Click here to download the resource Perfect Competition
advertisement

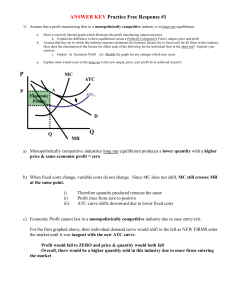
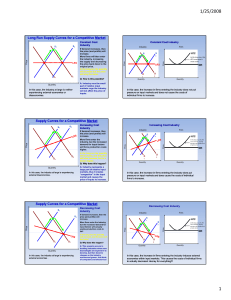
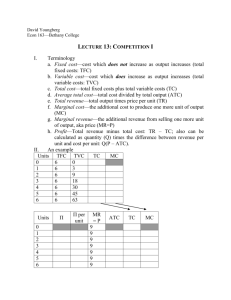
PERFECT COMPETTION In this example, imagine there is a local market place with a single seller of a homogenous product - potatoes Perfect Competition Market S1 Price P1 Individual firm Revenue/ Costs MC P1 ATC AR1 = MR1 = D1 D1 Q1 Quantity At this point, Initially there they is a single are making seller. They ‘take’ the price abnormal (supernormal) set by theprofits customers equal to the– red P1 shaded area above Q1 Quantity Perfect Competition Market S1 Price Individual firm Revenue/ Costs S2 MC ATC P1 P1 AR1 = MR1 = D1 P2 P2 AR2 = MR2 = D2 D1 Q1 Q2 Quantity Q2 The outward shift in to supply reduces Motivated by the desire make abnormal Now costs are higher than revenue profits and with no barriers of entryand more the individual sellers average and eachenter seller ismarket making a loss. suppliers the marginal revenue. Quantity Perfect Competition Market Individual firm Revenue/ Costs S3 Price MC P3 P3 ATC AR3 = MR3 = D3 D1 Q3 Quantity Q3 In the long run, the price will equal Firms now leave the market (there is In the long all revenue firms make marginal and run, average and no freedom of exit) causing an inward shift in more firms are motivated to leave or enter normal profits. supply. Prices rise to P3. the market. Quantity