Westside High School Lesson Plan
advertisement

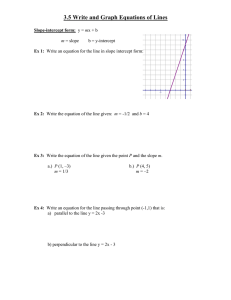
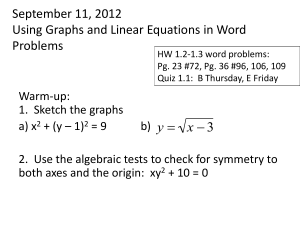
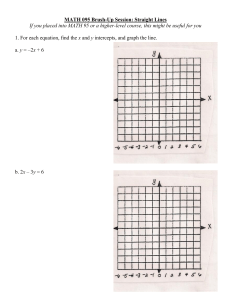
Westside High School Lesson Plan Teacher Name: Garrett, Shannen Unit Name and #: Unit 5: Representing Patterns as Equations and Graphs Unit 7: Relationships in Systems of Linear Equations Course: Algebra IB Dates: Jan 26 – Jan 30, 2015 What are we learning? Daily Objective: Students will be able to construct a graph given the slope and a point on the line. Students will be able to construct a graph given the slope and y-intercept. Students will be able to illustrate and analyze real world problems involving the definition of slope TEKS/AP/Standards: Ⓢ ALGI.2A Identify and sketch the graphs of the general forms of linear (f(x) = x) and quadratic (f(x) = x2) parent functions, and describe the graphs verbally and in writing. Ⓡ ALGI.6C Investigate, describe, and predict the effects of changes in m and b on the graph of y = mx + b. Ⓢ ALGI.6D Graph and write equations of lines given characteristics such as two points, a point and a Monday slope, or a slope and y-intercept when given graphically, symbolically or in written representations. Ⓡ ALGI.6F Interpret and predict the effects of changing slope and y-intercept in applied situations using tabular, graphical, symbolic, and written representations. Ⓢ ALGI.7A Analyze situations involving linear functions in forms of a graph, table, equation, or verbal description in order to formulate a linear equation or inequality to solve a problem. Ⓡ ALG.7B Investigate methods for solving linear equations and inequalities using concrete models, graphs, and the properties of equality, select a method, and solve the equations and inequalities involving one or two variables. How will we learn it? Learning Activities: Graphing with slope-intercept form. How will we tell if we’re learning it correctly? Assessment Methods: Checks for Understanding: Given a problem in Slope-intercept form, students will be able to graph the line using the information provided. What do I need to be successful? An understanding of how to read a problem in slope-intercept form and determine what the graph will look like. Materials: Calculators, graphs, slope and y-intercept formula, worksheet, study guide What do I need to before next class? Follow Up/HW: Students will be given a study guide for the test that will be given Wednesday and Thursday. Students will need to start studying for the test. What are we learning? Daily Objective: Students will be able to illustrate and analyze real world problems involving the definition of slope TEKS/AP/Standards: ALGI.6A Develop the concept of slope as rate of change, determine slopes from graphs, tables, and algebraic representations, and express slope as a ratio, decimal, or percent. Ⓡ ALGI.6F Interpret and predict the effects of changing slope and y-intercept in applied situations using tabular, graphical, symbolic, and written representations. Tuesday How will we learn it? Learning Activities: - Real-World problems using the slope-intercept form (y=mx+b) How will we tell if we’re learning it correctly? Assessment Methods: Worksheets involving real-world situations Checks for Understanding: Circulation around the room to assess individual understanding What do I need to be successful? Materials: Calculators, Notes, Pencils, Paper What do I need to before next class? Follow Up/HW: Slope and Equations of Lines Worksheet Wed/Thur What are we learning? Daily Objective: Students will be able to define slope in three different ways. Students will be able to identify the slope of a line as positive, negative, zero, or undefined. Students will be able to explain how to determine the slope of a line given two points Students will be able to construct a graph given the slope and a point on the line. Students will be able to illustrate and analyze real world problems involving the definition of slope TEKS/AP/Standards: ALGI.6A Develop the concept of slope as rate of change, determine slopes from graphs, tables, and algebraic representations, and express slope as a ratio, decimal, or percent. ALGI.6B Interpret the meaning of positive, negative, zero, and undefined slopes and x- and yintercepts in situations using data, symbolic representations, or graphs. ALGI.6E Determine the intercepts of the graphs of linear functions and zeros of linear functions from graphs, tables, and algebraic representations. How will we learn it? Learning Activities: Think Through Math – Pre-Assessment How will we tell if we’re learning it correctly? Assessment Methods: Paper-and-Pencil Slope Test Checks for Understanding: Teacher observation Friday What do I need to be successful? Materials: Computers, ThinkThroughMath, Pencils, calculators, copy of test What do I need to before next class? Follow Up/HW: What are we learning? Daily Objective: Students will be able to define slope in three different ways. Students will be able to identify the slope of a line as positive, negative, zero, or undefined. Students will be able to explain how to determine the slope of a line given two points Students will be able to construct a graph given the slope and a point on the line. Students will be able to illustrate and analyze real world problems involving the definition of slope TEKS/AP/Standards: Ⓢ ALGI.8A Analyze a problem situation that can be represented by a linear system in two unknowns, and develop a plan for solving the system using a concrete representation and linear equations. Ⓡ ALGI.8B Solve systems of linear equations using concrete models, graphs, tables, and algebraic methods (substitution and elimination). Ⓢ ALGI.8C Interpret and determine the reasonableness of solutions to systems of linear equations. How will we learn it? Learning Activities: Systems of Linear Equations PPT Systems of Linear Equations Practice Problems How will we tell if we’re learning it correctly? Assessment Methods: Student Worksheet Checks for Understanding: Teacher Observation What do I need to be successful? Materials: Pencils, Worksheet, computer, PPT What do I need to before next class? Follow Up/HW: