Inhibition of and V79 H1B1 Cells in Culture. Tuan M. Nguyen
advertisement

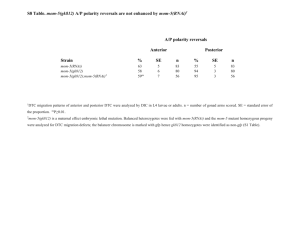
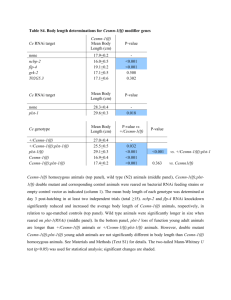
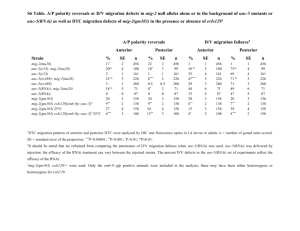
Inhibition of CYP1B1 in MCF-7 and V79 H1B1 Cells in Culture. Tuan M. Nguyen Major: General Science/Pre-Optometry Mentors: Dr. William M. Baird & Dr. Brinda Mahadevan Overview • Introduction • Methods • Results • Summary Introduction • Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) are environmental carcinogens • Cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes such as CYP1B1 have been identified to be involved in the activation of dibenzo[a,l]pyrene (DBP) Introduction • DBP is one of PAH forms • DBP commonly found in cigarette smoke, diesel exhaust, urban dust and other environmental carcinogens. 3 2 fjord re gion DNA adduct formation on exposure to DBP 6 7 13 12 8 11 10 dibenzo[a,l]pyrene ( DB[a,l]P) 9 CYP 1A1 CYP 1B1 O O + HO HO OH OH (+)-syn-DB[a,l]P11,12-dihydrodiol 13,14-epoxide HO DNA adducts 5 14 DBP diol-epoxides DBPDE 4 1 (–)-anti-DB[a,l]P11,12-dihydrodiol 13,14-epoxide HO HO HO NH OH N N N NH OH N N OH O OH (+)-syn-DB[a,l]P11,12-dihydrodiol 13,14-epoxidedA adduct N OH O OH (–)-anti-DB[a,l]P11,12-dihydrodiol 13,14-epoxidedA adduct Objective • To investigate the importance of CYP1B1 as key enzyme in metabolizing DBP to its metabolites. Aspects of Study • DNA adducts • CYP1B1 enzyme activity • CYP1B1 gene expression Experimental Design DNA Adducts MCF-7 Cells V79 H1B1 Cells • • • • • • • • TMS (- control) TMS+DBP DBP DBPDE (+ control) TMS (- control) TMS+DBP DBP DMSO (solvent ctrl) Methods Add fresh media to cells 24 hrs prior to treatment V79 H1B1 MCF-7 TMS (-) TMS+DBP DBP DBPDE (+) 20 ml media TMS (-) TMS+DBP DBP DMSO (solvent ctrl) 20 ml media 24hr DNA isolation Harvest RNA & isolation Microsome RT-PCR Postlabeling & HPLC P450 Glo Assay Measurement of DNA Adducts •Postlabeling •Sep-pak •HPLC Adducted dinucleotide monophosphates Dinucleotide adducts Nucleoside 5’ phosphate HPLC Profiles 6000 12000 (+)-anti-B[a]PDE-dG (+)-anti-DB[a,l]PDE-dA Radioactivity 5000 dG 10000 dA 4000 dA •DBPDE + control 8000 dG 3000 6000 2000 4000 1000 2000 0 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 0 20 Retention Time [min] 40 60 80 100 120 P450 Glo Assay Cytochrome P450 Glo Assay enable the measurement of the activity of CYP1B1. CYP1B1 Luciferin CEE luciferin firefly luciferase light (P450 Glo substrate) Luminescence reading P450-Glo Assay Luminescence (RLU) P450-Glo Assay: S9 Microsomes 90000 80000 70000 60000 50000 40000 30000 20000 10000 0 Room Temp 37ЎC 1mg/ml 10mg/ml 20mg/ml Concentration 30mg/ml 41.6mg/ml How does RNAi work? •Antler, C. ‘Antisense RNA’, http://www.bioteach.ubc.ca/MolecularBiology/AntisenseRNA/. RNAi Count Cells Untreated RNAi Ctrl V79 H1B1 NCsiRNA NC Ctrl Plate Cells V79 H1B1 + RNAi Transfect Isolate RNA V79 H1B1 + RNAi MCF-7 Ctrl MCF-7 + RNAi RNAi Untreated Ctrl Reverse Transcription Reaction Polymerase Chain Reaction RNAi Electrophoresis - V79 H1B1 cells - MCF-7 cells Isolated RNA 100 bp Ld V79H NC V79H1B1 Untreated V79H1B1+RNAi MCF-7 Ctrl MCF-7+V79H1B1 100 bp Ld RT-PCR RT-PCR and amplification of CYP1B1 cDNA Total RNA Random primers Superscript RT RNase inhibitor RP First strand cDNA RP SPP Amplify cDNA SPP PCR Amplified product RP – Random Primer SPP – Specific Pair Primer for CYP1B1(18-25 nt) Amplified CYP1B1 Gene Ld siRNA NC V79H1B1 Ctrl V79H1B1+RNAi MCF-7 Ctrl MCF-7+RNAi Summary • Familiarized with postlabeling technique • P450-Glo Assay • RNAi • Amplified CYP1B1 gene. Future Work Predictions DBP alone TMS alone TMS+DBP RNAi alone RNAi+DBP DNA Adducts Activity of CYP1B1 enzyme Expression of CYP1B1 gene + - + - + N/A N/A - Acknowledgements • William M. Baird • Brinda Mahadevan • Kevin Ahern • Jennifer Atkin • Howard Hughes Medical Institute