An Investigation into Zinc Transporter Expression in an Animal Model of Amyotrophic
advertisement

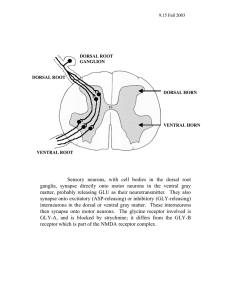
An Investigation into Zinc Transporter Expression in an Animal Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis By Thomas Lew Mentor: Dr. Joe Beckman Linus Pauling Institute Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis • Results from the death of motor neurons • Muscle degeneration • Paralysis • Death http://starklab.slu.edu/signal/Growth.htm Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis • • • Majority of ALS cases are sporadic but approximately 10% of all cases are familial Of these familial cases, 20% of individuals inherit dominant autosomal mutations in the SOD1 gene SOD1 gene codes for copper-zinc superoxide dismutase (SOD) Superoxide e- Superoxide e- Oxygen Hydrogen Peroxide SOD Mutations and ALS • Over 100 different ALS causing mutations have been discovered dispersed throughout the SOD1 gene • However, the toxicity of these mutations is not due to reduced superoxide scavenging ability • Something about these mutations causes them to become toxic to cells Mutant SOD and Familial ALS • • Mutant SODs have a reduced affinity for binding zinc. Copper atom in zinc-deficient SOD is much more reactive. Normal nerve fibre Normal nerve fibre Zinc-deficient SOD and ALS: Supporting Evidence • More Cu,Zn(-)SOD in Ventral Region • The question is - Why? Spinal cord Cross-section Objective The objective of this research is to investigate if a dysregulation of zinc transport pathways could account for the increased levels of zinc-deficient SOD in the ventral spinal cord Hypothesis • Levels of zinc-deficient SOD are increased in the ventral grey matter as a consequence of zinc transporter dysregulation Methods • Utilize real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (realtime PCR) to quantify the expression of three zinc transporter genes in the dorsal and ventral grey matter of the spinal cord: i) ZnT-1 ii) ZnT-3 iii) ZnT-4 Methods Add Taq polymerase, dGTP, dCTP, dATP, dTTP to synthesize complimentary strand. Add SYBR green for fluorescence Fluorescence Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction - can be used to quantify the expression level of a specific gene. Time or cycle number Results • Zinc Transporter 3 (ZnT-3) – Facilitates zinc transport from the cytosol into synaptic vesicles. ZnT-3 Gene Expression Level (per 1000 -actin transcripts) ZnT-3 Gene Copy Number 15 10 5 0 Ntg Dorsal Ntg Ventral G93A Dorsal Spinal Cord Region G93A Ventral Results • Zinc Transporter 4 (ZnT-4) – Facilitates zinc transport from the cytosol to the Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum ZnT-4 Gene Expression Level (per 10,00 b-actin transcripts) ZnT-4 Gene Copy Number 50 40 30 20 10 0 Ntg Dorsal Ntg Ventral G93A Dorsal Spinal Cord Region G93A Ventral Results • Zinc Transporter 1 (ZnT-1) – Facilitates zinc export from the cytosol into the extracellular space 80 (per -actin transcript) ZnT-1 Gene Copy Number ZnT-1 Gene Expression Level 60 40 20 0 Ntg Dorsal Ntg Ventral G93A Dorsal Spinal Cord Region G93A Ventral Summary • ZnT1: decline in expression in ventral spinal cord of G93A vs. NTG control – Indicative of dysregulation? •Neither ZnT-3 or ZnT-4 exhibit any change in expression level when comparing the dorsal and ventral region of the spinal cord. • However, these results were found in 40 day old rats, and it should be noted that we have been unable to detect zinc-deficient SOD in rats younger than 50 days. Acknowledgements • Howard Hughes Medical Institute • Dr. Kevin Ahern • Dr. Joe Beckman • Dr. Mark Levy • The Beckman Lab