Chapter 3 Comparative International Financial Accounting I
advertisement

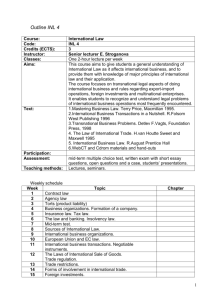
Chapter 3 Comparative International Financial Accounting I Strategic Decision Point IASB was created to increase comparability How will differing cultures interpret standards? Will standards be applied consistently? What can the IASB do to mitigate this issue? International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 3 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Founding Members of the IASC and IASB Exhibit 3.1 Economic Data for Developed Countries GDP PPP (in billions) GDP Per Capita Populatio n (in millions) Unemplo yment Inflation Area per sq km (in thousands) Imports (in billions) Exports (in billions) U.S $10,990.0 $37,800 293.0 6.0% 2.3% 9,631.4 $,1260.0 $714.5 U.K. $1,666.0 $27,700 60.3 5.0% 1.4% 244.8 $363.6 $304.5 Australia $571.4 $29,000 19.9 6.0% 2.8% 7,686.9 $82.9 $68.7 Netherlands $461.4 $28,600 16.3 5.3% 2.1% 41.5 $217.7 $253.2 Sweden $238.3 $26,800 9.0 4.9% 1.9% 450.0 $83.3 $102.8 Germany $2,271.0 $27,600 82.4 10.5% 1.1% 357.0 $585.0 $696.9 $239.3 $32,700 7.4 3.7% 0.6% 41.3 $102.2 $110.0 France $1,661.0 $27,600 60.4 9.7% 2.1% 547.0 $339.9 $346.5 Italy $1,550.0 $26,700 58.1 8.6% 2.7% 301.2 $271.1 $278.1 Spain $885.5 $22,000 40.3 11.3% 3.0% 504.8 $197.1 $159.4 Japan $3,582.0 $28,200 127.3 5.3% -0.3% 337.8 $346.6 $447.1 Switzerland International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 3 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Anglo-American Accounting Less conservative and more transparent United States Focused on large corporations and interests of investors Securities markets are the dominant influence on accounting regulation SEC has authority to formulate and enforce accounting standards Delegated to the FASB Only listed corporations are required by law to comply with GAAP Very public standards-setting process International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 3 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Anglo-American Accounting United Kingdom Focus on investors Company law has a much wider remit Accounting requirements are for all LLCs and corporations Accounts present a “true and fair view” of company results Accounting Standards Board (ASB) will incorporate International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) by 2005 International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 3 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Anglo-American Accounting Australia English influence Focus on investors rather than tax needs Australian Securities & Investments Commission Regulate and enforce company law Australian Accounting Standards Board – creates standards Urgent Issues Group (UIG) Financial Reporting Council oversees AASB Provides guidance for public and private sector International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 3 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black The Netherlands Business economics approach to accounting Tradition of “Generally Acceptable Accounting Principles” Public ownership of shares International business outlook Provided by Council for Annual Reporting Members from the accounting profession (NIVRA) and others Not mandated by law, but followed by most companies Company law is supplemented by case law IFRS required for listed companies in 2005 International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 3 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Nordic Accounting Nordic Countries: Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden Sweden Focus on creditors, government, and tax authorities Two-tier approach The law provides a framework rather than detailed requirements Individual accounts – traditional basis Consolidated accounts of major groups – international capital market needs Accounting Standards Board and Accounting Council provide guidance in the context of company law IFRS required for listed companies in 2005 International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 3 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Germanic Accounting Germany Focus on needs of creditors and tax authorities MNEs are becoming more investor-oriented Company law is predominant influence Accounting rules amend the Commercial Code Annual accounts are the basis for tax accounts Tax rules dominate legal accounting issues Limited impact of accounting profession German Accounting Standards Board IFRS required for listed companies in 2005 International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 3 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Germanic Accounting Switzerland Favors needs of creditors and authorities More companies are making further voluntary disclosures Very secretive and conservative system Dominated by company law and tax regulations New law – 1992 Improved disclosure and protection for investors Secret reserves are still allowed Accounting profession consists of Foundation for Accounting and Reporting Recommendations – supervises the Accounting Standards Board Recommendations elaborate and supplement company law International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 3 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Latin Accounting France Focus on needs of creditors and tax authorities Consolidated groups can report in U.S. GAAP or IAS Company law and tax law are the predominant influences Focus on national economic planning Tax laws tend to override accounting rules Small accounting profession established by law OECCA and CNCC for public accounting and auditing Small stock market Most capital contributed by banks, government, or family French equivalent of the SEC – Commission des Opérations de Bourse (COB) IFRS required for listed companies in 2005 International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 3 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Latin Accounting Italy Focus on interests of government and tax authorities Focus is shifting because of globalization Accounts are used as the basis for taxation Tradition of conservatism to minimize taxes Italian equivalent of the SEC – CONSOB Slow to adopt EU directives because External investor interests are seen as less important than family and state interests Tendency to protect the right of companies to keep business secrets Professional accounting bodies are advisory IFRS required for listed companies in 2005 International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 3 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Asian Accounting Many countries have a colonial accounting history or foreign influence Japan Focus on needs of creditors and tax authorities Commercial Code (similar to Germany) Corporate tax law is very influential Leads to conservative accounting Government institutions are directly involved in standardsetting Ministry of Finance – responsible for securities and exchange law Ministry of Justice – responsible for application of Commercial Code International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 3 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Asian Accounting Japan continued Accounting for business combinations is a source of concern Keiretsu – system of interlocking directorates of related businesses formed to work together Small accounting profession Makes recommendations on the practical application of legal accounting rules Tendency for secrecy and a lack of disclosure Increased international focus ASBJ in Japan is similar to the FASB in the U.S. Approximately 30 Japanese companies listed in the U.S. prepare financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP. International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 3 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Chapter 4 Comparative International Financial Accounting II Strategic Decision Point Developing nations Questionable integrity and transparency in financial reports Being left behind in creation of international standards Trouble in obtaining international capital Trouble reaching full potential What can the accounting profession do to aid these developing countries? What can be done to ensure proper compliance in these countries? IASB is discussing standards for small MNEs International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 4 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Comparative Information Exhibit 4.1 Economic Data for Developing Countries GDP PPP (in billions) GDP Per Capita Populatio n (in millions) Unemplo yment Inflation Area per sq km (in thousands) Imports (in billions) Exports (in billions) $3,033.0 $2,900 1,065.1 9.5% 3.8% 3,287.6 $74.2 $57.2 $207.8 $9,000 23.5 3.6% 1.1% 329.8 $74.4 $98.4 $1,375.0 $7,600 184.1 12.3% 14.7% 8,512.0 $48.3 $73.4 Argentina $435.5 $11,200 39.1 17.3% 13.4% 2,767.0 $13.3 $29.6 Mexico $941.2 $9,000 105.0 3.3% 4.5% 1,972.6 $168.9 $164.8 $6,449.0 $5,000 1,298.8 10.1% 1.2% 9,597.0 $397.4 $436.1 Indonesia $758.8 $3,200 238.5 8.7% 6.6% 1,919.4 $40.22 $63.89 Thailand $477.5 $7,400 64.9 2.2% 1.8% 514.0 $65.3 $76.0 Poland $427.1 $11,100 38.6 20% 0.7% 312.7 $63.7 $57.6 Russia $1,282.0 $8,900 143.8 8.5% 13.7% 17.075.2 $74.8 $134.4 $161.1 $15,700 10.2 9.9% 0.1% 78.9 $50.4 46.8% India Malaysia Brazil China Czech Republic International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 4 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Comparative Information Exhibit 4.2 Number of Companies in Developing Countries listed on Foreign Exchanges NYSE NASDAQ London Stock Exchange India 8 3 17 Malaysia 0 0 3 Brazil 37 1 0 Argentina 10 3 1 Mexico 22 3 0 China 17 0 5 Indonesia 2 0 2 Thailand 0 0 0 Poland 0 0 8 Russia 6 0 4 Czech Republic 0 0 3 International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 4 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Comparative Information Exhibit 4.3 IFRS Acceptance Not Permitted for Permitted for Domestic Domestic Listed Listed Companies Companies India ? Malaysia X Brazil X Argentina X Mexico X China ? Required for Some Domestic Companies Required for All Domestic Listed Companies ? X Indonesia X Thailand X Poland Russia ? X X Czech Republic X International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 4 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Comparative Information Exhibit 4.4 Other Country Data Legal Origin Income Group Rating on Accounting Standards* India English Low 45 Malaysia English Upper Middle 76 Brazil French Lower Middle 54 Argentina French Upper Middle 45 Mexico French Upper Middle 60 China German Lower Middle 52 Indonesia French Low 65 Thailand English Lower Middle 64 Poland German Upper Middle 36 Russia Socialist Lower Middle 32 Czech Republic German Upper Middle 38 *Higher scores indicate higher rating on accounting standards International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 4 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Anglo-American Influence Less conservative and more transparent than German and Latin countries India Significantly improved economy over past decade Focus on needs of investors Institute of Chartered Accountants in India (ICAI) and the Accounting Standards Board (ASB) Create and modify accounting standards Give consideration to IAS and IFRS issued by IASB International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 4 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Anglo-American Influence Malaysia Rapid growth over the last 30 years Anticipated growth in GDP, private consumption, and private investment Focus on needs of investors Financial Reporting Foundation (FRF) oversees the MASB MASB tries to converge with IFRS International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 4 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Latin Accounting More conservative and secretive compared to Anglo-American accounting Brazil Focus on needs to creditors and tax authorities Government, company law, and tax regulations influence accounting Corporation law of 1976 IBRACON and the Federal Accounting Council issue accounting standards CVM – Securities Exchange Commission Sets standards for listed companies Approves IBRACON and FAC standards Brazil has one of the major markets in Latin America International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 4 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Latin Accounting Argentina Focus on needs of creditors and tax authorities Standards set by the Argentine Federation of Expert Councils in Economies (FACPCE) Confusion on what standard to follow in regard to General Price Level (GPL) accounting Councils may ratify or amend each Technical Resolution (TR) Takes inflation into account Government no longer accepts GPL adjusted financials FACPCE – GPL is optional is inflation is below 8% FACPCE works toward harmonization with IFRS, but believes differences should still exist International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 4 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Latin Accounting Mexico Focus on needs of creditors and tax authorities Economic development has improved since NAFTA was created Strongly influenced by U.S. GAAP and GAAS Professional accountancy IMCP – similar to AICPA Issues standards and professional code of conduct Formed the Mexican Council for Research and Development of Financial Reporting Standards (CINIF) CINIF issues Mexican standards inline with IFRS 70% in line with international standards at beginning of 2005 International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 4 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Asian Accounting China Focus is shifting from government to investors, creditors, and management Information must now meet more than the needs of macroeconomic control The Accounting Law of the People’s Republic of China Established principles on nature & role of accounting Ministry of Finance empowered to issue standards New standards are unified and market-oriented Accounting Society of China and Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu have aided in reforming accounting International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 4 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Asian Accounting Indonesia Dutch influence in the beginning Focus on needs of investors Asian crisis hurt Indonesia, but reforms have returned Indonesia to pre-crisis levels Financial Accounting Standards Board (DSAK) of the Indonesian Institute of Accountants Working to harmonize standards with IFRS International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 4 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Thailand Accounting system values transparency Focus on needs of investors Asian crisis Implemented reforms to increase corporate governance and competition Economy recovered quickly and has since sustained growth Accounting standards issued by Institute of Certified Accountants and Auditors of Thailand (ICAAT) Standards approved by the Ministry of Commerce Thai SEC Requires all listed companies on the Exchange of Thailand to be reviewed by independent auditors Supervises all listed companies International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 4 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Eastern-European Accounting Poland Attempted the shock therapy model – 1990 All reforms made at once A leader among the transition countries Transition made in three stages 1991 – Decree issued by Ministry of Finance establishing rules for transition to market economy 1994 – “True and fair view” adopted 2002 – Standards more in line with IFRS Became EU member in 2004 Will adopt IFRS in 2005 International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 4 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Eastern-European Accounting Russia Differs from other transition economies Share of new enterprises is low compared to other economies Many soviet-style units still exist that are operating at losses Growth is constrained by reliance on oil and gas Dominated by unreformed monopolies Accounting rules created by Ministry of Finance Central Bank of Russia creates standards for Banks Credit institutions International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 4 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Eastern-European Accounting Russia Focus on taxation needs of the country Highly reflects the result of a planned economy Consolidated statements prepared using IFRS Individual company statements prepared with antiquated Russian Accounting Standards (RAS) Purpose of conversion to IFRS is to Increase transparency Encourage investment International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 4 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black Eastern-European Accounting Czech Republic Gained independence in 1993 Tried the shock therapy method Ran into problems with inflation Working to conform with IFRS Accounting Act of 2002 – companies can opt for IFRS over Czech rules Will adopt IFRS by 2005 as a member of the EU More market-driven accounting standards exist Tax system still depends on accounting rules Government must change this or lose power over tax base International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises - Chapter 4 - Radebaugh, Gray, Black