Diction, Syntax, Tone ppt
advertisement

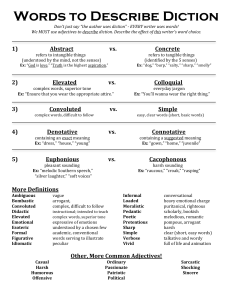
Diction Say What You Mean and Mean What You Say Diction = word choice Creates the writer’s voice Creates the tone of a text Diction Levels of language: Formal- (proper) Language characterized by a learned vocabulary and grammatically correct forms; does not usually include slang Informal- (casual) Language closest to everyday conversation; may include slang Denotation and Connotation Denotation What a word means (dictionary definition) What a word signifies without emotional associations, judgements, or opinions Connotation Emotions behind a word Usually determined through context Tone The speaker’s attitude or emotion toward the subject matter or audience, as revealed by the choice of language. Examples- sarcastic, matter-of-fact, cold, energetic, academic, humorous, etc. Syntax The order of the words; the text’s structure Sentences can be long or short, written in the active voice or passive voice. Syntax A good way to look at syntax is to see how a paragraph is punctuated. If a paragraph has a lot of short sentences, it is slower to read and choppy. EX: I hate people who lie. My brother lies. It makes me so mad. I can hardly think. It makes me so, so angry. Syntax If a sentence is really long, and has lots of clauses in it, it is faster to read. While I need to go to the grocery store, I actually want to go to the park, and then I want to go to the zoo. Syntax How does the change of syntax affect the tone of the story? EX: After we go to the park, I am ready to go to the zoo, and I really want to see the tigers. My mom warned my three year old brother, “ Do NOT go by the monkeys. They are mean!”