population ecology - ch 14
advertisement

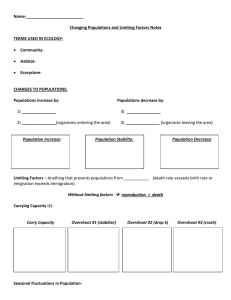
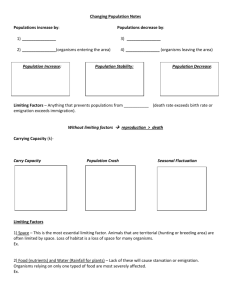
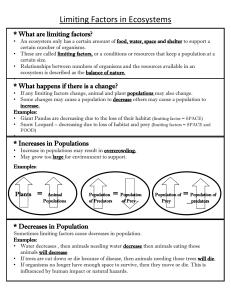
Population Ecology Chapter 14 Population Ecology • Population – group of one species – Interact and interbreed with each other • Based on density – Number of individ. In a given area – Can vary depending on dispersion • Uniform – evenly spaced • Random – position independent of others • Clumped – end to aggregate in patches Population Dispersion Population Growth • Changes in populations – Based on how many organisms are added and how many are taken away – Growth rate- change in population size • can be positive, negative or zero Population Growth • Under ideal conditions population will grow – More organisms are born than die – Exponential growth – the larger a population is, the faster it grows • Will not last forever- will slow down – Zero growth – population stays the same Limits to Population Growth • • Eventually nutrients run out Carry Capacity – average number of individuals an area can support – Based on density dependent factors • • • Limit large, dense populations Energy, shelter, predators, soil nutrients, water, competition, etc. Density – Independent Factors – Kill off organisms no matter how large the population is – Examples: weather, natural disasters, human activities Density Dependent Limiting Factors • Competition – – When individuals compete for resources (ie food, energy, etc) – More individuals in an area limits the amount of certain resources available • Helps determine the carrying capacity of an environment Density Dependent Limiting Factors • Predation – When one species eats another. – Tend to live in balance with each other • As one population goes up, so does the other and vise versa – Increase in prey, leads to an increase in predator – Decrease in predator, leads to an increase in prey Density Dependent Limiting Factors • Parasitism – An organism that takes nourishment from its host • Live at the expense of the host – Parasite populations grow only if host population is dense • Easier to spread Density Dependent Limiting Factors • Crowding and Stress – Most animals need a certain amount of space. – Higher the population, the less space available. – Also weaken immune system Demography • Study of population growth and other stats • Life Tables – age specific summary of birth and death rates – Determines survivorship curve • Types – Type I – many live to adulthood, then rapid die off – Type II – equal chance of dying at any age – Type III – lots of young, but not many make it to reproductive age