Government Theories part 1
advertisement

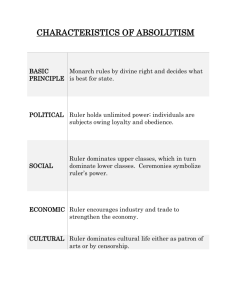
Do Now • What form of government do you believe America took after and why? Government Theories Major Categories of Government • A monarchy is a government led by a hereditary ruler. • In a dictatorship the leader has absolute power. • An oligarchy is a form of government with rule held by small, usually self-appointed elite. • In a democracy supreme authority rests with the people. Categories of Government • Each of these forms of government can exist in numerous varieties. For example, both democracies and monarchies can be constitutional. Elections occur in both democracies and dictatorships. Both democracies and dictatorships can be guilty of human rights violations. Social Contract Theory • The social contract theory is the basis for limited government and liberal democracy. In a limited government, constitutions, statements of rights, or other laws define the limits of power. Everyone must obey the laws. This reduces opportunities for those in authority to take advantage of their elected or appointed positions. In unlimited government, power/control is solely with the ruler with no limits on his/her authority. Force Theory • The state was born as a result of force i.e. aggression, war, conquest and subjugation. In ancient times a strong man with the help of supporters would dominate the weaker people of his tribe and establish the political relations of command and obiedence. Evolutionary Theory • The state developed out of the early primitive family in which one person was the head. Over the years the original family unit became a network of families, or a clan. Eventually, 20 or more clans grouped together created a tribe. Once these nomadic tribes began to settle and develop agricultural techniques, the state was born. Divine Right Theory • The state was created by God who gave those of royal birth the “divine right” to rule. People obeyed their ruler as they obeyed God. This was a widely held belief in several early civilizations such as the Aztec and Mayan, and those of Egypt, China, and Japan. It was also the basis for many governments in the Western world from the 15th to the 18th centuries. Similarities and Differences