P A U L I N A N... H H M I R E C I... M E N T O R : D...
advertisement
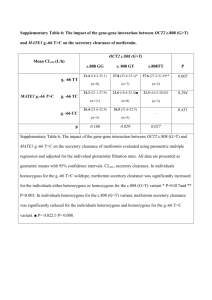
PAULINA NGUYEN HHMI RECIPIENT MENTOR: DR. GANESH CHERALA LAB: OSU-COLLEGE OF PHARMACY About 1 in every 12 babies in the United States is born with low birth weight Increased risk for serious health problems such as lasting disabilities and even death. Stunted growth Higher incidence of diseases Poor conditions in the womb • Greater susceptibility to diseases in adult life (Barker’s Hypothesis) Low protein diet (LPD)–Rodent model for LBW • Similar to human epidemiological findings • LPD in rodent model can be manipulated in laboratory conditions Altered tissue development leads to altered development of organs such as in kidney and liver ◦ Affect renal organic transporter functionality ◦ Affects drug transport and excretion in and out of the body LBW individuals will need different drug dosages LPD Low Birth Weight Various Organs Kidney Liver Heart, etc. Drug Transport & Pharmacokinetics Pharmacokinetics (PK) Study of how drug travels through the body A D M E o Absorption o Distribution o Metabolism o Excretion Drug Metabolism and Transport Renal Excretion LUMEN Basolateral Membrane Transporters • OAT • OCT • PGP • PEPT • MRP 5 Organic Cation Transporters found in rat OCT2 models 1. OCT1 2. OCT2 OCTN1 3. OCT3 4. OCTN1 5. OCTN2 OCTN2 Hypothesis • Low birth weight, as a result of altered perinatal environment, leads to permanent alterations in the expression of renal OCT transporters. Specific Aims To quantify mRNA expression of renal OCT2, OCTN1, and OCTN2 at various ages To quantify protein expression of renal OCT2 at various ages Study Design Weaned onto regular diet Birth weights noted; litters culled Control Low Protein (LP) Measure the mRNA level of OCT2, OCTN1, and OCTN2 expression in male and female offspring in both LP and Control groups using RT-PCR Measure the protein expression of OCT2 in male and female offspring in both LP and Control groups using western blotting Fold Difference (relative to control) Day 28 mRNA levels for males and females 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 -0.5 OCT2 OCTN1 -1 -1.5 -2 -2.5 -3 -3.5 Transporters Males Females OCTN2 Fold Difference (relative to control) Day 65 mRNA levels for males and females 3 2 1 0 -1 OCT2 OCTN1 OCTN2 -2 -3 -4 -5 Transporters Males Females Fold difference (relative to control) Day 150 mRNA levels for males and females 60 * 50 40 30 20 * 10 0 -10 OCT2 OCTN1 OCTN2 -20 -30 -40 -50 * Transporters Males Females * Statistically Significant Fold difference in Level of OCT Expression Fold difference (relative to control) 50 * 40 30 20 * 10 0 OCT2 OCTN1 OCTN2 OCT2 OCTN1 OCTN2 OCT2 OCTN1 OCTN2 -10 -20 Day 28 Day 65 Day 150 -30 -40 * Transporters Males Females * Statistically Significant Density of OCT2 Band (normalize to β-actin) 0.03 0.025 0.02 0.015 0.01 0.005 0 Day 28 Day 65 Control LBW Day 150 Density of OCT2 Band (normalize to β-actin) 0.3 0.25 0.2 0.15 0.1 0.05 0 -0.05 Day 28 Day65 Control LBW Day150 Tissue Tissue Homogenate 27 fold decrease in expression of OCT2 in Day 150 LP females relative to control (regular diet) females Effect of LP diet seen in later life Sex hormone regulation of OCT2 a possible reason for 27 fold difference in LP Day 150 females Sex hormone regulation of OCT2 • Testosterone up-regulates expression of OCT2 • Estrogen down-regulates expression of OCT2 Howard Hughes Medical Institute Cripps Funding Cherala Lab ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Dr. Ganesh Cherala Barent DuBois Jacob Pearson Dr. Shobana Ganesan Tahir Mahmood Shawn Mahmood Alexandru Cioara OSU-College of Pharmacy Dr. Kevin Ahern Cherala G, Shapiro BH, and D'mello AP (2006) Two low protein diets differentially affect food consumption and reproductive performance in pregnant and lactating rats and long-term growth in their offspring. J Nutr 136: 2827–2833 Kathleen M. Giacomini, et al. (2010) Membrane transporters in drug development Nature Reviews Drug Discovery , 215-236 Hagenbuch, B (2010) Drug Uptake Systems in Liver and Kidney: A Historic Perspective Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics 87 1, 39–47