... ...to prepare lesson plans and make prior arrangements for students' class activities. ...to organize and manage a class or a group of students for instructional activities ...to organize and manage student behavior and discipline satisfactorily. ...to use an effective mix of teaching strategies and instructional activities. ...to meet the instructional needs of students who are English language learners. ...to meet the instructional needs of students from diverse cultural backgrounds. ...to meet the instructional needs of students with special learning needs. ...to understand how personal, family and community conditions often affect learning. ...to learn about my students' interests and motivations, and how to teach accordingly. ...to get students involved in engaging activities and to sustain on-task behavior. ...to use computer-based technology to help students learn subjects of the curriculum. ...to use computer-based technology for instruction, research, and record keeping.. ...to monitor student progress by using formal and informal assessment methods. ...to assess pupil progress by analyzing a variety of evidence including exam scores. ...to adjust my teaching strategies so all pupils have chances to understand and learn. ...to adhere to principles of educational equity in the teaching of all students. ...to use class time efficiently by relying on daily routines and planned transitions. ...to know about resources in the school & community for at-risk students and families. ...to communicate effectively with the parents or guardians of my students. ...to work collaboratively on school issues with other teachers in our school. ...to think about problems that occur in teaching and to try-out various solutions. ...to understand my professional, legal, and ethical obligations. ...to evaluate and reflect and seek out assistance that leads to professional growth. N Well prepared Adequately prepared Somewhat prepared Not at all prepared 16 16 16 16 16 16 15 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 81% 63% 44% 69% 63% 69% 47% 81% 69% 56% 56% 69% 69% 75% 75% 63% 63% 56% 63% 63% 75% 75% 81% 6% 25% 44% 19% 19% 25% 33% 6% 19% 25% 25% 19% 19% 13% 19% 31% 25% 19% 19% 19% 13% 19% 13% 6% 6% 6% 6% 6% 0% 13% 0% 6% 13% 13% 6% 0% 0% 0% 0% 6% 13% 6% 6% 6% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 6% 0% 7% 6% 0% 0% 0% 0% 6% 6% 0% 0% 0% 6% 6% 6% 0% 0% 0% 50 CSU Exit Survey – Teacher Preparation: Part II Single Subject Credential: ACT Pathway 2012-2013 Completers As a new teacher, I am ... ...to know and understand the subject(s) in which I earned my teaching credential(s). ...to teach my primary subject according to State Academic Standards in my grade(s) ...to contribute to students' reading skills including comprehension in my subject area. ...to use textbooks and other materials that are aligned with State Standards in my area. ...to recognize adolescence as a period of intense pressure for students to be like peers ...to anticipate and address issues of drug, alcohol and tobacco use by my students. ...to anticipate and address possession of weapons and threats of violence at school. ...to anticipate and address the needs of students who are at risk of dropping out. ...to understand adolescent development, human learning and the purposes of schools ...to assist individual students in areas of their instructional needs in my subject area. ...to establish academic expectations that are intellectually challenging for students. ...to provide opportunities for students to develop advanced problem-solving skills. ...to communicate my course goals and requirements to students and parents. ...to develop fair criteria for course grades and to explain these to students and parents. ...to help students realize the connections between my subject and life beyond school. ...to help students realize the impact of academic choices on life- and career-options. ...to encourage/enable students to assume increasing responsibility for their learning. ...to encourage/enable students to learn behaviors that contribute to future success. N Well prepared Adequately prepared Somewhat prepared Not at all prepared 15 15 15 15 14 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 93% 100% 53% 93% 93% 67% 53% 60% 80% 87% 80% 73% 87% 87% 73% 67% 73% 73% 7% 0% 47% 7% 0% 20% 20% 20% 13% 7% 13% 20% 7% 7% 20% 27% 20% 20% 0% 0% 0% 0% 7% 7% 13% 13% 7% 0% 0% 7% 0% 0% 7% 7% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 7% 13% 7% 0% 7% 7% 0% 7% 7% 0% 0% 7% 7% 51 CSU Exit Survey – Instructional Preparation Single Subject Credential: ACT Pathway 2012-2013 Completers Instruction in your Teaching Credential Program Instruction in how children and adolescents grow and develop. Instruction in the implications of human learning and motivation. Instruction in school purposes, organization, issues and history. Instruction in methods of classroom teaching and management. Instruction in the teaching of English language learners (ELL). Instruction in cultural diversity and multicultural education. Instruction in teaching students with special learning needs. Instruction in using computer technology for classroom instruction. Instruction in ways of teaching English classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Language Other than English classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Mathematics classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Music classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Art classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Physical Education classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Science (Biological Sciences) classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Science (Physics) classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Science (Chemistry) classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Science (Geosciences) classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Health Science classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Social Science classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Agriculture classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Business classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Home Economics classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching Industrial and Technology classes in grades 7-12. N Well prepared Adequately prepared Somewhat prepared Not at all prepared 15 15 15 15 15 14 15 14 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 73% 87% 53% 80% 80% 100% 87% 57% 25% 6% 44% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 6% 6% 0% 0% 0% 0% 27% 13% 27% 20% 13% 0% 13% 36% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 6% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 20% 0% 7% 0% 0% 7% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 52 CSU Exit Survey – Value and Helpfulness of Program Single Subject Credential: ACT Pathway 2012-2013 Completers N Very valuable Somewhat valuable Little Value No value My supervised teaching experiences in K-12 schools. 15 87% 13% 0% 0% My fieldwork (e.g., school visits, observations, school-based course assignments, etc.) and observations prior to supervised teaching. 15 87% 13% 0% 0% Discussions sponsored by the university during student teaching. 14 50% 36% 14% 0% Guidance and assistance from field supervisor(s) from the campus. 15 53% 40% 0% 7% Guidance and assistance from supervising teacher(s) in K-12 schools. 15 67% 33% 0% 0% Information and support provided in initial program orientation. 15 67% 33% 0% 0% Information, support, and solutions provided by the credentials office 14 43% 43% 7% 7% Information, support and advice provided by faculty advisor(s) 15 80% 20% 0% 0% Information provided in written materials (e.g., handbook, catalogues, website) 15 87% 13% 0% 0% Rate the value of these elements of your credential program: 53 CSU Exit Survey – Teacher Preparation: Part I Single Subject Credential: FYI Pathway 2012-2013 Completers As a new teacher, I am ... ...to prepare lesson plans and make prior arrangements for students' class activities. ...to organize and manage a class or a group of students for instructional activities ...to organize and manage student behavior and discipline satisfactorily. ...to use an effective mix of teaching strategies and instructional activities. ...to meet the instructional needs of students who are English language learners. ...to meet the instructional needs of students from diverse cultural backgrounds. ...to meet the instructional needs of students with special learning needs. ...to understand how personal, family and community conditions often affect learning. ...to learn about my students' interests and motivations, and how to teach accordingly. ...to get students involved in engaging activities and to sustain on-task behavior. ...to use computer-based technology to help students learn subjects of the curriculum. ...to use computer-based technology for instruction, research, and record keeping.. ...to monitor student progress by using formal and informal assessment methods. ...to assess pupil progress by analyzing a variety of evidence including exam scores. ...to adjust my teaching strategies so all pupils have chances to understand and learn. ...to adhere to principles of educational equity in the teaching of all students. ...to use class time efficiently by relying on daily routines and planned transitions. ...to know about resources in the school & community for at-risk students and families. ...to communicate effectively with the parents or guardians of my students. ...to work collaboratively on school issues with other teachers in our school. ...to think about problems that occur in teaching and to try-out various solutions. ...to understand my professional, legal, and ethical obligations. ...to evaluate and reflect and seek out assistance that leads to professional growth. N Well prepared Adequately prepared Somewhat prepared Not at all prepared 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 50% 75% 50% 75% 50% 75% 75% 100% 75% 50% 100% 100% 75% 75% 100% 100% 100% 25% 50% 25% 50% 75% 75% 50% 25% 50% 25% 50% 25% 25% 0% 25% 50% 0% 0% 25% 25% 0% 0% 0% 75% 50% 50% 25% 0% 25% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 25% 25% 25% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 54 CSU Exit Survey – Teacher Preparation: Part II Single Subject Credential: FYI Pathway 2012-2013 Completers As a new teacher, I am ... ...to know and understand the subject(s) in which I earned my teaching credential(s). ...to teach my primary subject according to State Academic Standards in my grade(s) ...to contribute to students' reading skills including comprehension in my subject area. ...to use textbooks and other materials that are aligned with State Standards in my area. ...to recognize adolescence as a period of intense pressure for students to be like peers ...to anticipate and address issues of drug, alcohol and tobacco use by my students. ...to anticipate and address possession of weapons and threats of violence at school. ...to anticipate and address the needs of students who are at risk of dropping out. ...to understand adolescent development, human learning and the purposes of schools ...to assist individual students in areas of their instructional needs in my subject area. ...to establish academic expectations that are intellectually challenging for students. ...to provide opportunities for students to develop advanced problem-solving skills. ...to communicate my course goals and requirements to students and parents. ...to develop fair criteria for course grades and to explain these to students and parents. ...to help students realize the connections between my subject and life beyond school. ...to help students realize the impact of academic choices on life- and career-options. ...to encourage/enable students to assume increasing responsibility for their learning. ...to encourage/enable students to learn behaviors that contribute to future success. N Well prepared Adequately prepared Somewhat prepared Not at all prepared 4 4 4 3 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 3 4 4 4 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 50% 25% 50% 75% 75% 75% 75% 100% 100% 67% 100% 100% 100% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 50% 75% 50% 25% 25% 25% 25% 0% 0% 33% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 55 CSU Exit Survey – Instructional Preparation Single Subject Credential: FYI Pathway 2012-2013 Completers N Well prepared Adequately prepared Somewhat prepared Not at all prepared Instruction in ways of teaching English classes in grades 7-12. 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 50% 75% 25% 100% 50% 100% 75% 100% 100% 25% 0% 50% 0% 50% 0% 25% 0% 0% 25% 25% 25% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% Instruction in ways of teaching Language Other than English classes in grades 7-12. 5 0% 0% 0% 0% Instruction in ways of teaching Mathematics classes in grades 7-12. 5 0% 0% 0% 0% Instruction in your Teaching Credential Program Instruction in how children and adolescents grow and develop. Instruction in the implications of human learning and motivation. Instruction in school purposes, organization, issues and history. Instruction in methods of classroom teaching and management. Instruction in the teaching of English language learners (ELL). Instruction in cultural diversity and multicultural education. Instruction in teaching students with special learning needs. Instruction in using computer technology for classroom instruction. 56 CSU Exit Survey – Value and Helpfulness of Program Single Subject Credential: FYI Pathway 2012-2013 Completers N Very valuable Somewhat valuable Little Value No value My supervised teaching experiences in K-12 schools. 4 75% 25% 0% 0% My fieldwork (e.g., school visits, observations, school-based course assignments, etc.) and observations prior to supervised teaching. 4 75% 25% 0% 0% Discussions sponsored by the university during student teaching. 4 75% 25% 0% 0% Guidance and assistance from field supervisor(s) from the campus. 4 75% 25% 0% 0% Guidance and assistance from supervising teacher(s) in K-12 schools. 4 100% 0% 0% 0% Information and support provided in initial program orientation. 4 75% 25% 0% 0% Information, support, and solutions provided by the credentials office 4 50% 0% 50% 0% Information, support and advice provided by faculty advisor(s) 4 75% 0% 25% 0% Information provided in written materials (e.g., handbook, catalogues, website) 4 50% 25% 25% 0% Rate the value of these elements of your credential program: 57 CSU Follow-Up Survey (Completers’ Perceptions) The tables on the following pages show the ratings by our program completers (combining all pathways) after they had taught in Grades 7 – 12 for one year past earning their credential, compared to the responses across the CSU system as a whole. Effectiveness of 2011-12 CSU Single Subject Credential Programs as Evaluated by First-Year Teaching Graduates in 2013 General Concepts and Practices of Teaching This CSU Campus: Single Subject Programs Evaluation Questions Answered in 2013 by Teachers in Grades 7-12 Who Completed CSU Single Subject Credential Programs in 2011-12: (4) (5) (6) Mean SD N 21% 2.21 .79 418 87% 68% 32% 1.84 .96 426 19 53% 47% 1.53 .96 4 . . . prepare lesson plans and make prior arrangements for class activities. 19 74% 26% 2.11 5 . . . use an effective mix of teaching strategies and instructional activities. 19 79% 21% 6 . . . meet the instructional needs of students who are English language learners. 19 63% 7 . . . meet the instructional needs of students from diverse cultural backgrounds. 19 8 . . . meet the instructional needs of students with special learning needs. (1) (2) All CSU Campuses: Single Subject Programs (9) (10) Mean SD 13% 2.44 .73 73% 27% 2.07 .88 428 53% 47% 1.65 .98 .81 426 84% 16% 2.33 .77 2.16 .90 423 78% 22% 2.16 .85 37% 1.84 1.12 423 70% 30% 1.99 .88 89% 11% 2.37 .68 423 76% 24% 2.10 .86 19 74% 26% 1.89 1.05 423 64% 36% 1.82 .93 9 . . . communicate effectively with the parents or guardians of your students. 19 58% 42% 1.79 .92 419 62% 38% 1.80 .99 10 . . . maintain positive rapport and foster students' motivation and excitement. 19 74% 26% 2.11 .94 426 84% 16% 2.30 .80 11 . . . think about problems that occur in teaching and try out various solutions. 19 68% 32% 1.79 .92 421 75% 25% 2.05 .88 Once you finished your CSU credential program in 2012, and when you served as a 7-12 teacher in 2012-13, how well prepared were you to . . . N 1 . . . know and understand the subjects of the curriculum at your grade level(s). 19 79% 2 . . . organize and manage a class or a group of pupils for instructional activities. 19 3 . . . organize and manage student behavior and discipline satisfactorily. (3) Well or Somewhat Adequately or Not Prepared Prepared (7) (8) Well or Somewhat Adequately or Not Prepared Prepared 58 This CSU Campus: Single Subject Programs Evaluation Questions Answered in 2013 by Teachers in Grades 7-12 Who Completed CSU Single Subject Credential Programs During 2011-12: (4) (5) (6) Mean SD N 26% 2.00 1.00 423 76% 74% 26% 2.11 1.05 423 19 74% 26% 2.00 1.00 15 . . . get students involved in engaging activities and to sustain on-task behavior. 19 63% 37% 1.68 16 . . . use computer-based applications to help students learn curriculum subjects. 19 53% 47% 17 . . . use computer-based technology in class activities and to keep class records. 19 63% 18 . . . monitor student progress by using formal and informal assessment methods. 19 19 . . . assess pupil progress by analyzing a variety of evidence including test scores. (1) (2) All CSU Campuses: Single Subject Programs (9) (10) Mean SD 24% 2.11 .84 77% 23% 2.14 .87 423 78% 22% 2.14 .86 1.11 427 73% 27% 2.02 .90 1.74 1.05 420 60% 40% 1.79 1.01 37% 1.89 .94 417 65% 35% 1.92 1.00 74% 26% 2.11 .94 423 84% 16% 2.28 .80 19 74% 26% 2.05 1.03 424 79% 21% 2.14 .87 20 . . . assist individual students in areas of their instructional needs in reading/math. 19 68% 32% 2.11 .99 421 80% 20% 2.21 .84 21 . . . adjust teaching strategies so all pupils have chances to understand and learn. 19 74% 26% 1.89 1.05 422 76% 24% 2.10 .86 22 . . . adhere to principles of educational equity in the teaching of all students. 19 68% 32% 2.16 1.01 419 81% 19% 2.24 .84 23 . . . use class time efficiently by relying on daily routines and planned transitions. 19 74% 26% 1.95 .97 424 80% 20% 2.18 .86 24 . . . know about resources in the school & community for at-risk students/families. 19 32% 68% 1.37 1.01 417 54% 46% 1.61 .97 Once you finished your CSU credential program in 2012, and when you served as a 7-12 teacher in 2012-13, how well prepared were you to . . . N 12 . . . understand adolescent growth, human learning and the purposes of schools. 19 74% 13 . . . understand how personal, family and community conditions affect learning. 19 14 . . . learn about students’ interests and motivations, and how to teach accordingly. (3) Well or Somewhat Adequately or Not Prepared Prepared (7) (8) Well or Somewhat Adequately or Not Prepared Prepared 59 Effectiveness of 2011-12 CSU Single Subject Credential Programs as Evaluated by First-Year Teaching Graduates in 2013 Concepts and Practices for Single Subject Teaching (K-8) This CSU Campus: Single Subject Programs Evaluation Questions Answered in 2013 by First-Year 7-12 Teachers Who Completed CSU Single Subject Credential Programs During 2011-12: (1) Once you finished your CSU credential program in 2011-12, and when you were a 7-12 teacher in 2012-13, how well prepared were you to . . . A. 1 N (2) (3) Well or Somewhat Adequately or Not Prepared Prepared All CSU Campuses: Single Subject Programs (4) (5) (6) Mean SD N (7) (8) Well or Somewhat Adequately or Not Prepared Prepared (9) (10) Mean SD General Preparation for Teaching Major Subjects in Grades 7-12 . . . teach your primary subject according to State Academic Content Standards. 19 84% 16% 2.26 .87 421 86% 14% 2.35 .76 2 . . . use textbooks and other materials aligned with State Content Standards. 19 68% 32% 1.95 1.03 412 73% 27% 2.08 .93 3 . . . contribute to students’ reading skills including vocabulary and comprehension. 19 68% 32% 1.74 .99 418 65% 35% 1.85 .92 4 . . . recognize adolescence as a period of pressure for students to be like their peers. 19 79% 21% 2.21 1.03 424 79% 21% 2.19 .88 5 . . . anticipate and address the needs of students who are at-risk of dropping out. 19 32% 68% 1.11 1.10 417 46% 54% 1.46 .98 6 . . . establish academic expectations that are intellectually challenging for students. 19 68% 32% 1.79 1.03 420 79% 21% 2.11 .86 7 . . . provide opportunities for students to develop advanced problem-solving skills. 19 68% 32% 1.79 .79 420 71% 29% 1.96 .92 8 . . . communicate your course goals and requirements to students and their parents. 19 79% 21% 2.11 .88 419 78% 22% 2.16 .90 9 . . . develop fair criteria for course grades and explain these to students/parents. 19 74% 26% 2.05 .91 419 77% 23% 2.12 .91 10 . . . help students realize connections between your subject and life beyond school. 12 75% 25% 1.83 1.03 286 80% 20% 2.20 .82 11 . . . encourage/enable pupils to assume increasing responsibility for their learning. 6 50% 50% 1.67 1.51 232 77% 23% 2.09 .83 60 Value/Helpfulness of 2011-12 CSU Single Subject Credential Programs as Evaluated by First-Year Teaching Graduates in 2013 CSU Coursework and Fieldwork in Learning to Teach This CSU Campus: Single Subject Programs Questions Answered by Graduates of Single Subject Credential Programs: All CSU Campuses: Single Subject Programs (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) Based on your experience as a 7-12 teacher this year, how valuable or helpful was coursework and fieldwork in your CSU credential program? N Very or Somewhat Valuable A Little or Not Valuable Mean SD N A. How Valuable or Helpful was CSU Instruction in General Pedagogy? 1. Instruction in how children and adolescents grow and develop. 2. Instruction in the implications of human learning and motivation. 3. Instruction in school purposes, organization, issues and history. 4. Instruction in methods of classroom teaching and management. 5. Instruction in the teaching of English language learners (ELL). 6. Instruction in cultural diversity and multicultural education. 7. Instruction in teaching students with special learning needs. 8. Instruction in ways to communicate effectively with parents. 9. Instruction in ways to reflect on and improve my teaching practices. 16 16 17 16 17 17 16 16 17 88% 75% 53% 69% 88% 88% 69% 63% 82% 13% 25% 47% 31% 12% 12% 31% 38% 18% 2.31 2.13 1.71 2.19 2.35 2.41 2.06 2.06 2.41 .70 .96 1.05 1.05 .70 .71 1.00 .93 .94 400 402 394 405 407 408 402 384 405 76% 75% 68% 80% 79% 75% 73% 66% 81% B. How Valuable or Helpful Were Fieldwork Assignments in CSU Programs? 10. Your supervised teaching experiences in K-12 schools. 11. Your school visits and observations prior to supervised teaching. 12. Off-campus fieldwork assignments in my reading methods class. 13. Guidance and assistance provided by field supervisor(s) from the CSU. 14. Guidance and assistance provided by supervising teacher(s) in K-12 schools. 17 17 14 17 17 88% 76% 50% 82% 94% 12% 24% 50% 18% 6% 2.71 2.41 1.71 2.41 2.76 .69 .87 .99 .94 .56 407 405 321 407 410 C. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 2 4 5 2 -1 2 100% 100% 100% 50% -0% 100% 0% 0% 0% 50% -100% 0% 3.00 2.75 2.80 1.00 -1.00 3.00 5.29 2.47 2.26 1.41 --5.29 83 92 70 72 23 30 38 How Valuable or Helpful Was CSU Instruction in 7-12 Subject Pedagogy? Instruction in ways of teaching English classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching mathematics classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching science classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching history and social studies classes 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching foreign language classes in grades 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching art, music, drama and/or dance in 7-12. Instruction in ways of teaching physical education in grades 7-12. (7) (8) (9) (10) Mean SD 24% 25% 32% 20% 21% 25% 27% 34% 19% 2.11 2.09 1.91 2.25 2.13 2.06 2.05 1.87 2.32 .90 .90 .95 .87 .88 .98 .97 .98 .88 91% 82% 64% 83% 90% 9% 18% 36% 17% 10% 2.63 2.30 1.84 2.36 2.56 .72 .85 1.02 .89 .77 80% 83% 83% 88% 83% 87% 87% 20% 17% 17% 13% 17% 13% 13% 2.24 2.37 2.39 2.50 2.35 2.47 2.47 .94 .90 .91 .79 .88 .73 .80 Very or A Little Somewhat or Not Valuable Valuable 61 This CSU Campus: Single Subject Programs Questions Answered by Graduates of Single Subject Credential Programs: Based on your experience as a 7-12 teacher this year, how valuable or helpful was coursework and fieldwork in your CSU credential program? (1) N (2) (3) Very or A Little Somewhat or Not Valuable Valuable (4) All CSU Campuses: Single Subject Programs (5) (6) Mean SD N (7) (8) Very or A Little Somewhat or Not Valuable Valuable (9) (10) Mean SD A. How Valuable was CSU Instruction in California’s Academic Standards? 1. Instruction in the state’s academic content standards in my subject area. 17 82% 18% 2.47 .80 404 84% 16% 2.35 .85 2. Instruction in how to establish challenging academic expectations for students. 17 65% 35% 2.00 1.00 404 78% 22% 2.13 .88 B. CSU Instruction in the Role of Reading Lessons in Content Classes 3. Instruction on how reading instruction can add to content classes. 17 82% 18% 2.12 .99 399 73% 27% 2.05 .97 4. Instruction in how to develop academic vocabulary and writing skills. 17 82% 18% 2.29 .92 405 77% 23% 2.09 .94 5. Instruction in ways to develop my students’ general language skills. 17 71% 29% 2.12 .99 401 75% 25% 2.04 .91 C. How Valuable or Helpful was CSU Instruction in Education Technology? 6. Instruction in using computer technology for classroom instruction. 17 82% 18% 2.35 .79 394 69% 31% 1.92 1.01 7. Instruction in helping students use computers for class assignments. 17 82% 18% 2.29 .77 372 64% 36% 1.80 1.06 8. Instruction in computer terminology and operating procedures. 16 81% 19% 2.37 .81 369 63% 37% 1.75 1.08 9. Instruction in ways to use electronic media and educational websites. 16 75% 25% 2.19 .98 384 68% 32% 1.89 1.03 10. Instruction in ways to use software programs for group presentations. 16 75% 25% 2.19 .83 371 64% 36% 1.77 1.08 11. Instruction in federal and state laws that govern special education. 4 50% 50% 2.00 1.15 169 73% 27% 2.08 .96 12. Instruction in the assessment of students with disabilities. 4 75% 25% 2.50 1.00 163 72% 28% 2.00 .97 13. Instruction in positive behavioral support techniques. 4 75% 25% 2.50 1.00 169 76% 24% 2.12 .92 14. Instruction in adapting instruction for students with disabilities. 4 75% 25% 2.50 1.00 168 79% 21% 2.15 .90 15. Instruction in research-based teaching of students with disabilities. 4 75% 25% 2.50 1.00 163 71% 29% 1.94 .95 D. How Valuable or Helpful Was CSU Instruction in Inclusive Education? 62 Quality of Pedagogical Preparation Programs as Evaluated by First-Year Teaching Graduates in 2013 Relation to Professional Accreditation Standards in California This CSU Campus: Program Qualities Evaluated by SS Program Graduates: While you were enrolled in the CSU Credential Program that you finished, how true was each of the following statements about the program? All CSU Campuses: Single Subject Credential Programs Single Subject Credential Programs (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) (10) N True or Mostly True Somewhat Or Not True Mean SD N True or Mostly True Somewhat Or Not True Mean SD 1. The program had a sequence of courses and school experiences that addressed the complexities of teaching gradually over time. 16 69% 31% 1.94 .77 396 65% 35% 1.93 .95 2. The program provided an appropriate mixture of theoretical ideas and practical strategies, and I learned about links between them. 16 63% 38% 1.94 .85 396 64% 36% 1.88 .95 3. During the program, I saw evidence that university faculty and administrators worked closely with educators in K-12 schools. 16 63% 38% 1.81 1.28 395 57% 43% 1.72 1.07 4. At each stage of the teaching credential program, I felt ready to assume a little more responsibility for K-12 student instruction. 16 75% 25% 2.25 1.00 395 80% 20% 2.22 .88 5. I taught in at least one school that was a good environment for practice teaching and for reflecting on how I was teaching students. 16 94% 6% 2.69 .79 395 89% 11% 2.56 .75 6. My supervising teacher(s) frequently observed my teaching, met with me and offered suggestions and advice about my teaching. 16 88% 13% 2.69 .70 395 83% 17% 2.44 .88 7. My university supervisor(s) occasionally observed my class, met with me and offered suggestions and advice about my teaching. 16 88% 13% 2.56 .73 394 88% 12% 2.55 .79 8. During supervised teaching, my university-based supervisor and cooperating teacher communicated effectively with each other. 16 63% 38% 1.87 1.09 392 70% 30% 2.10 1.05 9. Over time, the credential program and its curriculum met my needs as I prepared myself to become a good teacher. 16 75% 25% 2.19 1.11 397 75% 25% 2.13 .93 63 CSU Follow-Up Survey (Employers’ Perceptions) The tables on the following pages show the ratings by employment supervisors of our program completers (combining all pathways) after they had taught in Grades 7 – 12 for one year past earning their credential, compared to the responses across the CSU system as a whole. Effectiveness of 2011-12 CSU Single Subject Credential Programs as Evaluated by the Employment Supervisors of First-Year Teaching Graduates in 2013 General Concepts and Practices of Teaching This CSU Campus: Single Subject Programs Evaluation Questions Answered in 2013 by the 7-12 Employment Supervisors of Teaching Graduates of CSU Single Subject Credential Programs: (1) Based on your observations of and conferences with this teacher (who was named in the survey), please assess how well s/he was prepared to . . . N (2) (3) Well or Somewhat Adequately or Not Prepared Prepared All CSU Campuses: Single Subject Programs (4) (5) (6) Mean SD N (7) (8) Well or Somewhat Adequately or Not Prepared Prepared (9) (10) Mean SD 1 . . . know and understand the subjects of the curriculum at her/his grade level. 12 100% 0% 3.00 .00 306 93% 7% 2.62 .62 2 . . . organize and manage a class or a group of pupils for instructional activities. 12 83% 17% 2.42 .79 308 78% 22% 2.25 .88 3 . . . organize and manage student behavior and discipline satisfactorily. 12 83% 17% 2.25 .97 307 73% 27% 2.08 .96 4 . . . prepare lesson plans and make prior arrangements for class activities. 12 92% 8% 2.75 .62 309 88% 12% 2.46 .77 5 . . . use an effective mix of teaching strategies and instructional activities. 12 100% 0% 2.50 .52 308 82% 18% 2.27 .83 6 . . . meet the instructional needs of students who are English language learners. 13 92% 8% 2.31 .63 298 76% 24% 2.07 .82 7 . . . meet the instructional needs of students from diverse cultural backgrounds. 13 77% 23% 2.46 .88 307 78% 22% 2.12 .83 8 . . . meet the instructional needs of students with special learning needs. 13 85% 15% 2.31 .75 294 73% 27% 2.00 .82 9 . . . communicate effectively with the parents or guardians of his/her students. 13 85% 15% 2.31 .95 308 74% 26% 2.06 .84 10 . . . maintain positive rapport and foster students' motivation and excitement. 13 92% 8% 2.54 .88 310 81% 19% 2.29 .87 11 . . . think about problems that occur in teaching and try out various solutions. 11 82% 18% 2.18 .98 293 78% 22% 2.10 .85 64 This CSU Campus: Single Subject Programs Evaluation Questions Answered in 2013 by the 7-12 Employment Supervisors of Teaching Graduates of CSU Single Subject Credential Programs: (4) (5) (6) Mean SD N 15% 2.38 .96 304 80% 85% 15% 2.46 .97 303 13 92% 8% 2.46 .88 15 . . . get students involved in engaging activities and to sustain on-task behavior. 13 92% 8% 2.54 16 . . . use computer-based applications to help students learn curriculum subjects. 12 100% 0% 17 . . . use computer-based technology in class activities and to keep class records. 11 100% 18 . . . monitor student progress by using formal and informal assessment methods. 13 19 . . . assess pupil progress by analyzing a variety of evidence including test scores. (1) (2) All CSU Campuses: Single Subject Programs (9) (10) Mean SD 20% 2.16 .83 78% 22% 2.11 .85 306 79% 21% 2.15 .86 .66 309 76% 24% 2.17 .89 2.75 .45 274 88% 12% 2.34 .70 0% 2.82 .40 293 91% 9% 2.40 .66 92% 8% 2.54 .88 304 81% 19% 2.21 .83 13 92% 8% 2.54 .88 304 80% 20% 2.18 .84 20 . . . assist individual students in areas of their instructional needs in reading/math. 13 92% 8% 2.54 .66 304 81% 19% 2.23 .81 21 . . . adjust teaching strategies so all pupils have chances to understand and learn. 13 85% 15% 2.38 .77 307 75% 25% 2.10 .86 22 . . . adhere to principles of educational equity in the teaching of all students. 12 92% 8% 2.67 .65 294 86% 14% 2.31 .75 23 . . . use class time efficiently by relying on daily routines and planned transitions. 12 92% 8% 2.58 .67 301 81% 19% 2.24 .86 24 . . . know about resources in the school & community for at-risk students/families. 11 82% 18% 2.18 .98 279 73% 27% 1.98 .87 Based on your observations of and conferences with this teacher (who was named in the survey), please assess how well s/he was prepared to . . N 12 . . . understand adolescent growth, human learning and the purposes of schools. 13 85% 13 . . . understand how personal, family & community conditions may affect learning. 13 14 . . . learn about students’ interests and motivations, and how to teach accordingly. (3) Well or Somewhat Adequately or Not Prepared Prepared (7) (8) Well or Somewhat Adequately or Not Prepared Prepared 65 Effectiveness of 2011-12 CSU Single Subject Credential Programs as Evaluated by the Employment Supervisors of First-Year Teaching Graduates in 2013 General Concepts and Practices of Teaching of Grades 7-12 Teachers This CSU Campus: Single Subject Programs Evaluation Questions Answered in 2013 by the Employment Supervisors of 7-12 Teaching Graduates of CSU Single Subject Credential Programs: (1) Based on your observations of and conferences with this teacher (who was named in the survey), please assess how well s/he was prepared to . . . A. N (2) (3) Well or Somewhat Adequately or Not Prepared Prepared (4) All CSU Campuses: Single Subject Programs (5) (6) Mean SD N (7) (8) Well or Somewhat Adequately or Not Prepared Prepared (9) (10) Mean SD General Preparation for Teaching Major Subjects in Grades 7-12 1 . . . teach her/his primary subject according to State Academic Content Standards. 12 100% 0% 2.67 .49 304 88% 12% 2.44 .75 2 . . . use textbooks and other materials aligned with State Content Standards. 12 100% 0% 2.67 .49 285 86% 14% 2.35 .75 3 . . . contribute to students’ reading skills including vocabulary & comprehension. 11 82% 18% 2.27 .79 274 72% 28% 2.04 .93 4 . . . recognize adolescence as a period of pressure for students to be like peers. 12 92% 8% 2.58 .67 295 80% 20% 2.20 .89 5 . . . anticipate and address the needs of students who are at-risk of dropping out. 13 69% 31% 2.15 .90 288 68% 32% 1.90 .88 6 . . . establish academic expectations that are intellectually challenging. 12 92% 8% 2.42 .90 295 80% 20% 2.17 .83 7 . . . communicate course goals and requirements to students and their parents. 12 92% 8% 2.58 .67 295 82% 18% 2.21 .79 8 . . . develop fair criteria for course grades and explain these to students/parents. 12 92% 8% 2.42 .90 297 82% 18% 2.22 .82 66 Effectiveness of 2011-12 CSU Single Subject Credential Programs as Evaluated by the Employment Supervisors of First-Year Teaching Graduates in 2013 General Concepts and Practices of Teaching of Grades 7-12 Teachers This CSU Campus: Single Subject Programs Evaluation Questions Answered in 2013 by the Employment Supervisors of 712 Teaching Graduates of CSU Single Subject Credential Programs: (1) Based on your observations of and conferences with this teacher (who was named in the survey), please assess how well s/he was prepared to . . . N (2) (3) Well or Somewhat Adequately or Not Prepared Prepared (4) All CSU Campuses: Single Subject Programs (5) (6) Mean SD N (7) (8) Well or Somewhat Adequately or Not Prepared Prepared (9) (10) Mean SD A. Specific Preparation to Increase Reading Skills in Content Classes (7 - 12) 1 . . . understand how reading lessons can make content-based classes more effective. 12 83% 17% 2.17 .94 264 72% 28% 2.02 .92 2 . . . develop academic vocabulary and writing skills in content-based classes. 12 92% 8% 2.42 .67 276 75% 25% 2.11 .85 3 . . . draw on students’ experiences to motivate them to learn reading/writing skills. 8 100% 0% 2.75 .46 183 73% 27% 2.05 .88 4 . . . to understand terminology and procedures for computer hardware/software. 11 100% 0% 2.91 .30 281 91% 9% 2.43 .65 5 . . . use electronic media and educational websites during classroom instruction. 11 100% 0% 3.00 .00 279 89% 11% 2.37 .72 6 . . use software programs and media presentations during classroom instruction. 11 100% 0% 3.00 .00 283 92% 8% 2.53 .67 B. Specific Preparation to Use Education Technology for Instruction 67 PART III and IV – Analyses and Discussion of Candidate and Program Data and Use of Assessment Results to Improve Candidate and Program Performance Overall Analysis Ratings on the Student Teaching Evaluations (STEs) are remarkably consistent, clustering around a score of 4 (“strong”) across pathways, years, and items, suggesting that our overall program is effective in building day-to-day teaching competence that exceeds the basic level expected of a brandnew teacher. Ratings by graduates and their employers on the Exit and Follow-Up Surveys confirm that our graduates are generally well prepared for first-year teaching—in many areas better prepared than the average CSU credential graduate. That PACT Teaching Event scores for the same candidates hew more closely to the basic level (2) than strong (3) leads to several (non-exclusive) explanations: 1) STEs may have a local, upward bias avoided in the more systematic, objective scoring of PACT Teaching Events. If so, our candidates may not be as strong as the STEs indicate. One potential remedy has been our regular implementation, in the past few years, of semesterly cooperating-teacher workshops, where clarifying discussions of STE items and ratings are often on the agenda. 2) Our candidates may be stronger in the day-to-day teaching performances assessed by the STE than in the deep, content-specific analysis and theoretical application required by the PACT Teaching Event (see further discussion below). 3) Our candidates may simply put more effort into their student teaching than their PACT Teaching Event, perceiving student teaching as “real work” with real pupils and where the consequences of poor preparation are significant, immediate, and obvious, while the pass/fail PACT Teaching Event offers no tangible reward for extra effort. 68 Areas of Concern or Interest and Proposed or Implemented Changes Teaching English Learners One small trend in STEs, across years and pathways, is comparatively low ratings by cooperating teachers and supervisors on the two STE items related to working with English learners (ELs), with candidates in the ACT pathway scoring lower than Traditional candidates. (Interns and FYI/JYI scores are not included in this comparison because of small Ns.) On Item 3.6, “Prepares lesson plans that address California English Language Development standards for English learners,” Traditional candidates’ scores ranged from 3.22 (Fall 2013) to 4.07 (Spring 2013), while ACT candidates’ scores ranged from 2.69 (Spring 2014) to 4.00 (Fall 2012 and Spring 2013). On Item 4.9, “Meets the instructional needs of English Learners,” Traditional candidates’ scores ranged from 3.04 (Spring 2014) to 4.13 (Fall 2012), while ACT candidates’ scores ranged from 2.96 (Spring 2014) to 4.00 (Spring 2012). In contrast, ACT candidates self-reported more confidence about working with ELs than did Traditional candidates. Out of the 57 items1 on the CSU Exit Survey, the item “As a new teacher, I am prepared in instruction in the teaching of English language learners” was one of only 9 items (in 2011-12) and one of only 11 items (in 2012-13) on which more than 20% of Traditional candidates felt less-than-adequately prepared. For ACT candidates, this same item did not appear among the 9 items on which more than 20% felt less-than-adequately prepared in 2011-12, and in 2012-13, there were no items on which more than 20% of ACT candidates felt less-than-adequately prepared. In the 2013 Follow-Up Surveys (of 2011-12 program completers and their employers, the only year for which we have survey results), only 5 of the 73 items were rated by 50% or more program completers at the lower two (of four) levels, indicating that these program aspects were only a little or not valuable or that graduates felt inadequately prepared. The item, “How valuable or helpful was coursework and fieldwork in your CSU 1 Not including the 16 items of the type “Instruction in ways of teaching [Art] classes in grades 7-12,” which were each answered by a very small number of candidates. 69 credential program for instruction in the teaching of English language learners?” was not among these 5 lowest-rated items. And while there were 8 items on the 38-question employers’ survey on which more than 15% of employers felt our graduates were inadequately prepared, the item “to meet the instructional needs of students who are English language learners” was not one of these. It is not clear why the cooperating teachers and supervisors of our candidates are more critical of candidates’ abilities to teach ELs than our graduates and their employers appear to be—or, more accurately, why cooperating teachers’ and supervisors’ greatest concerns about preparation fall in this area, while other preparation-related concerns take precedence for graduates and their employers. It may be that the small number of respondents in the Follow-Up Surveys work in schools with smaller EL populations than the schools in which we place student teachers, thus lowering the priority of this competence in employers’ and graduates’ eyes. In response to low ratings in this area in the years prior to 2011, we created (and filled) a new, fulltime, tenure-track position in Teaching English Learners and added a new course, Teaching English Learners in Multiethnic Classrooms (SED 529), to all credential pathways. The 3 years covered in this report have been the first 3 years that this course has been offered. Comparisons of 2011-14 STE ratings to those from prior years are difficult, because earlier data were aggregated by TPE. The closest comparison is to TPE 7, Teaching English Learners, which combines two items from the STE: Item 4.8, “Meets the instructional needs of students from diverse cultural backgrounds, demonstrating cultural awareness and sensitivity,” and item 4.9, “Meets the instructional needs of English Learners.” From 2007-2011, our Traditional and ACT candidates’ ratings on this TPE 7 composite item ranged fairly smoothly from 3.53 to 4.29. For the 3 years since SED 529 was offered, as stated above, Traditional and ACT candidates’ scores on Item 4.9 ranged from 2.96 to 4.13. This lack of improvement is disappointing, given that the latter group took a semester-long course dedicated to teaching ELs that prior candidates did not. One explanation may be that our cooperating teachers, supervisors, and at least our Traditional candidates have become more sophisticated about the challenges of and strategies for helping ELs acquire English proficiency and content knowledge, and thus are more critical of current levels 70 of preparation and skill. Certainly, our single-subject program has worked hard over the past few years to educate candidates and instructors, and to a lesser extent supervisors and cooperating teachers, about working effectively with ELs. The Los Angeles Unified School District, where the majority of our student teachers are placed, revised its Master Plan for English Learners in 2011-12 and may have provided related professional development for teachers. Thus, the additional training provided by SED 529 may indeed have elevated our candidates’ and graduates’ ability to teach ELs, but the standards of those who evaluate our candidates and graduates may also have increased. Several actions have been proposed or implemented in response to these EL-related data. We are completing the process of revising all credential-course syllabi to address the new California ELL and ELD Standards (along with Common Core and Next Generation Science Standards). We also plan to review the credential-course sequence, in particular the timing of the Teaching ELs course (SED 529), which currently may be taken at any point in the program. It may be that taking this course in the last semester, when may candidates do, is too late; if taken earlier, candidates would have more opportunity to apply what they learn about teaching ELs in their student-teaching assignments. To further enhance the potential of the student-teaching experience to help candidates teach ELs, we plan to more systematically identify cooperating teachers who are particularly skillful in this area and prioritize them for placements. Finally, our workshops for cooperating teachers often address language issues. This semester, our workshop for returning cooperating teachers will focus on how to mentor student teachers in the use of the new ELL and ELD standards in order to give ELs better access to content. 71 Deep Subject-Matter Pedagogy The vast majority of our candidates pass the PACT Teaching Event. We have seen a consistent failure rate, over the years, of about 10% on first attempts, but, after a remediation meeting with the PACT Coordinator, most of these candidates pass on their second attempt. Still, PACT data, in the form of weak rubric scores and evidence from remediation meetings, give some cause for concern that many of our candidates do not develop sufficiently deep pedagogical content knowledge. The Teaching Event for each subject centers on a focal practice that is quite sophisticated for beginning teachers (and some veteran ones): For example, the focal practice of the History-Social Science PACT Teaching Event is to “help students use facts, concepts, and interpretations to make and explain judgments about a significant historical event or social science phenomenon.” Our PACT data suggest that many of our candidates do not understand the focal practice in their subject and/or struggle to implement it. This has raised the questions of how thoroughly we address these focal practices in coursework and the degree to which cooperating teachers model them and offer candidates opportunities to rehearse and receive feedback on them. Two new department practices address these data. First, for the past two years, the department PACT Coordinator has been visiting every section of the initial course, Fundamentals of Secondary Education in Multiethnic Secondary Schools (SED 511), to introduce the Teaching Event. The focal practice for each subject’s Teaching Event is shared with these first-semester candidates and tips are given for how to prepare for it in courses, even if the Teaching Event is a year or two away. Candidates are encouraged to pay special attention in their coursework to: 1) strategies for engaging pupils in high-level thinking about their subject (because PACT’s focal practices exemplify high-level thinking) 2) the learning theories that ground the various teaching methods 3) what academic language means in their subject (e.g., what it means to talk or write like a scientist) and how to help pupils develop this. A second strategy has been to convene all instructors, supervisors, and PACT scorers in a subject for an extended “Subject-Matter Conversation” (SMC). In 2013-14 we conducted SMCs in math and English; this fall SMCs are being organized for social science and science. At 72 the SMC, participants try to come to consensus on an interpretation of the PACT focal practice, so that what occurs in coursework and fieldwork aligns with what PACT scorers are expecting. Participants examine artifacts, including video clips, from 1-2 PACT Teaching Events by our own candidates, and they identify evidence of the candidate engaging (or not) in the focal practice. Finally, participants discuss how to better support these candidates in the focal practice. Participants in the math and English SMCs reported that the SMC was extremely valuable and overdue; we have yet to see if these SMCs translate into higher PACT scores. Classroom Management Another trend noted on the STEs is a small discrepancy between the ratings of cooperating teachers (lower) and university supervisors (higher) on items related to classroom management: Items 5.1, “Maximizes instructional time, managing classroom routines and transitions,” and 5.2, “Maintains classroom control and consistently enforces policies.” Faculty discussion about this discrepancy elicited two possible (and somewhat competing) explanations. First, these two types of raters may be rating different evidence: The cooperating teacher observes the candidate’s day-today management skills, while the supervisor only observes 6 times during the semester. Not only does the supervisor miss many management events, but the candidate may work harder on classroom control for the supervisor’s visits; even the pupils might be on their best behavior for the special guest. Alternately, it may be that these two types of raters judge the same evidence differently. Cooperating teachers may have a more traditional view of classroom management, and/or may feel that learning to control pupils should take priority over other teaching skills. University supervisors may be more comfortable with less traditional formats, such as groupwork or stations, and the extra noise and movement that result. If our candidates are attempting the more active and collaborative learning formats encouraged in their CSUN coursework, university supervisors may be less inclined than cooperating teachers to criticize these candidates for looseness in pupil behavior. It should be noted that management was no of greater concern than other areas on the STE; it is only raised here because of the rater discrepancy. Classroom management generally did not rate as one of the most pressing concerns for most program completers, either in the Exit or 73 Follow-Up Survey; in fact, for Interns and ACT Candidates in 2011-12 it was an area in which more than 80% of respondents felt Well or Adequately Prepared. However, classroom management was one of the 8 items on which more than 15% of employers felt our graduates were inadequately prepared. Here, again, it may be that employers (generally principals or assistant principals) prioritize control of pupil behavior over other skills a new teacher might demonstrate—or are able to grasp a teachers’ ability to manage a classroom more readily during a quick classroom visit than other teaching skills or knowledge—and therefore be more concerned or critical about this skill. Because management was not an area of particular concern, no specific change or action has been proposed. However, the general purpose for our cooperating-teacher workshops is to attune cooperating teachers to the expectations and teaching practices emphasized at CSUN. Thus, these workshops could encourage cooperating teachers to allow their student teachers to try more active teaching methods than those with which the cooperating teachers feel most comfortable. Meeting the Needs of Challenging Pupils A final observation from the Exit and Follow-Up Surveys is that our graduates may be underprepared to work with pupils with certain challenges, such as dropout risk, violent behavior, and drug use. This problem seems less evident for Interns, which suggests that significant classroom experience is needed and coursework alone insufficient. We will communicate these data with the Health Sciences and Educational Psychology & Counseling departments, which offer the program courses we expect to address these issues: Health Issues of the Adolescent (HCSI 466ADO) and Educational Psychology of the Adolescent (EPC 420). We will also examine all syllabi for our initial course, Fundamentals of Secondary Education in Multiethnic Secondary Schools (SED 511) to ensure that these issues are consistently addressed across sections. 74