Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes and Endosymbiosis
advertisement

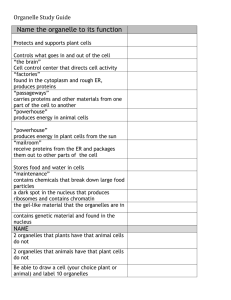
Prokaryotic vs eukaryotic: prokaryotic – no internal membranes therefore no membranebound organelles (they only have ribosomes) and no nucleus; their chromosomes are circular and do not have histone proteins; bacteria and archeae are the only examples. Eukaryotic – have organelles; DNA in linear chromosomes within a nucleus; Key organelles to know functions of: mitochondria, chloroplasts (only organelles that can do chemiosmosis – meaning they make ATP!) of course, you also need to know these two for questions on cell respiration and photosynthesis; Ribosomes – make proteins by putting together amino acids based on instructions in genes; Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum – network that carries products of ribosomes to vesicles for transport to… Golgi apparatus that packages and processes the proteins either for transport out of cell (secretions) or to remain in the cell (like hormones) or to form other organelles like the… Lysosomes that contain digestive enzymes for breaking stuff down. This system of organelles working together is called the endomembrane system.