Notes: Sustainable Agriculture
advertisement

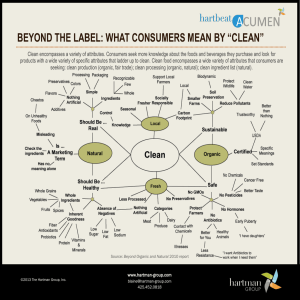
Sustainable Agriculture Pie in the sky or pie on your plate? Please read the board! What are the consequences of monoculture? Food Forward! A different vision! Sustainability considerations Processed food Transported food Stored food Monoculture Pesticides Inorganic Fertilizers Mechanization Short term gains Cost minimization priority over human rights Whole foods Local food Seasonal food Polyculture/polyvarietal IPM pest strategies Organic fertilizers People/animal power Long term soil fertility Fair trade = fair wages for fair work Sustainable System that can go on and on into the future because it doesn’t use up its resources faster than they are created. Conserving our balance by avoiding depletion of natural resources. Sustainable = ◦ Good for the environment ◦ Good for your health ◦ Good for your wallet Options! Organics in mainstream grocery stores Organics sales have increase by 20% every year for the past 5 years (other foods 24% increase) Organic agriculture is $28 Billion/2012 (+11% increase from 2011) Organic Foods production Act 1990 Farmers must develop an organic management plan, be inspected annually by certification agency Fields must be free of synthetic pesticides and fertilizers at least 3 years No use of GMO’s No use of sewage sludge No irradiation No antibiotics or growth hormones Organic advantages Healthier for farmers, consumers Safer for wildlife Doesn’t require as much fossil fuel for fertilizer/pesticides Encourages companies to pursue more sustainable practices Legal definition creates reliable label (unlike “natural”) Organic disadvantages Cost (short shelf life, lack of subsidies) Availability May be grown in monoculture, may not be local, can be highly processed Look for organics! So where can you get the good stuff? Grocery Stores – look for local foods “local” means the source of the food is near by. It does NOT mean the grocery store is near by! Salinas California is 1,850 miles from Houston! Compare/contrast Organic Local Eating local = eating seasonally! Tradeoffs? Local vs. Organic – the throwdown! Options! Grow your own! Community gardens/Urban Ag (ff12:49) Vermicompost! CSA’s – Community supported agriculture (ff15:50) Share holders pay annual fee; pick up produce regularly from central location or drop off Wood Duck farm This week’s share: Two big spaghetti squash Mixed salad greens Green beans Onions Sweet potatoes Zucchini Yellow squash Farmer’s markets (FF 5:16) Houston: ◦ Rice Tues pm ◦ 3000 Richmond ◦ St.Cyril on Westheimer @beltway All $ directly to farmer All local = all seasonal Interactions increase Often organic, but not certified The question of access and equity 3,200 farmer’s markets now take SNAP! (suplemental nutrition assistance program) Farmer’s market food costs reflect a real wage for the farmer Compare/contrast Farmer’s Market CSA Sustainability considerations – Processed food Transported food Stored food Monoculture Pesticides Inorganic Fertilizers Mechanization Short term gains Cost minimization priority over human rights Whole foods Local food Seasonal food Polyculture/polyvarietal IPM pest strategies Organic fertilizers People/animal power Long term soil fertility Fair trade = fair wages for fair work Current sustainability choices Advantages Disadvantages “Organic farming is a crucial WME (weapon of mass enlightenment). - Gary Hirshberg CEO of Stoneyfield organic yogurt Farmer’s Market Challenge So GO already! Visit a farmer’s market and talk with a vendor. Post a picture and your interview on the HUB by Dec 12th.