Category 9 printer friendly document
advertisement
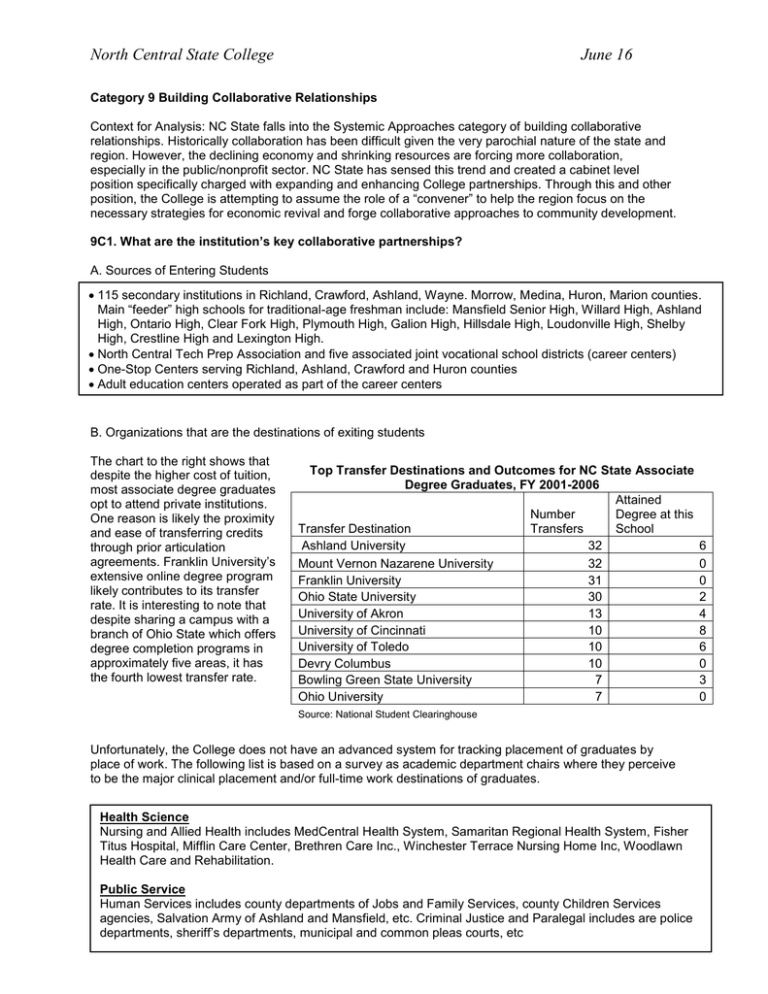
North Central State College June 16 Category 9 Building Collaborative Relationships Context for Analysis: NC State falls into the Systemic Approaches category of building collaborative relationships. Historically collaboration has been difficult given the very parochial nature of the state and region. However, the declining economy and shrinking resources are forcing more collaboration, especially in the public/nonprofit sector. NC State has sensed this trend and created a cabinet level position specifically charged with expanding and enhancing College partnerships. Through this and other position, the College is attempting to assume the role of a “convener” to help the region focus on the necessary strategies for economic revival and forge collaborative approaches to community development. 9C1. What are the institution’s key collaborative partnerships? A. Sources of Entering Students 115 secondary institutions in Richland, Crawford, Ashland, Wayne. Morrow, Medina, Huron, Marion counties. Main “feeder” high schools for traditional-age freshman include: Mansfield Senior High, Willard High, Ashland High, Ontario High, Clear Fork High, Plymouth High, Galion High, Hillsdale High, Loudonville High, Shelby High, Crestline High and Lexington High. North Central Tech Prep Association and five associated joint vocational school districts (career centers) One-Stop Centers serving Richland, Ashland, Crawford and Huron counties Adult education centers operated as part of the career centers B. Organizations that are the destinations of exiting students The chart to the right shows that despite the higher cost of tuition, most associate degree graduates opt to attend private institutions. One reason is likely the proximity and ease of transferring credits through prior articulation agreements. Franklin University’s extensive online degree program likely contributes to its transfer rate. It is interesting to note that despite sharing a campus with a branch of Ohio State which offers degree completion programs in approximately five areas, it has the fourth lowest transfer rate. Top Transfer Destinations and Outcomes for NC State Associate Degree Graduates, FY 2001-2006 Attained Number Degree at this Transfer Destination Transfers School Ashland University 32 Mount Vernon Nazarene University 32 Franklin University 31 Ohio State University 30 University of Akron 13 University of Cincinnati 10 University of Toledo 10 Devry Columbus 10 Bowling Green State University 7 Ohio University 7 Source: National Student Clearinghouse Unfortunately, the College does not have an advanced system for tracking placement of graduates by place of work. The following list is based on a survey as academic department chairs where they perceive to be the major clinical placement and/or full-time work destinations of graduates. Health Science Nursing and Allied Health includes MedCentral Health System, Samaritan Regional Health System, Fisher Titus Hospital, Mifflin Care Center, Brethren Care Inc., Winchester Terrace Nursing Home Inc, Woodlawn Health Care and Rehabilitation. Public Service Human Services includes county departments of Jobs and Family Services, county Children Services agencies, Salvation Army of Ashland and Mansfield, etc. Criminal Justice and Paralegal includes are police departments, sheriff’s departments, municipal and common pleas courts, etc Building Collaborative Partnerships Page 1 6 0 0 2 4 8 6 0 3 0 North Central State College June 16 Business/Accounting/Administrative Information Technology Accounting includes area county auditor and treasurer’s offices, Whitcomb and Hess, Riester, Lump & Burton CPAs, Inc., Sampsel & Associates. Business Administration includes Therm-O-Disc, Gorman Rupp, Warren Rupp, Inc. AIT includes Spherion Services, Richland Bank, MedCentral Health System, etc. Early Childhood Education/Educational Assisting Early Childhood Education includes Head Start Agencies, publicly-funded preschools, private child-care agencies that are state-funded. Educational Assisting includes all area public school districts. Engineering and Workforce General Motors, Hi-Stat Manufacturing, Therm-O-Disc, MTD Products, Pepperidge Farm, Inc., PPG Industries, Broschco Fabricated Products, Cole Tool & Die, Covert Manufacturing, etc. Computer Science and Digital Media MT Business Technologies, Gorman Rupp, MedCentral Health Systems, Embarq, Time-Warner Cable. C. Organizations that serve students There are numerous organizations serving students depending on their unique needs: educational, socioeconomic/transportation, health related and tuition assistance. Educational Resouce Partners Socioeconomic/Transportation Resource Follet Higher Education Group, on campus and online bookstore Bromfield Library, on-campus library with 50,000 circulation and 300 journal titles At least 18 public library branches and community centers with more than 250 public Internet terminals Area county departments of Job and Family Services through cash payments, food stamps, health benefits, basic life skills and job search training Richland County Transit Authority, providing three stops a day to campus Ocie Hill Community Center, Salvation Amry Dewald Community Center, and numerous nonprofit social services agencies Tuition Assistance Partners Health Care Partners North Central State Foundation, endowed scholarship assets of $915,000 Richland County Foundation, $290,000 directed endowment Various community and family foundations Employers offering tuition reimbursement: Richland County, State of Ohio, Embarq, GM, etc. New Directions Counseling Center, Center for Individual and Family Services – Shortterm personal counseling provided to students free of charge D. External Agencies and Consortia Partners NC State has formed affiliations with partners in a variety of missions. Partnerships with an asterisk have been recently formed or recently enhanced. Building Collaborative Partnerships Page 2 North Central State College June 16 Economic/Workforce Development Education/Student Success United Way of Richland County*: NC State led the 2006-07 needs assessment workgroup for workforce development. Bioscience Consortium of Northeast Ohio*: NC State helped launch the formal consortium of educators and industry to meet the workforce needs of regional bioscience companies. Future NEO:* NC State helped form this collaboration of Northeast Ohio community colleges and economic development agencies to spur workforce development. Ohio Economic Development Region 6 Regional Innovation Grant Partnership*: NC State was a key stakeholder in $5 million project to provide training in advanced manufacturing. Now that project has ended, it obtained $250,000 federal planning grant for region stakeholders to craft workforce strategies for dislocated workers. See Category 2 for more information. North Central Ohio P-16 Council*: NC State obtained a planning grant and convened a P16 Council of leaders across all sectors of the region to improve transition points along the education pipeline. Achieving the Dream:* NC State is sharing and receiving data from community colleges across the nation to develop student success strategies. Connex Project:* NC State partnered with an area career center to open a credit recovery lab on campus for high school dropouts and developmental college students. Outreach Centers*: NC State launched satellite centers at high schools in three adjoining counties (Willard, Bucyrus, Ashland-West Holmes) where evening students take general education classes via video conference. Dual Credit Partnership: NC State is leading a local coalition to expand dual credit offerings in the high school setting, successfully obtaining $450,000 in grants to fund student tuition and other activities. Social Services Accreditation Success Unlimited*: NC State has relocated to campus a highly effective program to provide basic skills remediation and employment preparation to first-time public assistance (TANF) recipients. Six public and private agencies are partner providers. Project Search*: NC State and Ohio State have partnered with the Richland NewHope Center to provide a year-long work transition experience on campus for developmentally delayed/disabled young adults. The Higher Learning Commission, North Central Association of Colleges and Schools. Association of Business Schools and Programs. Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs. Commission on Accreditation in Physical Therapy Education. Committee on Accreditation for Respiratory Care. Joint Review Committee on Education in Radiological Technology. National League for Nursing Accrediting Commission. National Association for the Education of Young Children. 9C2: NC State has attempted to link its strategic initiatives for 2007-08 (See Category 8, p #) to these collaborative efforts. Linkages include: Enrollment Development Initiative: The partnerships surrounding sources for entering students (including consortia) are the key element to enhancing enrollment at NC State. Achieving the Dream (AtD) Initiative: The Connex project, AtD community college networks, Success Unlimited and the P-16 Council are all examples of collaborations supporting student success. Building Collaborative Partnerships Page 3 North Central State College June 16 Workforce and Economic Development: The individual employer relationships, as well as the various workforce/economic development consortia all support this strategic initiative. Implementation of Core Learning Outcomes: The partnerships with transfer colleges and universities support this strategic initiative, especially in ensuring transfer of general education courses. Enhancement of Health Care Education: The relationship with health care employers, specialized consortia such as the Bioscience Consortium and the various accrediting agencies support this. 9P1. NC State creates, prioritizes and builds relationships with external partners in the following manner: Educational institutions and other organizations from which we receive our students Historically, NC State has pursued several strategies to enhance relationships with “feeder” institutions, including: College Tech Prep articulation agreements covering 14 programs with area five area career centers (Ashland County/West Holmes Career Center, Knox County Career Center, Madison Comprehensive High School, Mansfield Senior High School, and Pioneer Career and Technology Center). A high school guidance counselor advisory board representing twenty area school districts meets quarterly with Admissions staff. The annual President’s Day College Campus Visit is attended by 300-500 high school students and students can register to attend College-For- a- Day throughout the year to experience college life. Offers nearly $150,000 in institutional scholarships to qualifying graduates at designated high partner high schools. Offering NC State offers Post Secondary Enrollment Options PSEO credit for area high school students who qualify. These courses are taught on campus, or in some cases taught in the area High Schools. College-NOW, allowing students to concurrently graduate with a high school diploma and associate degree in Engineering Technology. This advanced credit is earned at no cost to the student, funded largely through state career-technical funds which minimizes burdens to local school districts. Along with formal agreement and programs, a high school guidance counselor advisory board representing twenty area school districts meet quarterly with Admissions staff. Four college recruiters meet with all new students and walk-in prospects (average # of weekly appointments 100-300). Additionally the recruiters visit 120 schools/career centers in the area at least bi-annually and conduct recruiting events at regional libraries, churches, job fairs, and the One-Stops. During January-March, admissions staff, along with the College Financial Aid Director present Post-Secondary Enrollment Option information at area high schools (29 individual events in 2007). NC State hosts FASFA Fridays and also hosts College Goal Sunday each year in collaboration with the Ohio Association of Student Financial Aid Administrators (OASFAA). Admissions and Student Services Staff partner with an active college student work-study and Foundation sponsored student ambassador program to maximize recruitment through the College’s Welcome Center, outbound Call Center and through conducting campus tours for visitors. In 2006 it shared costs with the Pioneer Career and Technology Center to open a credit recovery lab using acclaimed PLATO software on campus aimed allowing high school dropouts to earn their diplomas. NC State is also working to establish and ABLE site on campus in 2007 for GED completion. That year it also obtained a $225,000 dual credit grant from the state in 2006 to allow more students to take dual credit classes in science and math with no loss of funds to local school districts. Funds were also used to develop more high school teachers into dual credit instructors at their sites. In addition to secondary institutions, NC State has developed a strategic partnership with the OneStop Centers to retrain dislocated workers in credit and noncredit coursework. Since 2005 a local workforce Building Collaborative Partnerships Page 4 North Central State College June 16 investment board consultant has been housed at NC State helping to coordinate between the College Workforce Development Department and the OneStop Centers. Educational Institutions/Employers that depend on NC State Graduates North Central State College hosts a variety of activities that connect our student population with potential employment, and/or continuing educational opportunities for training or advanced degrees including an annual campus Career & Transfer Expo in May with 20 Universities and 40 employers participating. Throughout the year, regional employers submit an average of 15 job openings weekly which are posted to the online Community Job Listings, on bulletin boards in campus buildings, and in the Career Resource Center located in Kee Hall. NC State has formal transfer agreements with several colleges and universities. To further assist our students, North Central State College participates in the Course Applicability System, a free online service to anyone interested in learning of ways in which courses will transfer from one institution to another, and the degree programs offered. NC State envisions two prime areas to enhance relationships with four-year institutions for transfer students. Also, in June 2006 the Ohio Legislature authorized technical colleges to offer specific transfer degrees (Associate of Arts or Science), and NC State envisions using this tool to enhance relationships with both current and future university partners. NC State works closely with area agencies/businesses through a number of advisory committees to remain on the cutting edge of technological and economic trends in our area. Most academic programs have business advisory committees composed of area professionals. Faculty routinely interact with these professionals (and often are these professionals as adjuncts) at local agencies, businesses, health care facilities, as well as through professional networks. NC State’s College-NOW program has partnered with 24 area companies to develop real-world problems students must solve according to a given time-frame and design parameters. Student teams must even make formal presentations of their proposed solutions before panels of industrialists Finally, NC State maintains relationships with local employers through a series of surveys on their experience with NC State College. The College’s Career Services Department conducts an annual survey of employers who have hired recent graduates. In addition, several health-related programs conduct their own surveys as a part of their program accreditation. Organizations the Provide Services to Students NCSC collaborates with a variety of agencies and civic organizations that help to increase access to higher education to underserved populations- These agencies/programs include but are not limited to: Richland County Job and Family Services/Local Workforce Board Area 10. North Central is a key partner with these agencies in terms of services to spur workforce development. NC State maintains constant communication with county and WIB officials, including having a WIB consultant housed right at NC State with proximity to key NC State employees including the President. In addition, NC State has partnered with these agencies on various state and federal grant programs resulting in millions of training and equipment dollars for NC State workforce students. The county also provides credit-based tuition for unemployed and dislocated workers through WIA funds. The NC State Foundation collaborates with a variety of local funders including foundations, corporations and individuals to provide institutional scholarships. To date there are two broad scholarship categories based on both merit and need. NC State constantly communicates with the Richland Transit Authority to ensure efficient and effective transportation services for its students. It has recently expanded service to the campus with three stops during the day. NC State contracts with the Center for Individual and Family Services, a nonprofit mental health provider, to provide mental health services to students. Building Collaborative Partnerships Page 5 North Central State College June 16 The United Way has recognized the importance of Workforce development as it is doing its community needs assessment. NCSC is playing a key role in contributing to this year’s needs assessment. For example, it has suggested metrics to the United Way to track to progress of Workforce Development. Education associations, external agencies, consortia partners, general community NC State has dramatically increased its community partnerships in the past. It formed community “Outreach Centers” in 2006 at high schools in three surrounding counties. These sites provide general education evening classes to cohorts of students in their own communities. To increase the efficiency of this service, courses are synchronously offered via video conference to the three outreach sites. Two of the three counties had no established post-secondary presence prior to this service. NC State has partnered with Richland County Newhope, the county agency serving developmentally disabled/delayed individuals through Project Search. Through the program, young adults nearing graduation through the Newhope school system are providing year-long interships on NC State’s campus in various capacities. The College is also hosting/administering a program for TANF cash assistance recipients to help end the dependence of needy parents on governmental benefits by promoting job preparation, education, work, and marriage. This program, set to begin in summer 2007, entails a collaboration with Richland Job and Family Services, Mansfield City Schools, Pioneer Career and Technology Center, Newhope Center, Lew Petit Driving School, Parent Aide and WIA Youth programs. It envisions encouraging these individuals to complete their high school diploma/GED on campus, or even take postsecondary classes. NC State has helped spearhead intensive bioscience workforce development collaboration amongst businesses, K-16 education, government and nonprofit agencies in the Ashland area. It initially wrote a proposal obtaining a $150,000 federal earmark grant to support a planning period. Even after this earmark grant was canceled by the new Congress, it still rallied with partners to keep the effort moving with the result true result being established of a pilot Project Lead the Way Tech Prep program in biomedical sciences. NC State serves on various committees (survey, marketing, education, etc) of this consortium which has drawn statewide attention. NC State is a member of the Achieving five in Ohio. It has developed strong relationships with these colleges, which has included a joint submission for a FIPSE grant in 2006 by three of the Ohio consortium members (Zane State and Jefferson Community). It regularly networks with these colleges at statewide meetings and conference calls. the Dream Consortium of community colleges, of which there are Major Board and Association Positions Held by NC State Employees Ohio Governor’s Child Care Advisory Council Ohio Board of Nursing Governor’s Workforce Policy Board Ohio Workforce, Education and Training Advisory Council Ohio Association of Community Colleges Executive Committee Ohio Association of Student Financial Aid Administrators Faculty and staff at NC State belong to various state and national professional associations. They build relationships with these associations through serving them in various capacities. In addition, the college has strong relationships with its numerous accrediting agencies. 9P2. How do you ensure the varying needs of those involved in these relationships are being met? In 2006, NC State created the Cabinet-level position of Special Assistant to the President for Government and Community Relations. This position was tasked with building and maintaining partnerships given the quickly changing educational and political climate in Ohio. The College hired the former Superintendent of Building Collaborative Partnerships Page 6 North Central State College June 16 Pioneer Career and Technology Center, a joint vocational school district affiliated with 16 regional school systems. This individual had built immense contacts/clout with community and statewide stakeholders, and was a natural fit in this position. This person serves on boards or is otherwise affiliated with 22 different educational, business, governmental and philanthropic organizations at both the local and state level. Further, this person has a very collaborative “breaking down the silos” approach that has helped College personnel comprehend the “Win-Win” nature of strengthening partnerships. For example, this person counseled the College to maximize the effectiveness of a large state workforce grant by subcontracting training work to regional adult education centers that may have been better suited for certain training. The College referred hundreds of individuals to these partners, building on regional strengths and capacities in delivering training. The College has also created a community education department with a major focus of strengthening partnerships in the outlying counties of its service region. The Department has contracted with a wellknown resident in each of these counties to help coordinate key information about college services with stakeholders in each of these counties, in addition to efforts of the Department Chair. NC State is spearheading an effort to create a regional P-16 Council that will develop data-informed strategies having a wide-scale impact on student success at all levels. NC State has received a $10,000 state grant to form a strategic plan for a P-16 Council to take effect in January 2008. It has obtained commitment from 14 regional stakeholders in early childhood, K-12, higher education, business/industry, local government and other sectors to develop the plan and become the executive committee of the Council. NC State feels this Council will be THE guiding body for ensuring that significant policy changes in education involve wide-scale stakeholder North Central Ohio P-16 Steering Committee input. In a linked effort, Special Assistant to Government and Community Relations, NC State NC State is Early Childhood Education Program Director, NC State simultaneously Consultant, Richland Commissioners and Job and Family Services receiving grant-funded Superintendent of Pioneer Career & Technology Center technical assistance Superintendent of Ashland-West Holmes Career Center from the American Superintendent of Crestview Local Schools Association of Superintendent of Loudonville-Perrysville Exempted Village Schools Community Colleges to Superintendent of Crestline Exempted Village Schools help devise strategies Superintendent of Shelby City Schools to better align workforce Mayor of Village of Lexington and economic Mayor of City of Ontario development. It will Director of Crawford County Economic Development Department integrate the talents of President/CEO of Galion Community Hospital its assigned AACC expert consultant with the P-16 efforts. Finally, NC State is constantly reviewing, and when strategically feasible, applying for grants to better ensure the needs of its partners. For example, it has filed a preliminary application with the National Science Foundation for a grant to fund an engineering capstone project proposal that would significantly integrate College Tech Prep students and Miami University Engineering Technology distance students, all of whom are educated in the same building as NC State’s engineering students. 9P3. How do you create and build relationships within your institution? How do you ensure integration and communication across these relationships? See Category 4. 9P4. What measures of building collaborative relationships do you collect and analyze regularly? Building Collaborative Partnerships Page 7 North Central State College June 16 9R1. What are your results in building your key collaborative relationships? Educational institutions and other organizations from which we receive our students Below are select outcomes for 2003 graduates from area high schools immediately enrolling in NC State: Select Information and Outcome of Recent High School Graduates Enrolled as First-Time NC State Students in Fall 2003 Top 10 Feeder High Schools Ashland Galion Shelby Lexington Madison Mansfield Ontario Hillsdale Clear Fork Plymouth High School Grads 2003 311 144 166 234 243 251 145 100 144 51 First Year Students 24 18 18 17 14 10 10 9 Took Minimum College Prep 43% 33% 50% 43% 50% NA 33% 0% 9 8 NA NA Complete FASFA 67% 78% 83% 76% 71% 70% 70% 78% First Generation College 75% 57% 47% 38% 50% 71% 57% 57% Persisted in College After One Year 46% 50% 44% 71% 64% 30% 70% 67% Transfer to Another Institution 8% 6% 17% 6% 7% 0% 30% 22% Took Remedial Courses 54% 44% 67% 35% 50% 60% 50% 33% 63% 100% NA 75% 50% 38% 13% 25% 63% 63% A key element impacting a high school graduate’s decision to attend NC State could be the relationship the College fostered with that student in high school. There are several encouraging trends, such as an average 78% of students completing a FASFA and 62% of students being first-generation college. But challenges remain, such as the uneven percentage enrollment by high school, the low percentage of students (42%) taking minimum college prep coursework, the resulting high number of remedial coursework (54%) and the somewhat low persistence rate (56%). In the long-term, the low academic preparation rate will be assisted by new legislation signed into law in early 2007. The Ohio Core will require students, beginning with the high school graduating class of 2014, to complete a rigorous curriculum (including 4 years math with Algebra II and three years of lab-based science) as a requirement for high school graduation and on prerequisite for admission to Ohio's four-year state assisted institutions of higher education. To enhance this plan, the legislation directs increased cooperation between the secondary and postsecondary levels, especially in opportunities to earn college credit while in high school. NC State has had mixed results in terms of enrolling students in dual credit coursework. Total College HC PSEO HC Post-Secondary Enrollment Options Fall Enrollment Trends F-98 F-99 F-00 F-01 F-02 F-03 F-04** 2722 2853 2824 3102 3547 3335 3362 40 139 191 281 365 286 389 Building Collaborative Partnerships Page 8 F-05 3130 310 F-06 3193 316 North Central State College % of Total HC HC - PSEO HC 1% 2682 June 16 5% 2714 7% 2633 9% 2821 10% 3182 9% 3049 12% 2973 10% 2820 Dual credit enrollment has grown to represent a material portion of NC State’s student population at 10% total headcount equaling 43.8 FTE. Two-thirds of these students took classes right in their high schools from adjunct instructors, who were often credentialed high school instructors. However, PSEO enrollment has remained flat the past several years, with many students comprising area private schools which do not lose state foundation as a result of having dual credit students. The funding issue appears to be the major factor limiting dual credit enrollment growth, as even districts that previously offered onsite dual credit classes close down the sections for fiscal reasons. Many school districts were supportive of the state grant offsetting the loss of state foundation, as the majority of the 150 headcount students funded through this grant in spring quarter were offered at various high school sites without supplanting PSEO. Educational Institutions/Employers that depend on NC State Graduates Chart plotting out transfer outcomes for graduates in select programs 2002-2006 (data pending) Analysis of chart NC State collaborates with a variety of agencies/ businesses to not only provide access to clinical sites, but also extend tuition remission to their employees. For example, it has established 100 sites for Human Services, six for Radiology, 29 for Paralegal, 26 for Criminal Justice, 23 for Respiratory, 29 for Nursing and 29 for Physical Therapy. NC State faculty are actively involved with their students and the professional sites during the practicum experience. Building Collaborative Partnerships Page 9 10% 2877 North Central State College June 16 Organizations the Provide Services to Students Transfer Chart>>>> What this really shows is the need to increase articulation with Ohio State. . It is working with Ohio State University Mansfield on transfer agreement for Early Childhood Education majors, which would hopefully pave the way for future bachelor completion agreements. Education associations, external agencies, consortia partners, general community 9R2. How do you results compare with the results of other higher education institutions and, if appropriate, organizations outside the education community? 9I1. How do you improve your current processes and systems for building collaborative relationshiops? Strategic initiatives 9I2. With regard to your current results for student learning and development, how do you set targets for improvement? What specific improvement priorities are you targeting and how will these be addressed? How do you communicate your current results and improvement priorities to relationship partners, faculty, staff, administrators, and appropriate students and stakeholders. Building Collaborative Partnerships Page 10 Transfer programs/institutions On-campus degree completion programs - Electromechanical Engineering Technology (Miami University videoconference); Nursing (Ashland University); North State College 16(Youngstown SocialCentral Sciences/Addiction Studies (University of Cincinnati videoconference); Criminal June Justice State University video conference); Business Administration (Mt. Vernon Nazarene University); Technical Education and Training (The Ohio State University) On-line degree completion - Advanced Technical Education, Bachelor of Liberal Studies (Bowling Green State University); Bachelor in Accounting, Applied Management, Business Administration, Computer Science, Digital Communication, Financial Management, Health Care Administration, Human Resource Management, Information Technology, Marketing, Management, Management Information Systems & Public Safety Management (Franklin University); Business/Management, Information Technology, Business/Administration, Drafting and Design, Nursing & Technical Management (University of Phoenix); Nursing (University of Wisconsin-Green Bay) Off campus degree completion offered in numerous disciplines -Ashland University; Bowling Green State University; Ohio Northern University; Tiffin University; University of Akron; University of Findlay; University of Toledo; Wilberforce University Building Collaborative Partnerships Page 11






